-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate [MW 1,000] | Polysciences, Inc.](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25485.png) Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 1000)Catalog Number 25485
Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 1000)Catalog Number 25485Long-chain, hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer. MW of PEG Block= 1,000
Diacrylate: >95%
-
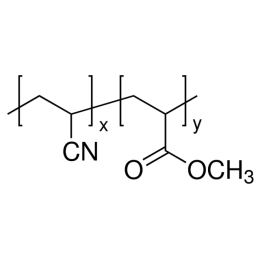 Polyacrylonitrile, co-polymer with 6% methyl acrylate, MW 80,000Catalog Number 25562
Polyacrylonitrile, co-polymer with 6% methyl acrylate, MW 80,000Catalog Number 25562Powder with 40 micron average particle size. Soluble in DMF, DMAc, DMSO.
-
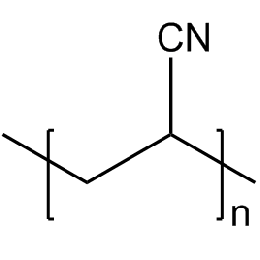 Polyacrylonitrile, MW 200000 (PAN 200000)Catalog Number 25563
Polyacrylonitrile, MW 200000 (PAN 200000)Catalog Number 25563Powder with 40 micron average particle size. Soluble in DMF, DMAc, DMSO.
-
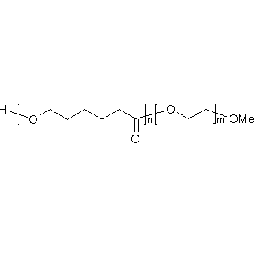 PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(1,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25010
PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(1,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25010Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
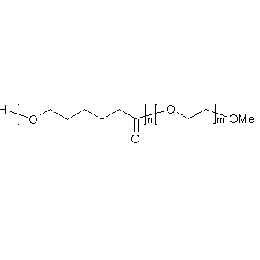 PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(5,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25012
PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(5,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25012Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
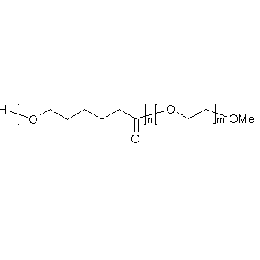 PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(1,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25022
PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(1,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25022There is increased interest in biodegradable polymers for both biomedical and industrial applications. Among the leading candidates for biodegradation are caprolactone based materials due to it's approved uses by the FDA for drug delivery systems, sutures, long term implants and adhesion barriers as well as new tissue scaffold host systems.
-
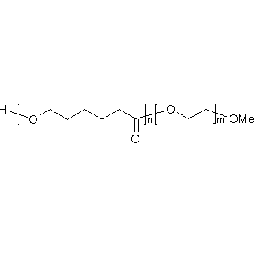 PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(2,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25023
PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(2,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25023Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
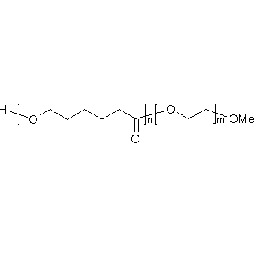 PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(5,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25024
PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(5,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25024Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
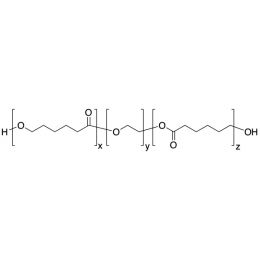 PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25013
PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25013Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
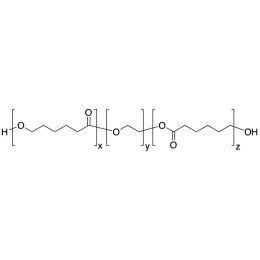 PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25014
PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25014Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
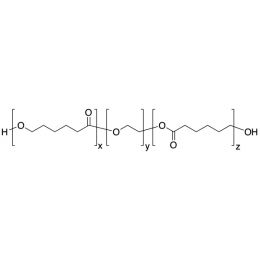 PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(2,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25015
PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(2,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25015Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
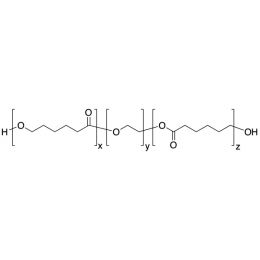 PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(5,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25016
PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(5,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25016Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
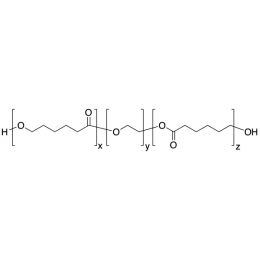 PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25019
PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(1,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25019Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
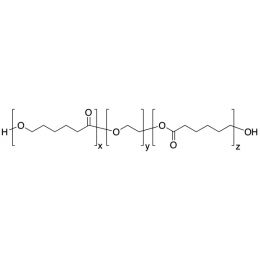 PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(2,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25020
PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(2,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25020Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
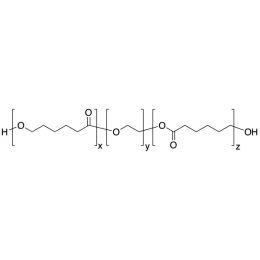 PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(6,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25021
PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(6,000)-b-PCL(1,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25021Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
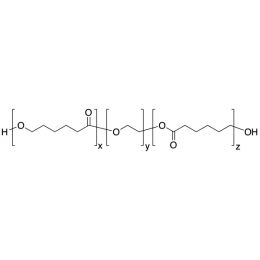 PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25025
PCL(5,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PCL(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25025Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
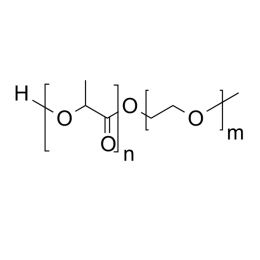 PEG(350)-b-PLA(300), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24375
PEG(350)-b-PLA(300), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24375Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
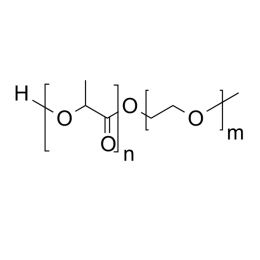 PEG(1000)-b-PLA(750), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24378
PEG(1000)-b-PLA(750), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24378Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
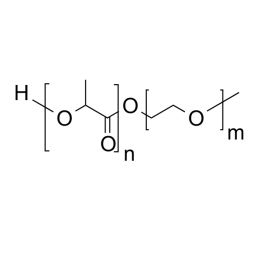 PEG(1000)-b-PLA(5000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24381
PEG(1000)-b-PLA(5000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24381Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
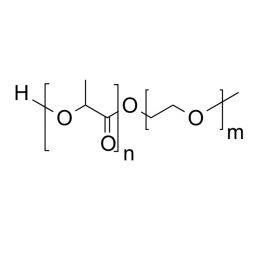 PEG(5000)-b-PLA(1000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24386
PEG(5000)-b-PLA(1000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24386Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
 PEG(5000)-b-PLA(5000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24389
PEG(5000)-b-PLA(5000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 24389Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
 PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25017
PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25017Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
 PEG(5000)-b-PLA(10,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25018
PEG(5000)-b-PLA(10,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25018Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
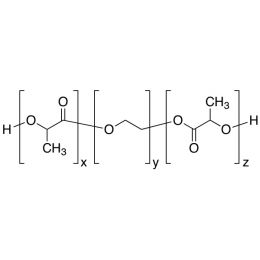 PLA(1000)-b-PEG(1000)-b-PLA(1000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24500
PLA(1000)-b-PEG(1000)-b-PLA(1000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24500Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
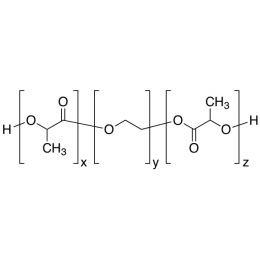 PLA(2000)-b-PEG(1000)-b-PLA(2000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24501
PLA(2000)-b-PEG(1000)-b-PLA(2000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24501Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
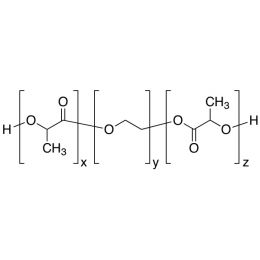 PLA(5000)-b-PEG(1000)-b-PLA(5000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24502
PLA(5000)-b-PEG(1000)-b-PLA(5000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24502Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
 PLA(1000)-b-PEG(4000)-b-PLA(1000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24503
PLA(1000)-b-PEG(4000)-b-PLA(1000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24503Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
A new class of polymeric biomaterials is emerging. The biodegradability of polymers based on lactic acid(LA) and its copolymers with ethylene glycol (EG) opens up new avenues for drug delivery, gene therapy, tissue engineering and determination of cellular pathway mechanisms.
-
 PLA(1000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(1000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24509
PLA(1000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(1000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 24509Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
A new class of polymeric biomaterials is emerging. The biodegradability of polymers based on lactic acid(LA) and its copolymers with ethylene glycol (EG) opens up new avenues for drug delivery, gene therapy, tissue engineering and determination of cellular pathway mechanisms.
-
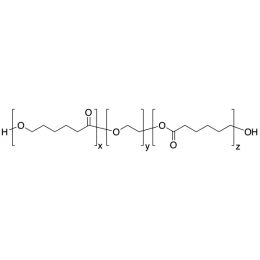 PLA(5,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25026
PLA(5,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(5,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25026Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
A new class of polymeric biomaterials is emerging. The biodegradability of polymers based on lactic acid(LA) and its copolymers with ethylene glycol (EG) opens up new avenues for drug delivery, gene therapy, tissue engineering and determination of cellular pathway mechanisms.
-
 PLA(10,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(10,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25027
PLA(10,000)-b-PEG(10,000)-b-PLA(10,000), Triblock PolymerCatalog Number 25027Polymer structures featuring polyethylene glycol (PEG), with biodegradable or biocompatabile segments offering micelluar, nano and microsphere morphologies which are useful for controlled release formulations. Molecular weights of blocks controlled by GPC. Alternative structures can be synthesized.
-
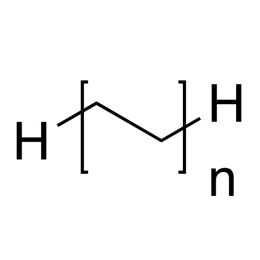 Polyethylene, Chromatographic GradeCatalog Number 15184
Polyethylene, Chromatographic GradeCatalog Number 15184Hydrophobic, easily processed or fabricated, resin.
