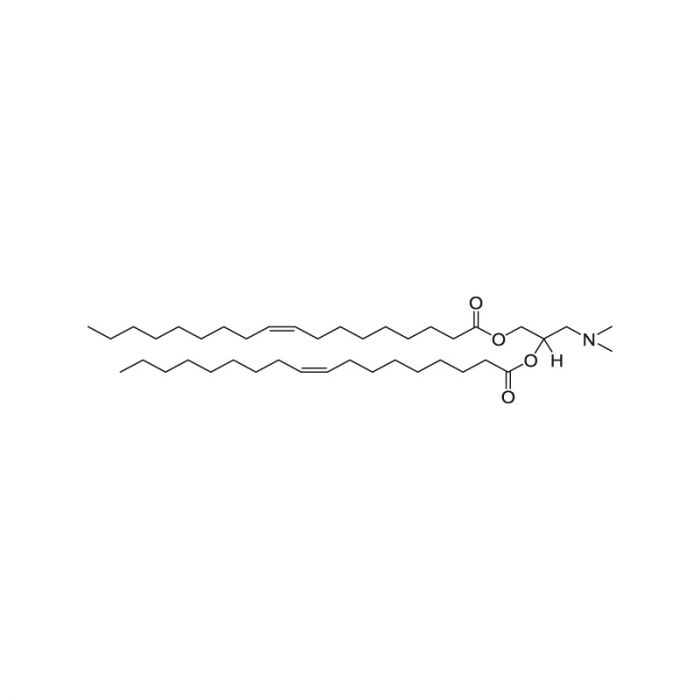
DODAP (1,2-dioleoyl-3-dimethylammonium propane)
C41H77NO4
- Key Features
- High transfection efficiency and low cytotoxicity
- Efficient delivery of plasmid DNA, siRNA/miRNA, and CRISPR/Cas9 components
- Widely used in nanomedicine
- Flexible and scalable
DODAP (1,2-dioleoyl-3-dimethylammonium-propane) is an ionizable cationic lipid with lower cytotoxicity and high transfection efficiency. DODAP is neutral at physiological pH, but acquires a positive charge inside the endosome due to the protonation of free amines when pH is lower than its pKa (<7). The electrostatic interactions between DODAP and naturally occurring anionic lipids in endosomal membranes trigger the release of nucleic acid. These interactions promote membrane lytic non-bilayer structures to enable the intracellular delivery of nucleic acid. A common application is in nanomedicine as an ionizable lipid component of nanocarriers (lipid-polymer hybrid nanoparticles, LPNs), widely used to encapsulate bioactive molecules, including mRNA, siRNA, and plasmid DNA as a treatment for diseases.
Contact us at [email protected] to know about our cGMP grade DODAP manufactured under 21 CFR part 210,211.
Fattore, L., Campani, V., Ruggiero, C.F., Salvati, V., Liguoro, D., Scotti, L., Botti, G., Ascierto, P.A., Mancini, R., De Rosa, G., Ciliberto, G. (2020). In Vitro Biophysical and Biological Characterization of Lipid Nanoparticles Co-Encapsulating Oncosuppressors miR-199b-5p and miR-204-5p as Potentiators of Target Therapy in Metastatic Melanoma. Int J Mol Sci. 12;21(6):1930.
Granot, Y., & Peer, D. (2017). Delivering the right message: Challenges and opportunities in lipid nanoparticles-mediated modified mRNA therapeutics-An innate immune system standpoint. Semin Immunol. 34:68-77.
Pardi, N., Hogan, M.J., Porter, F.W., Weissman, D. (2018). mRNA vaccines -- a new era in vaccinology. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 17:261 -279.
Herrington, T., Patlolla, R., & Altin, J. (2009). Targeting of plasmid DNA-lipoplexes to cells with molecules anchored via a metal chelator lipid. J. Gene Med. 11(11): 1048-63.
Sahin, U., Karikó, K., Türeci, Ö. (2014). mRNA-based therapeutics -- developing a new class of drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 13:759 -780.
Semple, S., Klimuk, S., Harasym, T., Dos Santos, N., Ansell, S., Wong, K., Maurer, N., Stark, H., Cullis, P., Hope, M., & Scherrer, P. (2001). Efficient encapsulation of antisense oligonucleotides in lipid vesicles using ionizable aminolipids: formation of novel small multilamellar vesicle structures. Biochemimica et Biophysica Acta. 1510(1-2): 152-166.