Styrenic Monomers
Popular alternatives to acrylic and related monomers, styrenic monomers generally provide polymers of higher glass transition temperature, higher modulus, increased hydrophobic character and nominal UV absorbance. As such, coatings made with high concentrations of styrenic monomers can yellow with time if exposed to UV light. Crosslinked styrene resins (especially in microsphere form) are tough and chemically resistant. These form the basis for ion exchange resins and microbeads used as supports for biochemical reactions.
-
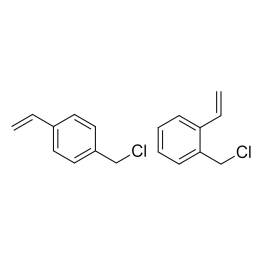 Chloromethylstyrene, mixture of isomers, ≥ 97%Catalog Number 02718
Chloromethylstyrene, mixture of isomers, ≥ 97%Catalog Number 02718Reactive styrene monomer. Can be used to prepare Merrifield resins without using a chloromethylation step.
(vinylbenzyl chloride)
Typically contains isomer ratio of Ortho (15 - 50%), Para (50 - 85%).
-
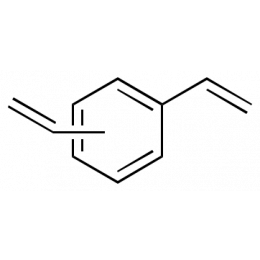 Divinylbenzene (80% Active)Catalog Number 22478
Divinylbenzene (80% Active)Catalog Number 22478Crosslinking monomer used primarily with styrene.
mixed mp,p-isomer impurities mainly m,p-ethylstyrenes 80% active (remainder mainly m,p-ethylvinylbenzenes)