Soluble in: xylene, tetralin, TCE @ 50-60°
20μ powder chromatographic (reverse phase HPLC) grade
-
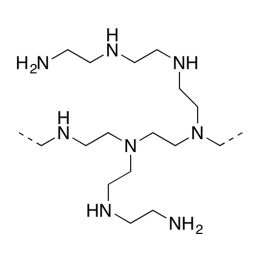
 Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 70,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 70000 30% soln.)Catalog Number 00618Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 70,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 70000 30% soln.)Catalog Number 00618Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Highly branched polyamine with high charge density. Liquid polymers. Polymers contain primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio. 30% soln. in water.
Polydispersity: 17±5.2
-
 Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 1,200 (bPEI 1200)Catalog Number 06088Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 1,200 (bPEI 1200) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 1200 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio.
Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 1,200 (bPEI 1200)Catalog Number 06088Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 1,200 (bPEI 1200) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 1200 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio. -
 Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 2000 (bPEI 2000)Catalog Number 06089Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 1,800 (bPEI 1800) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 1800 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio.
Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 2000 (bPEI 2000)Catalog Number 06089Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 1,800 (bPEI 1800) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 1800 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio. -
![Halocarbon 400 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene)]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25074.jpg) Halocarbon 400 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 400 centistokes]Catalog Number 25074
Halocarbon 400 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 400 centistokes]Catalog Number 25074Inert, non-flammable lubricating oil. Polymer is a blend of oligomers. Also used as an inert medium in transgenic studies of fruit fly Drosophilia embryos.
-
![Halocarbon 700 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene)]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25075.jpg) Halocarbon 700 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 700 centistokes]Catalog Number 25075
Halocarbon 700 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 700 centistokes]Catalog Number 25075Inert, non-flammable lubricating oil. Polymer is a blend of oligomers.
Also used as an inert medium in transgenic studies of fruit fly Drosophilia embryos.
-
![Halocarbon 1000N Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene)]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25076.jpg) Halocarbon 1000N Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 1,000 centistokes]Catalog Number 25076
Halocarbon 1000N Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 1,000 centistokes]Catalog Number 25076Inert, non-flammable lubricating oil. Inert, non-flammable lubricating oil. Polymer is a blend of oligomers.
Also used as an ultraviscous solvent for ¹H NMR spectroscopy to better identify individual components in a complex mixture. The ultraviscous polymer solvent (mixed as 80% Halocarbon / 20% CDCl3) greatly reduces the molecular tumbling of small molecules, thereby making the nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE) very large and of negative sign.
-
![Poly(4-vinylphenol) [MW 9,000 - 11,000] | Polysciences, Inc.](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25447.jpg) Poly(4-vinylphenol) [MW 9,000 - 11,000]Catalog Number 25447
Poly(4-vinylphenol) [MW 9,000 - 11,000]Catalog Number 25447Reactive polyphenol. Has applications in photoresists.
Polydispersity ~3
-
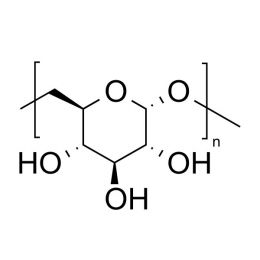 DextranCatalog Number 01341
DextranCatalog Number 01341Water soluble carbohydrate with many pharmaceutical and technical uses.
-
![Dextran [MW 100,000-200,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/5/05056.jpg) Dextran [MW 100,000-200,000]Catalog Number 05056
Dextran [MW 100,000-200,000]Catalog Number 05056Water soluble carbohydrate with many pharmaceutical and technical uses.
-
![Dextran [MW 200,000-300,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/2/22500.jpg) Dextran [MW 200,000-300,000]Catalog Number 22500
Dextran [MW 200,000-300,000]Catalog Number 22500Water soluble carbohydrate with many pharmaceutical and technical uses.
-
![Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [3-6 cP]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25730_3.png) Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [3-6 cP]Catalog Number 25727
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [3-6 cP]Catalog Number 25727HPC is a hydrophilic polymer used for drug encapsulants, opthalmic lubricants and transdermal patches. Also used as a general thickener.
-
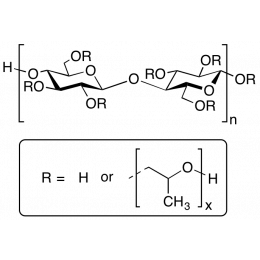 Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [6-10 cP]Catalog Number 25728
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [6-10 cP]Catalog Number 25728HPC is a hydrophilic polymer used for drug encapsulants, opthalmic lubricants and transdermal patches. Also used as a general thickener.
-
![Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [150-400 cP]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25730_2.png) Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [150-400 cP]Catalog Number 25729
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [150-400 cP]Catalog Number 25729HPC is a hydrophilic polymer used for drug encapsulants, opthalmic lubricants and transdermal patches. Also used as a general thickener.
-
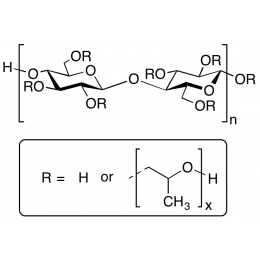 Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [1,000-4,000 cP]Catalog Number 25730
Hydroxypropyl Cellulose [1,000-4,000 cP]Catalog Number 25730HPC is a hydrophilic polymer used for drug encapsulants, opthalmic lubricants and transdermal patches. Also used as a general thickener.
-
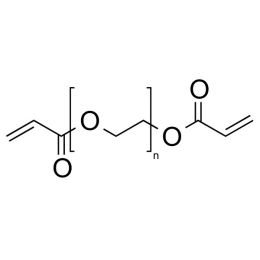 Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 200)Catalog Number 00669
Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 200)Catalog Number 00669Long-chain, hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer. MW PEG Block = 200
-
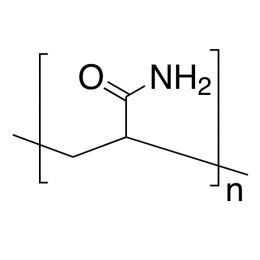 Polyacrylamide, Mw 10,000, 50 wt. % in H2OCatalog Number 22581
Polyacrylamide, Mw 10,000, 50 wt. % in H2OCatalog Number 22581Low molecular weight nonionic water-soluble polymer, used primarily as a flocculant. 50% solution in water. Unit weights are weights of solution.
-
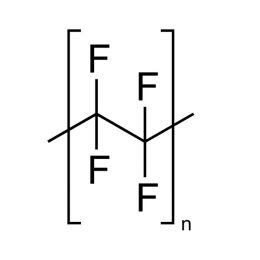 Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (Teflon™ 30B) 60 wt % DispersionCatalog Number 21539
Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (Teflon™ 30B) 60 wt % DispersionCatalog Number 21539This inert, non-ionic Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) dispersion can be used for applications that require excellent chemical and temperature stability. Typical uses include electronic and metallic surface coatings, anti-drip additive for plastics, and binder for battery anode/cathode matrixes. Can be used anywhere a highly inert, stable, non-stick coating is desirable.
-
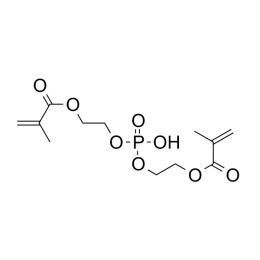 Bis(2-methacryloxyethyl) phosphateCatalog Number 16041
Bis(2-methacryloxyethyl) phosphateCatalog Number 16041Crosslinking monomer. Adhesion promoter through free phosphoric acid group.
-
 Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 25000, Transfection Grade (PEI 25K™)Catalog Number 23966Email: [email protected]PEI 25K is a powerful, trusted, and cost-effective transient transfection reagent. In HEK293 and CHO expression systems, PEI offers consistently high gene expression on a wide scale (96 well plates up to 100 L bioreactors). Each year, more researchers and companies turn to Polysciences PEI to gain a critical edge in their work. Relative to most other options, using PEI to prepare transfection reagents in-house can offer as much as a 40% reduction in total transfection costs.
Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 25000, Transfection Grade (PEI 25K™)Catalog Number 23966Email: [email protected]PEI 25K is a powerful, trusted, and cost-effective transient transfection reagent. In HEK293 and CHO expression systems, PEI offers consistently high gene expression on a wide scale (96 well plates up to 100 L bioreactors). Each year, more researchers and companies turn to Polysciences PEI to gain a critical edge in their work. Relative to most other options, using PEI to prepare transfection reagents in-house can offer as much as a 40% reduction in total transfection costs. -
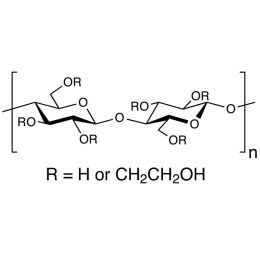 Cellulose, hydroxyethyl ether (MW 1,000,000)Catalog Number 05568
Cellulose, hydroxyethyl ether (MW 1,000,000)Catalog Number 05568Water-soluble cellulose ether, used as a binder and thickening agent
1,500-2,500 cps (1% soln. in water)
-
 Cellulose, hydroxyethyl ether (MW 720,000)Catalog Number 05569Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Cellulose, hydroxyethyl ether (MW 720,000)Catalog Number 05569Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Water-soluble cellulose ether, used as a binder and thickening agent
Viscosity of 2% AQ = 4,500-6,500 cps
-
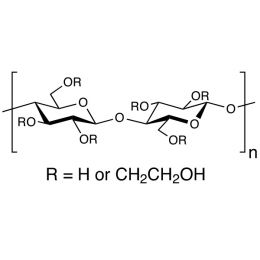 Cellulose, hydroxyethyl ether (MW ~90,000)Catalog Number 05570
Cellulose, hydroxyethyl ether (MW ~90,000)Catalog Number 05570Water-soluble cellulose ether, used as a binder and thickening agent
-
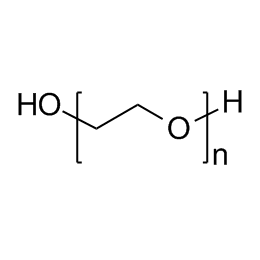 Poly(ethylene oxide), MW 100000 (PEO 100K)Catalog Number 06104
Poly(ethylene oxide), MW 100000 (PEO 100K)Catalog Number 06104Water-soluble polymer in a white, free flowing powder. Used to impart viscosity to and modify flow of aqueous solutions. See poly(ethylene glycol) for lower molecular weight analogs. Poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: acetone, alcohol, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEO Contains 0.01% BHT, SiO2 1.5% max, alkaline earth oxide as CaO 0.5%,
-
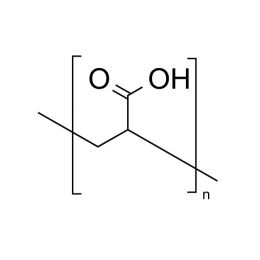 Poly(acrylic acid), 63% soln. in water [MW ~2,000]Catalog Number 06513
Poly(acrylic acid), 63% soln. in water [MW ~2,000]Catalog Number 06513Important anionic water-soluble polymer. Can be crosslinked covalently or ionically to form hydrogels.
