-
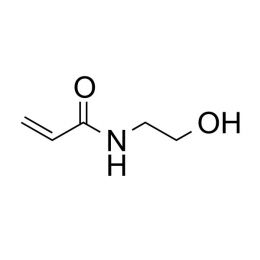 N-Hydroxyethyl acrylamide (HEAA), 98%Catalog Number 25109
N-Hydroxyethyl acrylamide (HEAA), 98%Catalog Number 25109Increases hydrophilic properties of polymers when copolymerized into a range of acrylate and methacrylate systems. Has been used in hydrogel systems for ocular delivery of ophthalmic drugs. The homopolymer has been used as a novel adsorbed coating for protein separation by capillary electrophoresis.
-
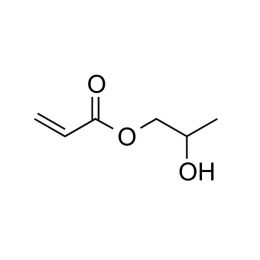 2-hydroxypropyl acrylateCatalog Number 25353
2-hydroxypropyl acrylateCatalog Number 253532-hydroxypropyl acrylate will increase the hydrophilic properties of polymers when copolymerized into a range of acrylate and methacrylate systems. This monomer has been used in hydrogel polymers and in RAFT polymerizations.
This product is a mixture of isomers in the approximate ratio of: 75% 2-hydroxypropyl acrylate, 25% 1-methyl-2-hydroxyethyl acrylate.
-
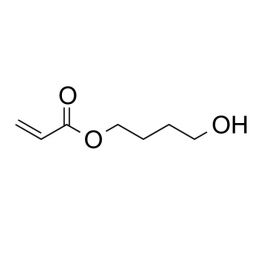 4-hydroxybutyl acrylateCatalog Number 25352
4-hydroxybutyl acrylateCatalog Number 25352Increases hydrophilic properties of polymers when copolymerized into a range of acrylate and methacrylate systems. Used in polymers for contact lenses and other ophthalmic devices.
-
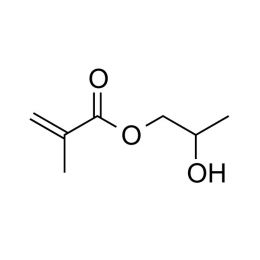 Hydroxypropyl methacrylate, mixture of isomersCatalog Number 00730
Hydroxypropyl methacrylate, mixture of isomersCatalog Number 00730Hydrophilic monomer.
-
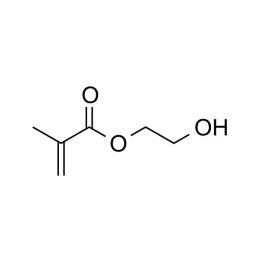 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate, Low Acid GradeCatalog Number 03699
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate, Low Acid GradeCatalog Number 036992-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) is perhaps the most widely studied and used neutral hydrophilic monomer. The monomer is soluble, its homopolymer is water-insoluble but plasticized and swollen in water. This monomer is the basis for many hydrogel products such as soft contact lenses, as well as polymer binders for controlled drug release, absorbants for body fluids and lubricious coatings. As a comonomer with other ester monomers, HEMA can be used to control hydrophobicity or introduce reactive sites.
-
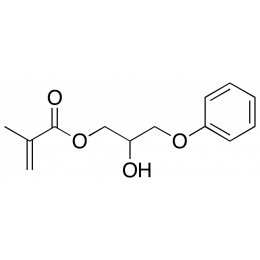 3-Phenoxy 2 hydroxy propyl methacrylate (PHPM)Catalog Number 25506
3-Phenoxy 2 hydroxy propyl methacrylate (PHPM)Catalog Number 25506Hydrophilic monomer useful in medical device and ophthalmic applications.
-
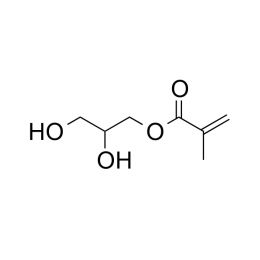 Glycerol monomethacrylateCatalog Number 04180
Glycerol monomethacrylateCatalog Number 04180Hydrophilic monomer useful in hydrogel preparation.
