-
 Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres - Broad DistributionCatalog Number 19130
Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres - Broad DistributionCatalog Number 19130Poly(methyl methacrylate) or PMMA is less hydrophobic than polystyrene and should show reduced nonspecific protein and peptide binding. The density of these beads, 1.19 g/cc, is considerably higher than that of polystyrene beads, making them easier to concentrate by centrifugation. The beads are not free of surfactant and contain surface carboxylic acid groups at higher concentration than the standard Polybead Polystyrene Carboxylate Microspheres.
-
 Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres with Anionic SurfactantCatalog Number 23570
Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres with Anionic SurfactantCatalog Number 23570Poly(methyl methacrylate) or PMMA is less hydrophobic than polystyrene and should show reduced nonspecific protein and peptide binding. The density of these beads, 1.19 g/cc, is considerably higher than that of polystyrene beads, making them easier to concentrate by centrifugation. The beads are not free of surfactant and contain surface carboxylic acid groups at higher concentration than the standard Polybead Polystyrene Carboxylate Microspheres.
-
 Phenolic Beads, HollowCatalog Number 17806
Phenolic Beads, HollowCatalog Number 17806In many uses of liquid resins, it is desirable to reduce the weight of the finished product. One way to reduce the weight below the original resin weight is to incorporate a suitable additive. Hollow phenolic microspheres are excellent for use in a variety of industrial applications. They are lightweight, chemically inert, and mechanically strong. They can be excellent adhesives, gap filling formulations, sandable putties, syntactic foams, and molded and laminated structures that must be lightweight and strong. About 30% by weight will make most resins unpourable. Filling casting are quite machinable; turns casting brown.
-
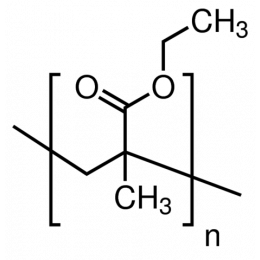 Poly(ethyl methacrylate) Beads (PEMA Beads)Catalog Number 03197
Poly(ethyl methacrylate) Beads (PEMA Beads)Catalog Number 03197Tough methacrylate resin.
Particle size (D50): 140-220µm
-
 Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres - MonodisperseCatalog Number 12083
Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres - MonodisperseCatalog Number 12083Poly(methyl methacrylate) or PMMA is less hydrophobic than polystyrene and should show reduced nonspecific protein and peptide binding. The density of these beads, 1.19 g/cc, is considerably higher than that of polystyrene beads, making them easier to concentrate by centrifugation. The beads are not free of surfactant and contain surface carboxylic acid groups at higher concentration than the standard Polybead Polystyrene Carboxylate Microspheres.
-
 Polybead® Crosslinked Melamine ParticlesCatalog Number 23579
Polybead® Crosslinked Melamine ParticlesCatalog Number 23579These melamine particles are crosslinked by acid-catalyzed reaction with formaldehyde. The particles have a much higher density (1.51 g/cc) than polystyrene, are hydrophilic with amine and methylolamine groups, and, being crosslinked, are not noticeably swelled by organic solvents. The particles can be lyophilized and then redispersed in water. The particles are supplied as a suspension of 2.5% solids in water.
~1.00µm
-
 Polybead® Hollow Microspheres (0.40μm)Catalog Number 23567
Polybead® Hollow Microspheres (0.40μm)Catalog Number 23567The biomedical advantages of a polystyrene surface are combined with a low effective density in a new class of microspheres. Polybead® Hollow Microspheres are spherical styrene / acrylic beads supplied in suspension. A relatively dense shell of a polystyrene based copolymer is formed around a void in the particle. Sphere voids are water-filled in the as-supplied 5% aqueous suspension, and the water-filled particle will have an effective density near 1.0 g/cm3. Water is lost from the void upon drying as the particles are slightly porous. This results in a hollow particle with a shell approximately 0.10µm thick. Surfactants on the surface of the spheres help stabilize the particles.
-
 Polybead® Hollow Microspheres (0.55μm)Catalog Number 23568
Polybead® Hollow Microspheres (0.55μm)Catalog Number 23568The biomedical advantages of a polystyrene surface are combined with a low effective density in a new class of microspheres. Polybead® Hollow Microspheres are spherical styrene / acrylic beads supplied in suspension. A relatively dense shell of a polystyrene based copolymer is formed around a void in the particle. Sphere voids are water-filled in the as-supplied 5% aqueous suspension, and the water-filled particle will have an effective density near 1.0 g/cm3. Water is lost from the void upon drying as the particles are slightly porous. This results in a hollow particle with a shell approximately 0.10µm thick. Surfactants on the surface of the spheres help stabilize the particles.
-
 Polybead® Hollow Microspheres (1.00μm)Catalog Number 23569
Polybead® Hollow Microspheres (1.00μm)Catalog Number 23569The biomedical advantages of a polystyrene surface are combined with a low effective density in a new class of microspheres. Polybead® Hollow Microspheres are spherical styrene / acrylic beads supplied in suspension. A relatively dense shell of a polystyrene based copolymer is formed around a void in the particle. Sphere voids are water-filled in the as-supplied 5% aqueous suspension, and the water-filled particle will have an effective density near 1.0 g/cm3. Water is lost from the void upon drying as the particles are slightly porous. This results in a hollow particle with a shell approximately 0.10µm thick. Surfactants on the surface of the spheres help stabilize the particles.
-
 Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres - Broad Distribution (Dry)Catalog Number 26305
Polybead® Poly(methyl methacrylate) Microspheres - Broad Distribution (Dry)Catalog Number 26305
Additional Polymer Particles