Mw/Mn 2.4
63% soln. in water (157.5 g polymer)
-
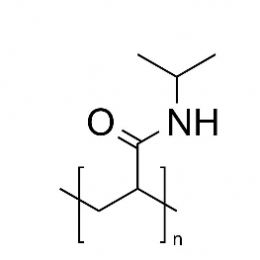 Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNiPAM)Catalog Number 21458
Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNiPAM)Catalog Number 21458Polymer is water-soluble at room temperature, insoluble above ~40º. Solubility ceiling has been used in mold and cell growth techniques since cells adhere to polymer film at incubation temperatures and are released as medium is cooled and polymer is dissolved.
-
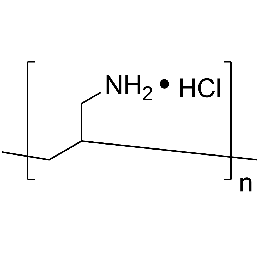 Poly(allylamine hydrochloride), MW 150000, 40% aq. soln.Catalog Number 25673
Poly(allylamine hydrochloride), MW 150000, 40% aq. soln.Catalog Number 25673Polymeric primary amine. 40% AQ solution.
-
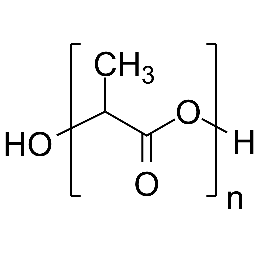 Poly(D,L-lactide), IV 0.2 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26267
Poly(D,L-lactide), IV 0.2 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26267 -
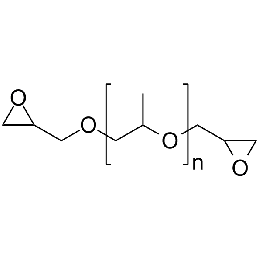 Poly(propylene glycol) (600) diglycidyl etherCatalog Number 24046Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(propylene glycol) (600) diglycidyl etherCatalog Number 24046Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Crosslinker for amine-, hydroxyl-, and carboxyl-functional polymers.
WPE ~ 530
-
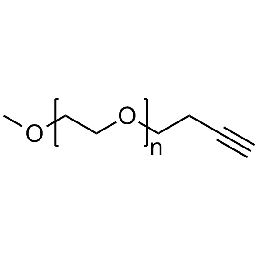 Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 750Catalog Number 26019
Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 750Catalog Number 26019 -
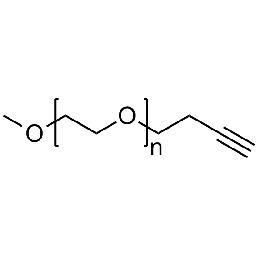 Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26020
Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26020 -
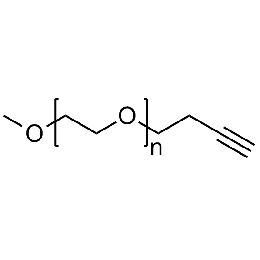 Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26021
Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26021 -
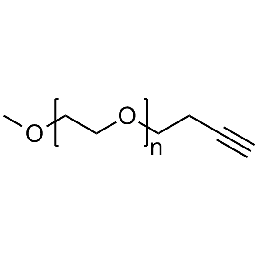 Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26022
Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26022 -
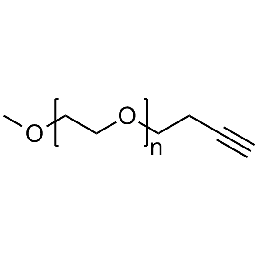 Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26023
Methoxy PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26023 -
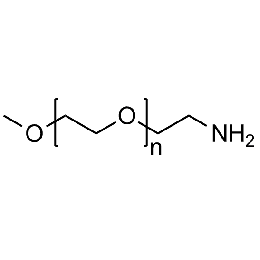 Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 750Catalog Number 26024
Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 750Catalog Number 26024 -
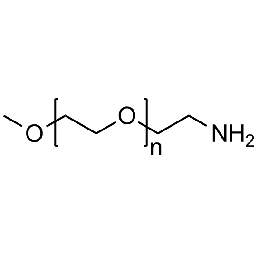 Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26025
Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26025 -
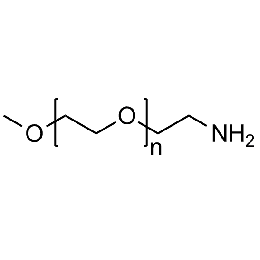 Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26026
Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26026 -
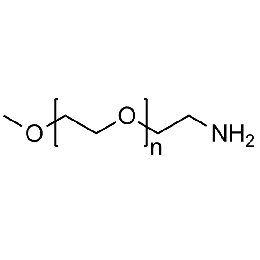 Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26027
Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26027 -
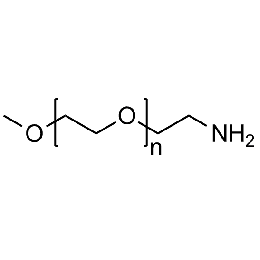 Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26028
Methoxy PEG amine, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26028 -
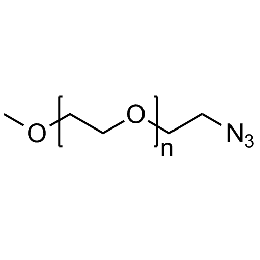 Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 750Catalog Number 26029
Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 750Catalog Number 26029 -
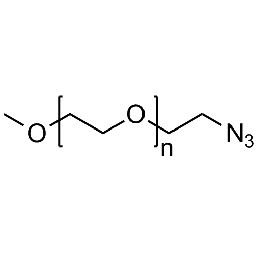 Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26030
Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26030 -
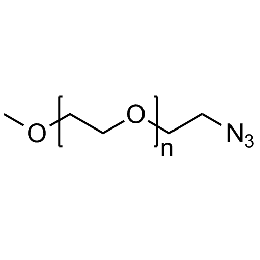 Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26031
Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26031 -
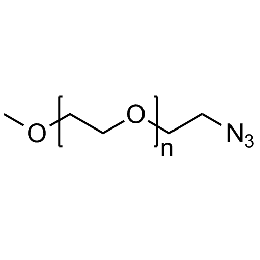 Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26032
Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26032 -
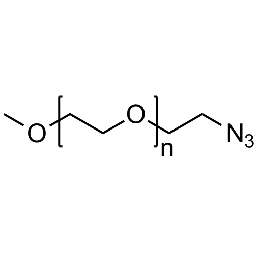 Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26033
Methoxy PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26033 -
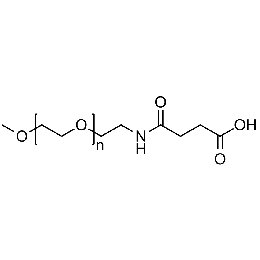 Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 750Catalog Number 26034
Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 750Catalog Number 26034 -
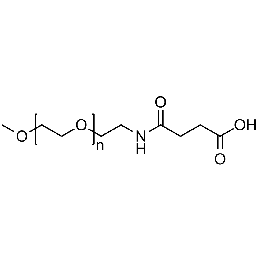 Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26035
Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26035 -
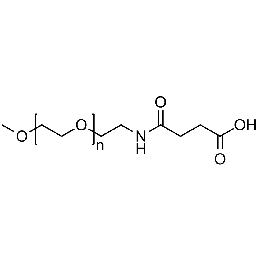 Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26036
Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26036 -
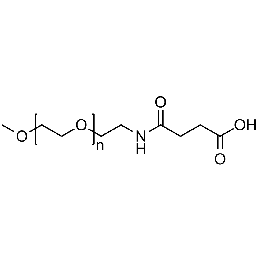 Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26037
Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26037 -
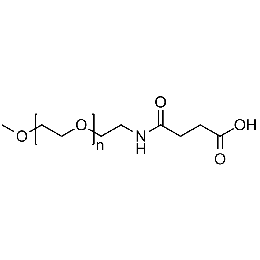 Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26038
Methoxy PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26038 -
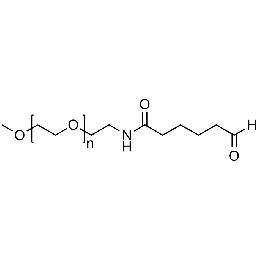 Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 750Catalog Number 26039
Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 750Catalog Number 26039 -
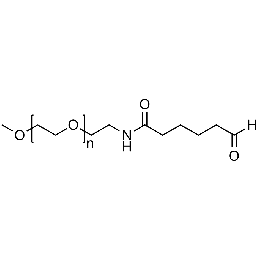 Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26040
Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26040 -
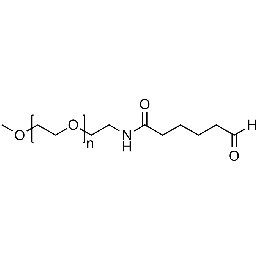 Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26041
Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26041 -
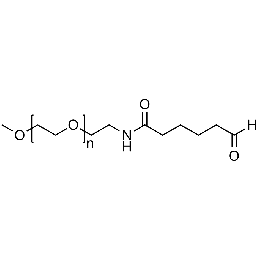 Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26042
Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26042 -
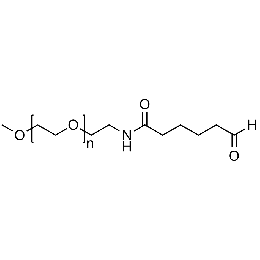 Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26043
Methoxy PEG aldehyde, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26043 -
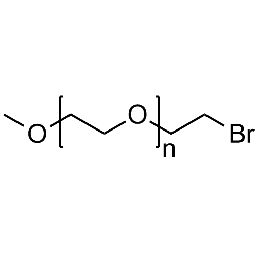 Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 750Catalog Number 26044
Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 750Catalog Number 26044 -
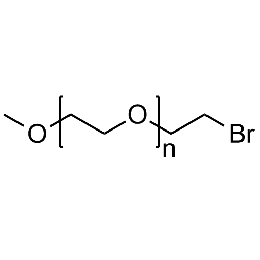 Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26045
Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26045 -
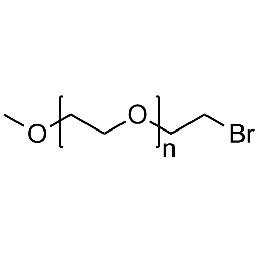 Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26046
Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26046 -
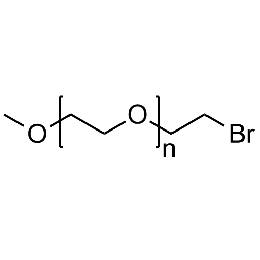 Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26047
Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26047 -
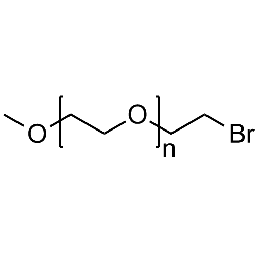 Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26048