-
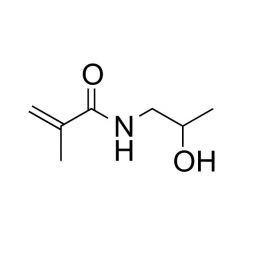 N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA)Catalog Number 08242
N-(2-Hydroxypropyl)methacrylamide (HPMA)Catalog Number 08242Hydrolytically stable hydrophilic monomer.
-
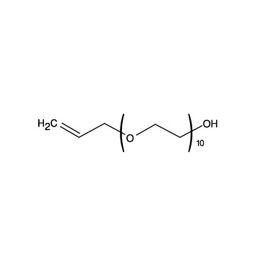 Hydroxypolyethoxy (10) Allyl Ether, 98%Catalog Number 24899
Hydroxypolyethoxy (10) Allyl Ether, 98%Catalog Number 24899Difunctional molecule reactive in vinyl polymerization through its allylic group, to impart hydrophilic properties to aqueous solution or emulsion polymers. Hydroxypolyethoxy (10) Allyl Ether is a high purity material, clear, slightly viscous liquid (5 cps at 20°C) which undergoes partial solidification below 10°C to form a viscous paste. In particular, solution copolymers of Hydroxypolyethoxy (10) Allyl Ether with Acrylic acid have shown useful properties as dispersants and scale inhibitors in boiler water applications.
-
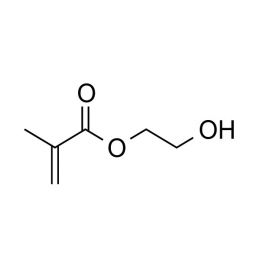 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate, Ophthalmic GradeCatalog Number 04675
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate, Ophthalmic GradeCatalog Number 046752-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) is perhaps the most widely studied and used neutral hydrophilic monomer. The monomer is soluble, its homopolymer is water-insoluble but plasticized and swollen in water. This monomer is the basis for many hydrogel products such as soft contact lenses, as well as polymer binders for controlled drug release, absorbants for body fluids and lubricious coatings. As a comonomer with other ester monomers, HEMA can be used to control hydrophobicity or introduce reactive sites.
glycol methacrylate
Opthalmic grade: Purity %=min. 99; Acid Content %=max 0.05; EGDMA content %=max 0.15; Color=30
-
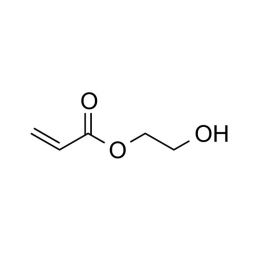 2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate, ≥ 97.5%Catalog Number 01902
2-Hydroxyethyl acrylate, ≥ 97.5%Catalog Number 01902Hydrophilic monomer, reactive site for reactions.
-
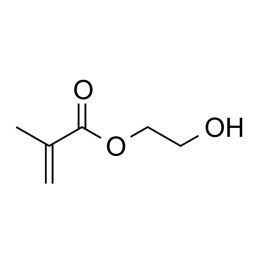 2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), Technical GradeCatalog Number 00227
2-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), Technical GradeCatalog Number 002272-Hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) is perhaps the most widely studied and used neutral hydrophilic monomer. The monomer is soluble, its homopolymer is water-insoluble but plasticized and swollen in water. This monomer is the basis for many hydrogel products such as soft contact lenses, as well as polymer binders for controlled drug release, absorbants for body fluids and lubricious coatings. As a comonomer with other ester monomers, HEMA can be used to control hydrophobicity or introduce reactive sites.
Hydroxyl Monomers
Hydroxyl groups have utility as hydrogen bonding sites and can provide polymers with compatibility for water or polar solvents. These versatile functional groups can be derivitized broadly. Polymers containing free –OH groups can be post reacted with acids, epoxies, isocyanates, etc. to create novel polymer properties and architectures.
