Fast Blue (FB)
C20H17N5O . 2HCl
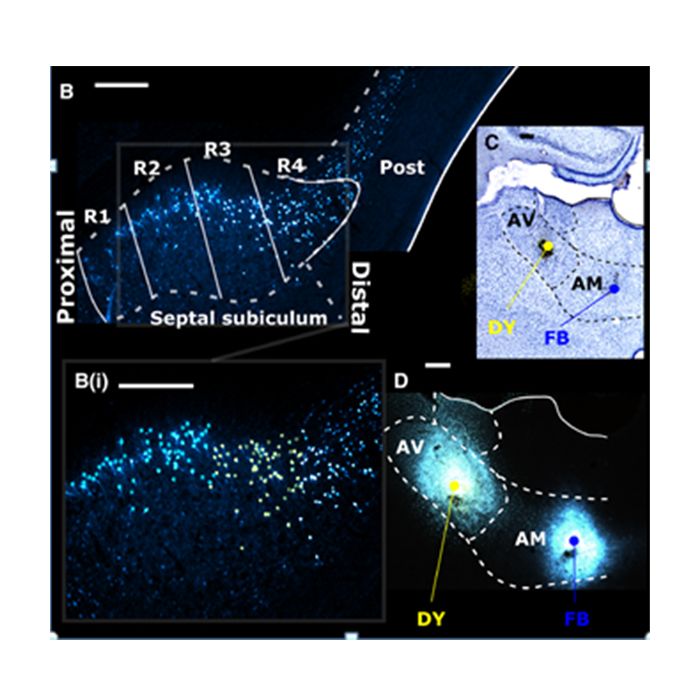
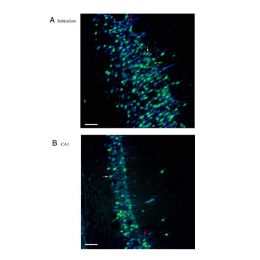
Fast blue (FB) is a fluorescent dye most commonly used as a retrograde neuronal tracer. FB is the tracer of choice for motoneuronal labeling in long-term experiments as it is effectively transported retrogradely over long distances in various animal models, e.g. rats, cats and monkeys. The retrograde tracing techniques allow for detailed assessment of neuronal connections from a single population of neurons to their various targets throughout the nervous system. These techniques allow the "mapping" of connections between neurons in a particular structure (e.g. the eye) and the target neurons in the brain.
Fast Blue can be used alone or with other types of fluorescent retrograde and anterograde tracer dyes to develop picture of neuronal pathway. Other neuronal tracers such as Diamidino Yellow (DY), True Blue (TB), Granular Blue (GB), Evans Blue and Nuclear Yellow are used in conjunction with FB.
FB and DY are the most commonly used tracers for single or double retrograde fluorescent labeling. These dyes can be injected into laboratory animals at a concentration of 2-5% w/v in water. Common protocols recommend injecting 1-2 microliters of the 5.0% concentration into the desired area of the laboratory animal. Prepared solution can be stored at 4 deg C for up to 2 weeks.
These protocols are offered as guides. Depending on the situation alternations may be needed due to the laboratory animal or research being done.
- Excitation Wavelength: 365nm
- Emission Wavelength: 420nm
Christiansen, K. et al. Complementary subicular pathways to the anterior thalamic nuclei and mammillary bodies in the rat and macaque monkey brain. The European journal of neuroscience(2016). doi:10.1111/ejn.13208
Schofield, B.R. (2008) Retrograde Axonal Tracing with Fluorescent Markers, Curr. Protoc. Neurosci. 43, 1.17.1-1.17.24.
Choi, D., Li, D., Raisman, G. (2002) Fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracers that label the rat facial nucleus: a comparison of Fast Blue, Fluoro-ruby, Fluoro-emerald, Fluoro-Gold and DiI, J. Neurosci. Meth. 117, 167-172.
Puigdellívol-Sánchez, A., Valero-Cabré, A., Prats-Galino, A., Navarro, X. & Molander, C. On the use of fast blue, fluoro-gold and diamidino yellow for retrograde tracing after peripheral nerve injury: Uptake, fading, dye interactions, and toxicity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods 115, 115–127 (2002). doi:10.1016/S0165-0270(01)00532-5
Novikova, L., Novikov, L., Kellerth, J.-O. (1997) Persistent neuronal labeling by retrograde fluorescent tracers: a comparison between Fast Blue, Fluoro-Gold and various dextran conjugates, J. Neurosci. Meth. 74, 9-15.
Skirboll, L. et al. A method for specific transmitter identification of retrogradely labeled neurons: Immunofluorescence combined with fluorescence tracing. Brain Research Reviews 8, 99–127 (1984). doi:10.1016/0165-0173(84)90001-8
Kuypers, H.G.J.M., Huisman, A.M. (1984) Fluorescent neuronal tracers, Adv. Cellular. Neurobiol. 5, 307-340
Keizer, K., Kuypers, H. G. J. M., Huisman, A. M. & Dann, O. Diamidino yellow dihydrochloride (DY.2HCl); a new fluorescent retrograde neuronal tracer, which migrates only very slowly out of the cell. Experimental Brain Research 51, 179-191 (1983). doi:10.1007/BF00237193