Methoxy PEG bromide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26048 -
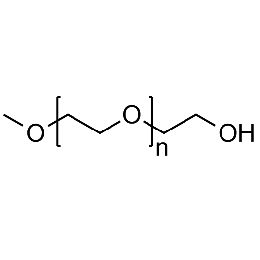 PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 750Catalog Number 26049
PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 750Catalog Number 26049 -
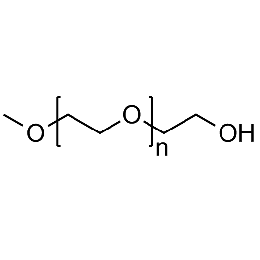 PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26050
PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26050 -
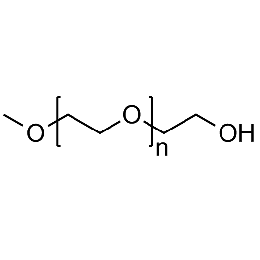 PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26051
PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26051 -
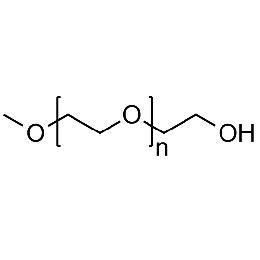 PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26052
PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26052 -
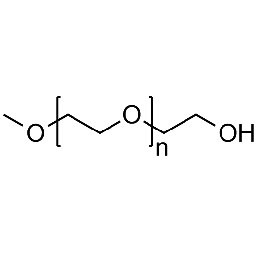 PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26053
PEG monomethyl ether, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26053 -
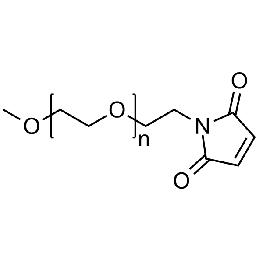 Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 750Catalog Number 26054
Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 750Catalog Number 26054 -
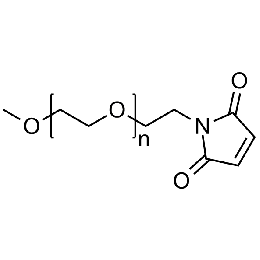 Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26055
Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26055 -
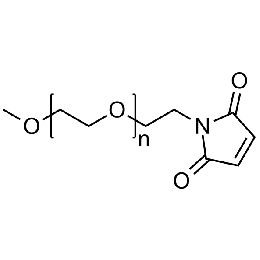 Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26056
Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26056 -
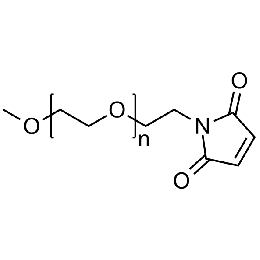 Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26057
Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26057 -
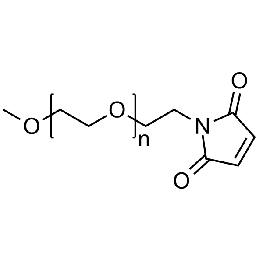 Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26058
Methoxy PEG maleimide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26058 -
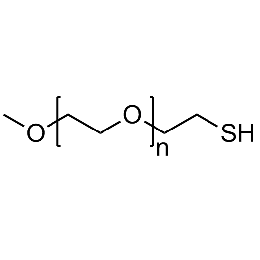 PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 750Catalog Number 26059
PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 750Catalog Number 26059 -
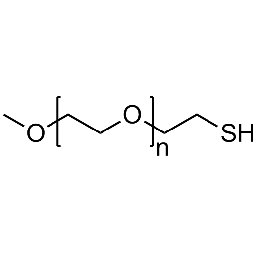 PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26060
PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26060 -
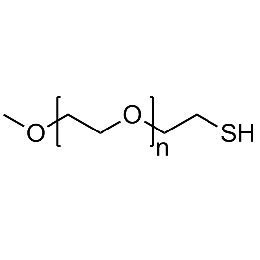 PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26061
PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26061 -
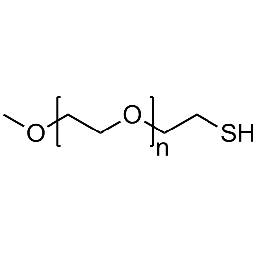 PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26062
PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26062 -
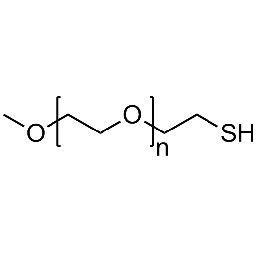 PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26063
PEG methyl ether thiol, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26063 -
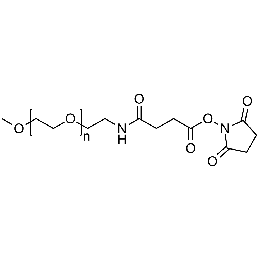 Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 750Catalog Number 26064
Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 750Catalog Number 26064 -
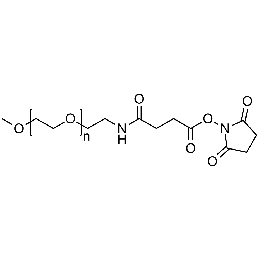
 Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26065
Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26065 -
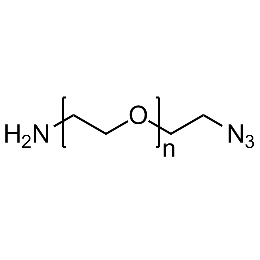 Amine PEG azide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26248
Amine PEG azide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26248 -
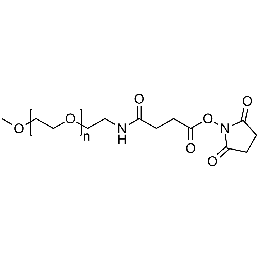
 Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26066
Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26066 -
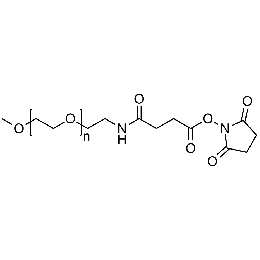 Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26067
Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26067 -
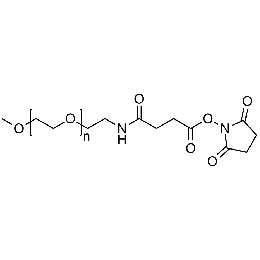 Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26068
Methoxy PEG NHS, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26068 -
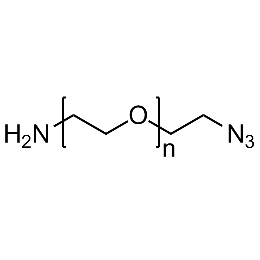 Amine PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26249
Amine PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26249 -
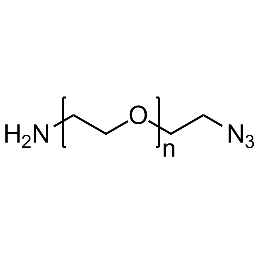 Amine PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26250
Amine PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26250 -
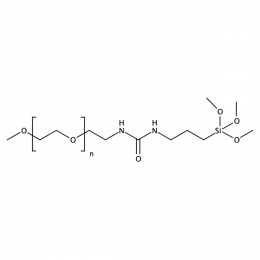 Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26069
Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26069 -
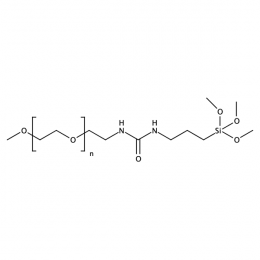 Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26070
Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26070 -
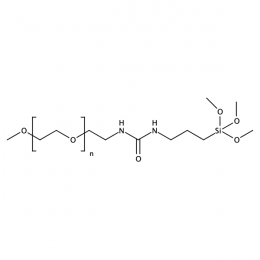 Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26071
Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26071 -
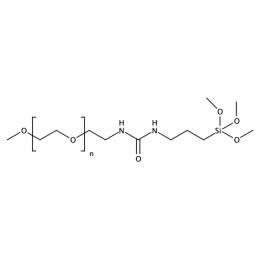 Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26072
Methoxy PEG silane, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26072 -
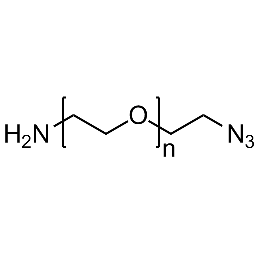 Amine PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26251
Amine PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26251 -
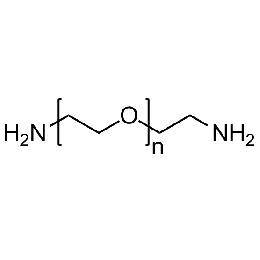 PEG diamine, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26078
PEG diamine, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26078 -
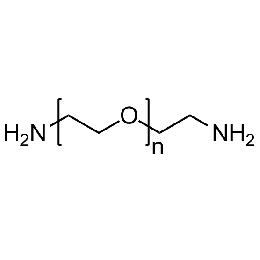 PEG diamine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26079
PEG diamine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26079 -
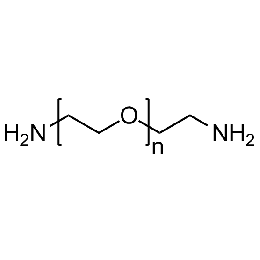 PEG diamine, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26080
PEG diamine, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26080 -
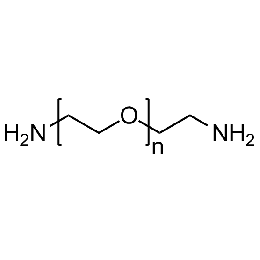 PEG diamine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26081
PEG diamine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26081 -
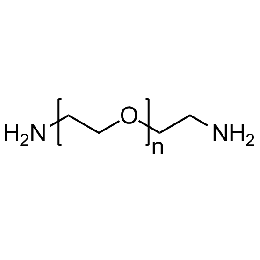 PEG diamine, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26082
PEG diamine, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26082 -
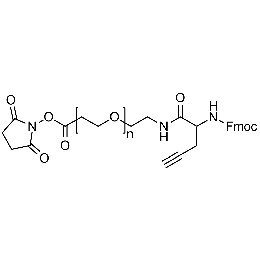 NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26247
NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26247 -
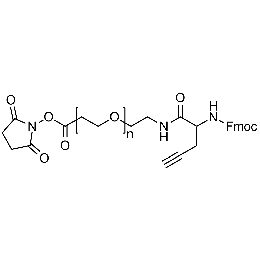 NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26246
NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26246 -
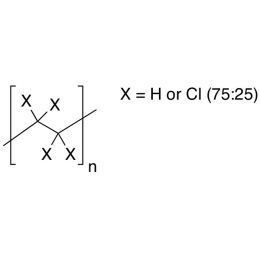 Polyethylene, chlorinated, 25% ClCatalog Number 01814
Polyethylene, chlorinated, 25% ClCatalog Number 01814Useful as primer or coating resin due to good adhesion properties. Randomly chlorinated HDPE.
-
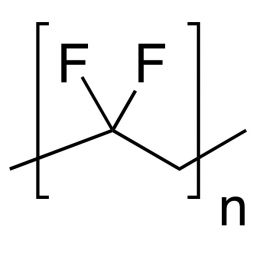 Poly(vinylidene fluoride)Catalog Number 18734
Poly(vinylidene fluoride)Catalog Number 18734Inert coating resin.
Polydispersity 2.5-3.0
-
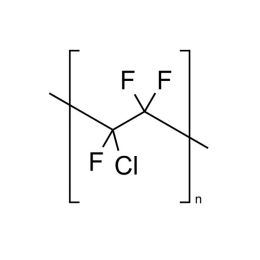 Poly(chlorotrifluroethylene)Catalog Number 15176
Poly(chlorotrifluroethylene)Catalog Number 15176Inert liquid for high temperature baths.
-
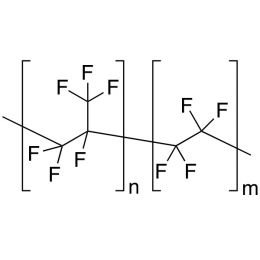 Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene Copolymer (Melt Flow Index 10-35 MI)Catalog Number 24778
Fluorinated Ethylene Propylene Copolymer (Melt Flow Index 10-35 MI)Catalog Number 24778Fluorinated copolymers of ethylene and propylene improve overall performance when formulated into plastics, elastomeric polymers, paints and coatings or inks and lubricants. Exhibits high release characteristics, excellent wear and mar resistance and slip resistance properties when used alone or in blends with other materials. The inherent toughness and high fluorine content imparts improved tear resistance, surface smoothness and flammability resistance in coating and ink formulations.
-
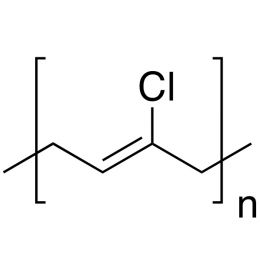 Poly(2-chloro-1,3-butadiene)Catalog Number 21289
Poly(2-chloro-1,3-butadiene)Catalog Number 21289Widely used rubber for applications requiring good solvent resistance.
Neoprene®
-
![Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) [powder]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/9/09689.jpg) Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) [powder]Catalog Number 09689
Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) [powder]Catalog Number 09689Polymer is water-insoluble but water-swellable. Used as a hydrogel. See 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate Soluble in: 95% lower alcohols (5% water), DMF
-
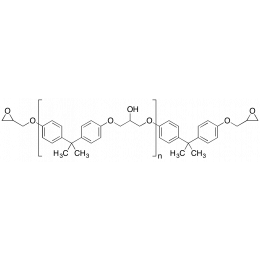 Epon® Resin 1001FCatalog Number 24305
Epon® Resin 1001FCatalog Number 24305(Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether) WPE: 525-550
Higher MW epoxy resin cured by amine catalyst, used for embedding.
-
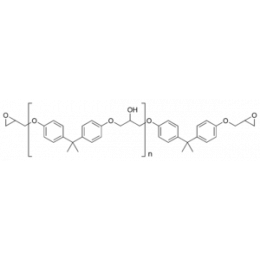 Epon® Resin 828Catalog Number 02334
Epon® Resin 828Catalog Number 02334(Bisphenol A diglycidyl ether) WPE: 185-192
Epon® Resin 828 is a standard epoxy resin used in formulation, fabrication and fusion technology. Widely used for embedding and potting. When cross-linked or hardened with appropriate amine curing agents, very good mechanical adhesive, dielectric and chemical resistance properties are obtained.
-
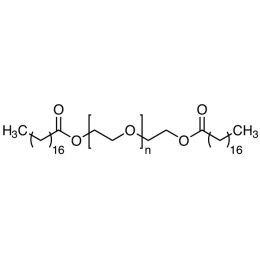 Poly(ethylene glycol) distearate 6,000Catalog Number 19234
Poly(ethylene glycol) distearate 6,000Catalog Number 19234A removable embedding medium for thin and thick sections. In thicker sections the exterior surface of mitochondria can be observed whereas in resin-embedded thin sections the mitochondria are most frequently observed in a cross section. DGD is used to prepare tissue for immunofluorescent localization of cytoskeletal components. Also used for tissue preparation for in-situ hybridization with nucleic acid probes.
MW = Molecular weight of PEG.
-
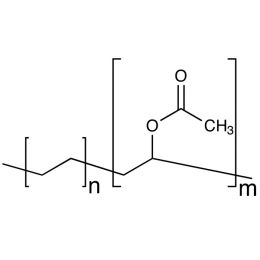 Ethylene-vinyl acetate, 20% ethylene, fine powderCatalog Number 24763
Ethylene-vinyl acetate, 20% ethylene, fine powderCatalog Number 24763Just add water to this solid grade polymer and it quickly responds by dispersing into latex particles that are useful bonding agents in composites. After evaporation of the water, a solid article may be formed from admixtures of the polymer and other solid components.
-
![Poly[methylene(polyphenyl) isocyanate]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/3/03099_1.jpg) Poly[methylene(polyphenyl) isocyanate]Catalog Number 03099
Poly[methylene(polyphenyl) isocyanate]Catalog Number 03099Low molecular weight polyisocyanate, reacts with glycols, polyamines to form gels.
Soluble in: acetone, THF, toluene
NCO content ~30%
-
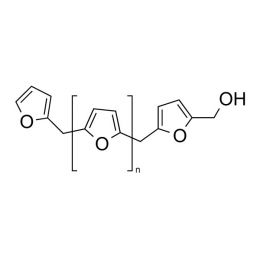 Poly(furfuryl alcohol)Catalog Number 15794
Poly(furfuryl alcohol)Catalog Number 15794Dark, viscous, fluid with double bonds in the polymer backbone.
-
![Polybutadiene [MW 1,600]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/2/22395_1.jpg) Polybutadiene [MW 1,600]Catalog Number 22395
Polybutadiene [MW 1,600]Catalog Number 22395Liquid polyene that can be cured with sulfur or peroxides.
1,2-vinyl content: 80%
-
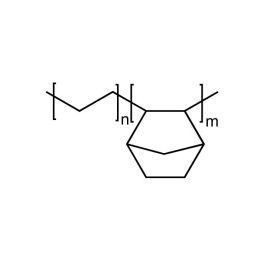 Cyclic Olefin Copolymer, HDT= 170°CCatalog Number 24746
Cyclic Olefin Copolymer, HDT= 170°CCatalog Number 24746Cyclic Olefin Copolymers are high transparency, low specific gravity, high heat resistant and have excellent optical properties and superior water vapor barrier characteristics. Combined with outstanding stiffness/ strength and favorable sterilization properties, they have found applications ranging from FDA approvals for pharmaceutical and food applications to optical applications and electronics materials. Whether used by itself or as a modifier for other resins, the ethylene-norbornene copolymer offers the optical clarity of polymethylmethacryate (pMMA), the heat resistance of polycarbonate (PC) and superior dimensional stability.
-
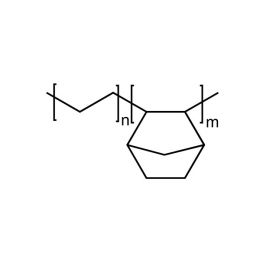 Cyclic Olefin Copolymer, HDT= 130°CCatalog Number 24749Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Cyclic Olefin Copolymer, HDT= 130°CCatalog Number 24749Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Cyclic Olefin Copolymers are high transparency, low specific gravity, high heat resistant and have excellent optical properties and superior water vapor barrier characteristics. Combined with outstanding stiffness/ strength and favorable sterilization properties, they have found applications ranging from FDA approvals for pharmaceutical and food applications to optical applications and electronics materials. Whether used by itself or as a modifier for other resins, the ethylene-norbornene copolymer offers the optical clarity of polymethylmethacryate (pMMA), the heat resistance of polycarbonate (PC) and superior dimensional stability.
Applications:
-
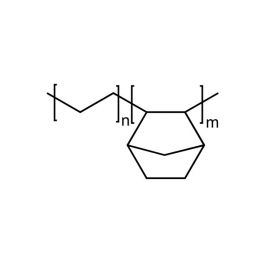 Cyclic Olefin Copolymer, HDT= 75°CCatalog Number 24750
Cyclic Olefin Copolymer, HDT= 75°CCatalog Number 24750Cyclic Olefin Copolymers are high transparency, low specific gravity, high heat resistant and have excellent optical properties and superior water vapor barrier characteristics. Combined with outstanding stiffness/ strength and favorable sterilization properties, they have found applications ranging from FDA approvals for pharmaceutical and food applications to optical applications and electronics materials. Whether used by itself or as a modifier for other resins, the ethylene-norbornene copolymer offers the optical clarity of polymethylmethacryate (pMMA), the heat resistance of polycarbonate (PC) and superior dimensional stability.
-
![Polybutadiene [MW 3,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06081_1.jpg) Polybutadiene [MW 3,000]Catalog Number 06081
Polybutadiene [MW 3,000]Catalog Number 06081Liquid polyene that can be cured with sulfur or peroxides
liquid vinyl-1,2=80%
-
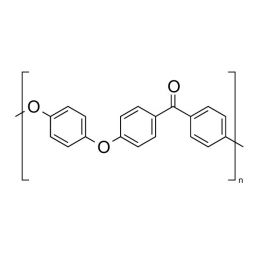 Poly ether ether ketone (PEEK)Catalog Number 23969
Poly ether ether ketone (PEEK)Catalog Number 23969High Temperature Resistant Polymer
Granules are dusted with a nominal 0.01% Calcium Stearate as a processing lubricant
-
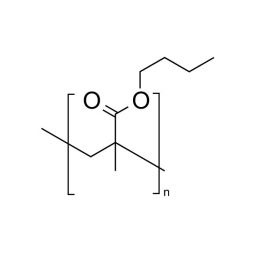 Poly(n-butyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 02061
Poly(n-butyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 02061Firm, water-insensitive, polymer.
- [η] = 0.50
- purity >95% polymer
-
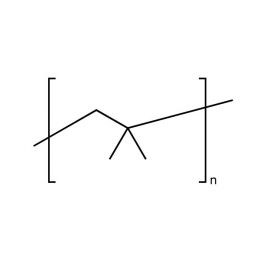 PolyisobutyleneCatalog Number 09894Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
PolyisobutyleneCatalog Number 09894Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Generally inert, tacky, polymers. Primarily used as tackifying agent in polymer formulations
-
![Polyisobutylene [MW 1,350]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/9/09896_1.jpg) Polyisobutylene [MW 1,350]Catalog Number 09896
Polyisobutylene [MW 1,350]Catalog Number 09896Generally inert, tacky, polymers. Primarily used as tackifying agent in polymer formulations.
-
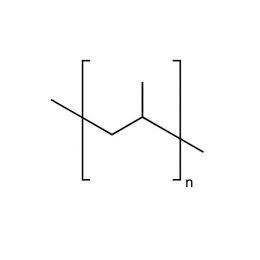 Polypropylene, IsotacticCatalog Number 06536
Polypropylene, IsotacticCatalog Number 06536Widely used polyolefin.
Soluble in: chlorinated hydrocarbons, aromatic hydrocarbons, isoamyl acetate.
Isotactic Mn 40,000 flakes
-
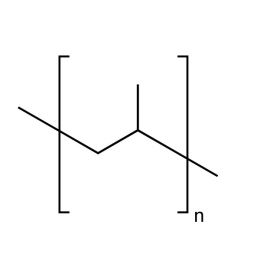 PolypropyleneCatalog Number 23968
PolypropyleneCatalog Number 23968Widely used polyolefin.
Atactic
-
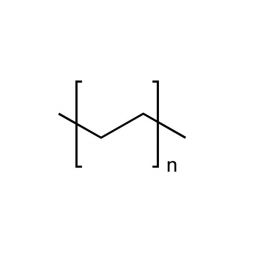 PolyethyleneCatalog Number 07652Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
PolyethyleneCatalog Number 07652Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Hydrophobic, easily processed or fabricated, resin
Soluble in: xylene, tetralin, TCE @ 50-60°
Mw/Mn = 1.10
lumps
-
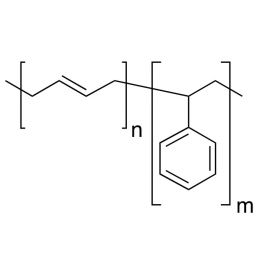 Poly(styrene/butadiene) 85:15Catalog Number 07073
Poly(styrene/butadiene) 85:15Catalog Number 07073Rubber modifier, random copolymer.
-
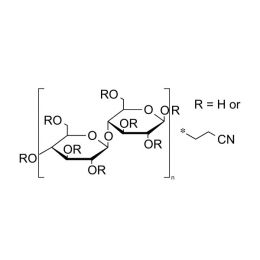 Cellulose, cyanoethyl etherCatalog Number 04687
Cellulose, cyanoethyl etherCatalog Number 04687Solvent-soluble cellulose ether. Soluble in polar solvents. High dielectric constant.
-
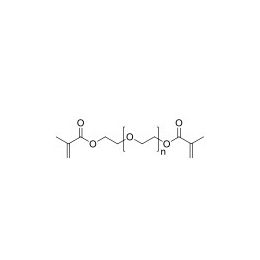 Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 600)Catalog Number 02364
Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 600)Catalog Number 02364Long-chain hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer. Molecular weight of PEG unit is approximately 600.
-
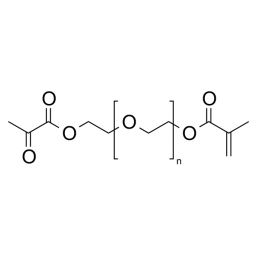 Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 200)Catalog Number 00096
Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 200)Catalog Number 00096Long-chain hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer. Molecular weight of PEG unit is approximately 200.
-
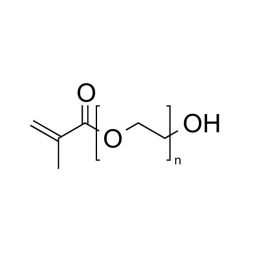 Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 200)Catalog Number 16712
Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 200)Catalog Number 16712Long-chain hydrophilic macromonomers. Used to introduce hydrophilic sites into polymers, to stabilize emulsion polymers, and to prepare comb polymers. (n) value is MW of PEG unit.
n= 200 (MW of PEG Block= 200)
-
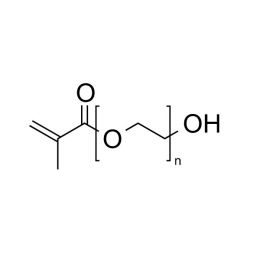 Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 400)Catalog Number 16713
Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 400)Catalog Number 16713PEGMA 400 (HO-PEG-MA 400) is a long-chain hydrophilic macromonomer used to introduce hydrophilic sites into polymers, to stabilize emulsion polymers, and to prepare comb polymers.
MW of PEG Block = 400
-
 Parafilm, 4" x 250' per rollCatalog Number 3989A
Parafilm, 4" x 250' per rollCatalog Number 3989AUsed for sealing or protecting vessels such as flasks or cuvettes. Molds quickly and seals laboratory vessels with a disposable translucent film. Parafilm is stretchable, moldable, waterproof, odorless, thermoplastic and self-adhering.
-
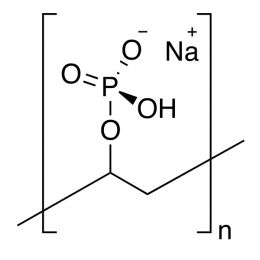 Poly(vinyl phosphoric acid), sodium saltCatalog Number 04391
Poly(vinyl phosphoric acid), sodium saltCatalog Number 04391Water-soluble polymeric phosphate ester. Uncrosslinked.
Phosphorous content min 5%
-
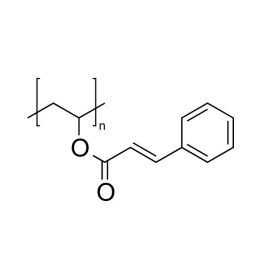 Poly(vinyl cinnamate)Catalog Number 02648
Poly(vinyl cinnamate)Catalog Number 02648Photocrosslinkable polymer.
-
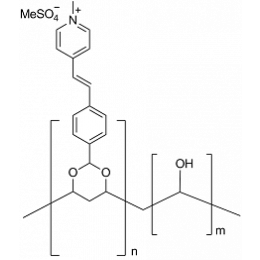 Poly(vinyl alcohol), N-methyl-4(4’-formylstyryl)pyridinium methosulfate acetalCatalog Number 22570
Poly(vinyl alcohol), N-methyl-4(4’-formylstyryl)pyridinium methosulfate acetalCatalog Number 22570Water-soluble, photocrosslinkable polymer. Polymer has high dielectric constant. Commercially used for making screen-printing emulsions for direct and direct/indirect methods.
Other applications include non-silver films such as contact films, color proofing, deep-etch plates, color filters, suitable for UV curable films for biomedical coatings.
13.3% solution in water. 10g polymer PVA-SbQ 4.1 mol % SbQ
-
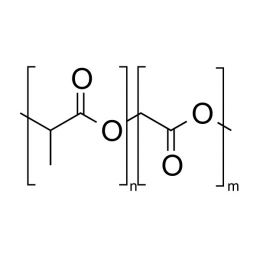 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 19076
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 19076Biodegradable polymers. Copolymers are easier to fabricate than homopolymers.
-
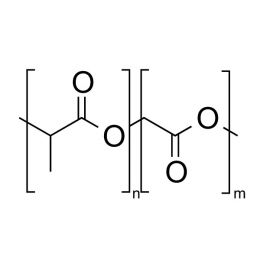 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 85:15, IV 0.85 dL/gCatalog Number 23989
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 85:15, IV 0.85 dL/gCatalog Number 23989Biodegradable polymers. Copolymers are easier to fabricate than homopolymers.
Soluble in: MDC, THF, ethyl acetate, acetone
85/15 i.v. 0.55-0.75
-
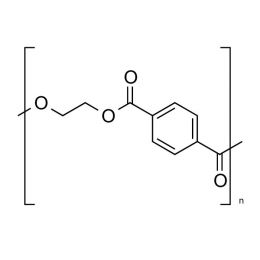 Poly(ethylene glycol terephthalate)Catalog Number 04301
Poly(ethylene glycol terephthalate)Catalog Number 04301Polymer widely used in films, fibers, and drink bottles. Low gas permeability.
(PET)
-
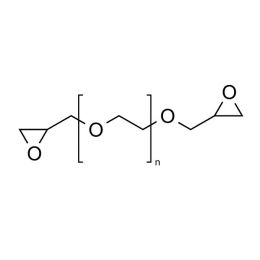 Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 1000)Catalog Number 24047Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (n ~22; also known as PEGDE) is a difunctional, water-soluble crosslinker for amine-, hydroxyl-, and carboxyl-functional polymers.
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 1000)Catalog Number 24047Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (n ~22; also known as PEGDE) is a difunctional, water-soluble crosslinker for amine-, hydroxyl-, and carboxyl-functional polymers. -
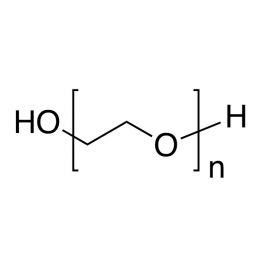 Poly(ethylene glycol) MW 2,000Catalog Number 25360
Poly(ethylene glycol) MW 2,000Catalog Number 25360Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 1,450]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/0/00679.jpg) Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 1,450]Catalog Number 00679Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 1,450]Catalog Number 00679Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
PEG
-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 600]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/0/00684.jpg) Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 600]Catalog Number 00684
Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 600]Catalog Number 00684Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
-
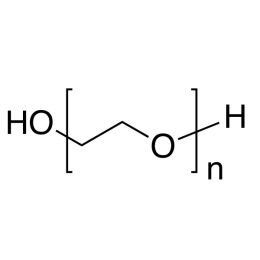 Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 400 (PEG 400)Catalog Number 01109
Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 400 (PEG 400)Catalog Number 01109Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: alcohol, acetone, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
-
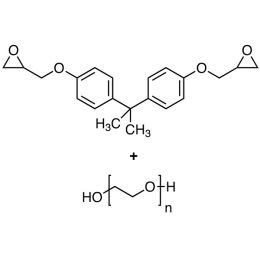 Poly(ethylene glycol)-bisphenol A diglycidyl ether adductCatalog Number 04686
Poly(ethylene glycol)-bisphenol A diglycidyl ether adductCatalog Number 04686Polymer contains more hydroxyl groups (4 or more) than poly(ethylene glycol)
-
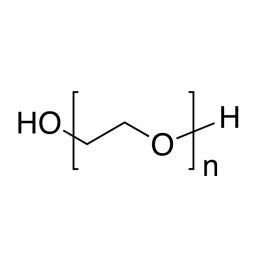 Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 3400, pharma grade (PEG 3400)Catalog Number 06102
Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 3400, pharma grade (PEG 3400)Catalog Number 06102Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
PEG
-
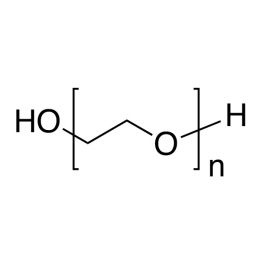 Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 7,500 (PEG 7500)Catalog Number 06103
Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 7,500 (PEG 7500)Catalog Number 06103Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: alcohol, acetone, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEG
-
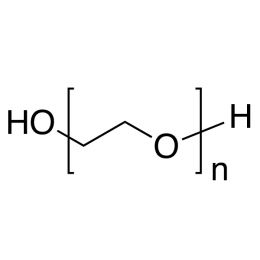 Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 10,000-16,000 (PEG 10K-16K)Catalog Number 22567
Poly(ethylene glycol), MW 10,000-16,000 (PEG 10K-16K)Catalog Number 22567Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: alcohol, acetone, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEG
-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 20,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/2/22568.jpg) Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 20,000]Catalog Number 22568
Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 20,000]Catalog Number 22568Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: alcohol, acetone, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEG
-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 8000; pharma grade]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/7/17243.jpg) Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 8000; pharma grade]Catalog Number 17243
Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 8000; pharma grade]Catalog Number 17243Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
PEG
-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 1,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/0/00682.jpg) Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 1,000]Catalog Number 00682
Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW 1,000]Catalog Number 00682Water-soluble, nonionic, relatively inert, liquids or solids. Confers slip and humectant properties to coatings. See poly(ethylene oxide) for higher molecular weights. The terms poly(ethylene glycol) and poly(ethylene oxide) refer to polymers which are chemically identical. Polymer chains are hydroxyl-terminated at both ends. At all except the lowest molecular weights poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: alcohol, acetone, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
-
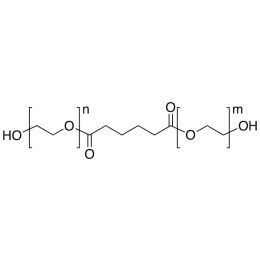 Poly(ethylene glycol) (200) adipateCatalog Number 21509
Poly(ethylene glycol) (200) adipateCatalog Number 21509Water-soluble, biodegradable, polymer. Reaction product of one molecule of adipic acid and two molecules of PEG 200
-
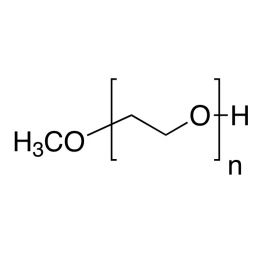 Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl etherCatalog Number 04457
Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl etherCatalog Number 04457Neutral, water-soluble, polymers with hydroxyl group at one end only
-
![Poly(ethylene/vinyl acetate) [60:40 (wt)]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06107_1.jpg) Poly(ethylene/vinyl acetate) [60:40 (wt)]Catalog Number 06107
Poly(ethylene/vinyl acetate) [60:40 (wt)]Catalog Number 06107Used as a hot-melt adhesive, wax additive, and precursor to poly (ethylene/vinyl alcohol) resins.
60:40 (wt) Antioxidant 540 ppm BHT
-
![Poly(ethylene/vinyl acetate) [72:28 (wt)]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06108_1.jpg) Poly(ethylene/vinyl acetate) [72:28 (wt)]Catalog Number 06108
Poly(ethylene/vinyl acetate) [72:28 (wt)]Catalog Number 06108Used as a hot-melt adhesive, wax additive, and precursor to poly (ethylene/vinyl alcohol) resins.
72:28 (wt))
-
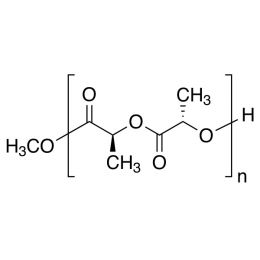 Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 1.8 dl/gCatalog Number 18402
Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 1.8 dl/gCatalog Number 18402Biodegradable polymer. Degradation rate is inversely related to polymer molecular weight.
Crystalline polymer with higher molecular weight polymers having a crystallinity of about 70%.
i.v. 1.30-1.60 Polydispersity ~1.8
-
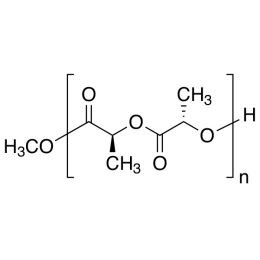 Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 5.0 dl/gCatalog Number 18582
Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 5.0 dl/gCatalog Number 18582Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer for medical device and pharmaceutical applications. It is used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions. Due to their history, polylactides are one of the easiest and most affordable biodegradable polymers for medical devices.
-
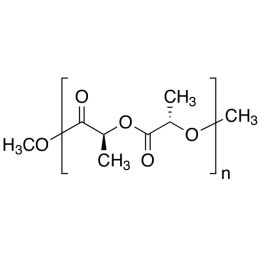 Poly(L-lactic acid) Molecular Weight KitCatalog Number 18599
Poly(L-lactic acid) Molecular Weight KitCatalog Number 18599Biodegradable polymer. Degradation rate is inversely related to polymer molecular weight.
Kit contains:
5g each of polymers with i.v. values of:
- 0.10 - 0.20
- 0.80 - 1.20
- 1.30 - 1.60
- 4.00 - 5.20
-
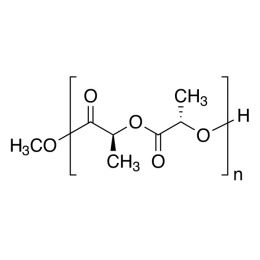 Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 6.5 dl/gCatalog Number 21512
Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 6.5 dl/gCatalog Number 21512Biodegradable polymer. Degradation rate is inversely related to polymer molecular weight.
Crystalline polymer with higher molecular weight polymers having a crystallinity of about 70%.
i.v. >7.00 Polydispersity ~1.8
-
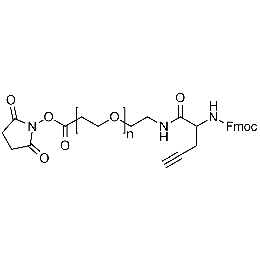 NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26245
NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26245 -
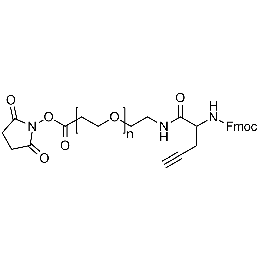 NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26244
NHS PEG Fmoc-amine alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26244 -
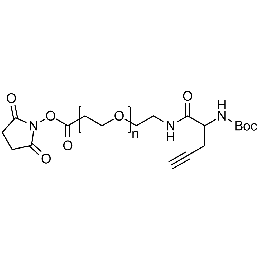 NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26243
NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26243 -
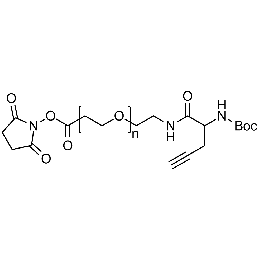 NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26242
NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26242 -
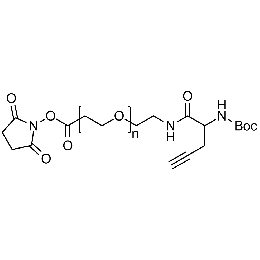 NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26241
NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26241 -
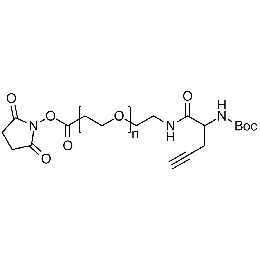 NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26240
NHS PEG Boc-amine alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26240 -
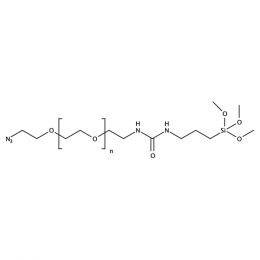 Silane PEG azide, MP 20000Catalog Number 26235
Silane PEG azide, MP 20000Catalog Number 26235 -
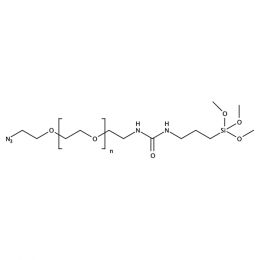 Silane PEG azide, MP 10000Catalog Number 26234
Silane PEG azide, MP 10000Catalog Number 26234 -
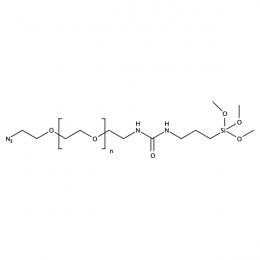 Silane PEG azide, MP 5000Catalog Number 26233
Silane PEG azide, MP 5000Catalog Number 26233 -
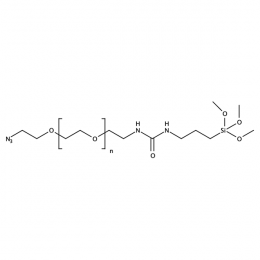 Silane PEG azide, MP 3000Catalog Number 26232
Silane PEG azide, MP 3000Catalog Number 26232 -
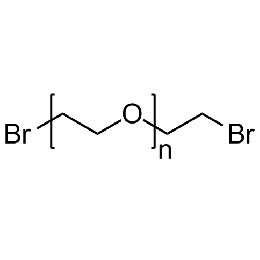 PEG dibromide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26083
PEG dibromide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26083 -
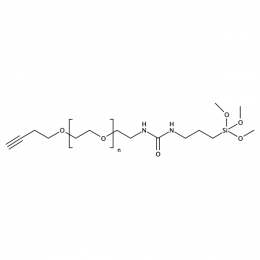 Silane PEG alkyne, MP 20000Catalog Number 26231
Silane PEG alkyne, MP 20000Catalog Number 26231 -
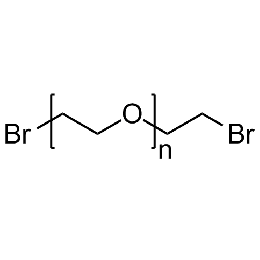 PEG dibromide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26084
PEG dibromide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26084 -
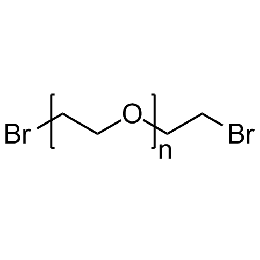 PEG dibromide, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26085
PEG dibromide, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26085 -
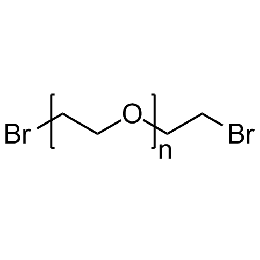 PEG dibromide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26086
PEG dibromide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26086 -
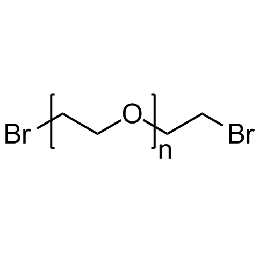 PEG dibromide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26087
PEG dibromide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26087 -
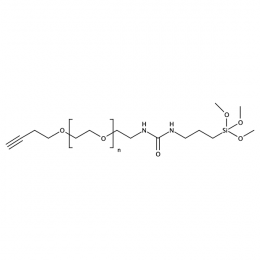 Silane PEG alkyne, MP 10000Catalog Number 26230
Silane PEG alkyne, MP 10000Catalog Number 26230 -
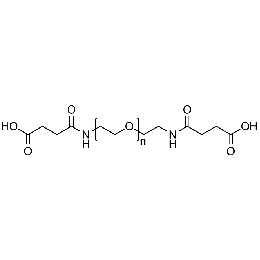 PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 2000Catalog Number 26088
PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 2000Catalog Number 26088 -
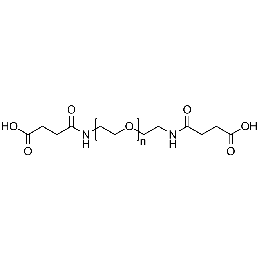 PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 3000Catalog Number 26089
PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 3000Catalog Number 26089 -
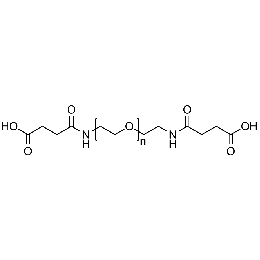 PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 6000Catalog Number 26090
PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 6000Catalog Number 26090 -
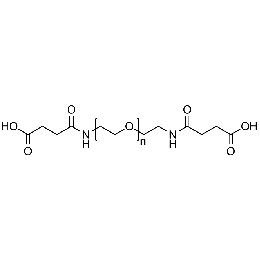 PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 10000Catalog Number 26091
PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 10000Catalog Number 26091 -
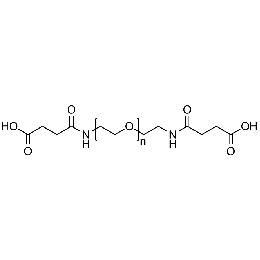 PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 20000Catalog Number 26092
PEG di(carboxylic acid), Mp 20000Catalog Number 26092 -
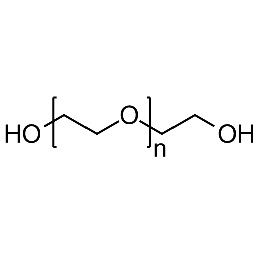 PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26098
PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26098 -
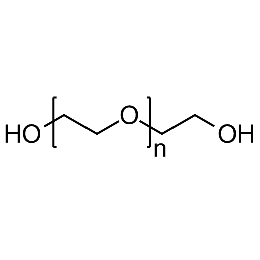 PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26099
PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26099 -
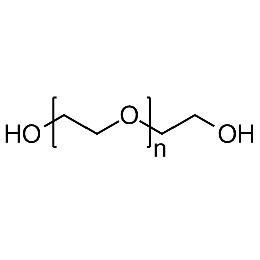 PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26100
PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26100 -
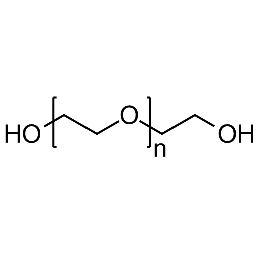 PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26101
PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26101 -
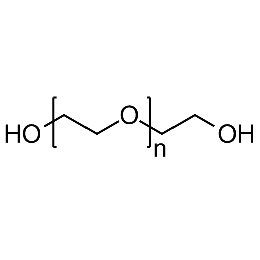 PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26102
PEG dihydroxyl, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26102 -
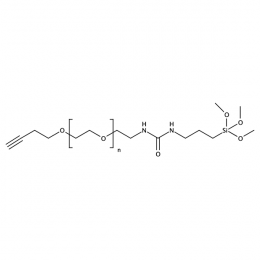 Silane PEG alkyne, MP 5000Catalog Number 26229
Silane PEG alkyne, MP 5000Catalog Number 26229 -
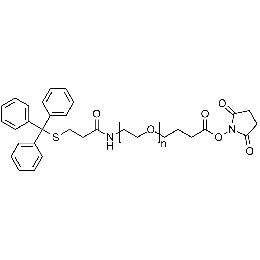 Tritythiol PEG NHS, MP 10000Catalog Number 26227
Tritythiol PEG NHS, MP 10000Catalog Number 26227 -
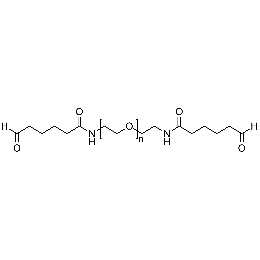 PEG dialdehyde, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26093
PEG dialdehyde, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26093 -
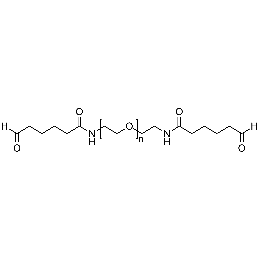 PEG dialdehyde, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26094
PEG dialdehyde, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26094 -
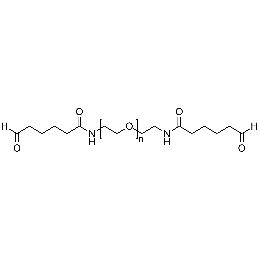 PEG dialdehyde, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26095
PEG dialdehyde, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26095 -
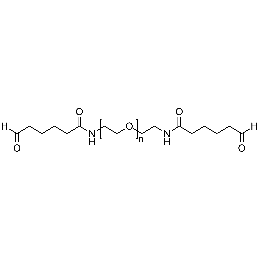 PEG dialdehyde, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26096
PEG dialdehyde, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26096 -
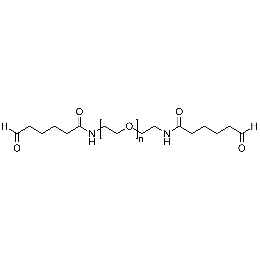 PEG dialdehyde, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26097
PEG dialdehyde, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26097 -
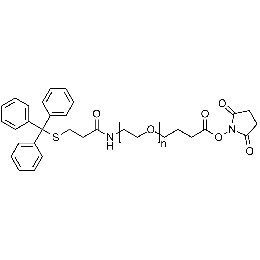 Tritythiol PEG NHS, MP 5000Catalog Number 26226
Tritythiol PEG NHS, MP 5000Catalog Number 26226 -
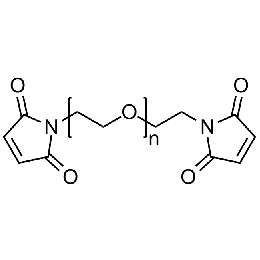 PEG dimaleimide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26103
PEG dimaleimide, Mp 2000Catalog Number 26103 -
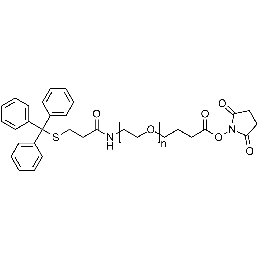 Tritythiol PEG NHS, MP 3000Catalog Number 26225
Tritythiol PEG NHS, MP 3000Catalog Number 26225 -
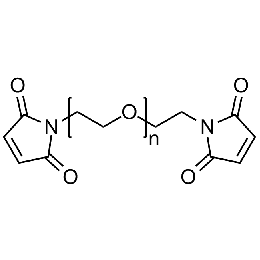 PEG dimaleimide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26104
PEG dimaleimide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26104 -
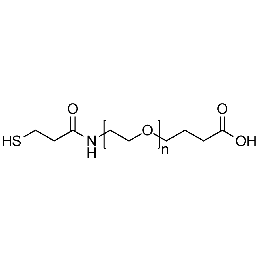 Thiol PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26224
Thiol PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26224 -
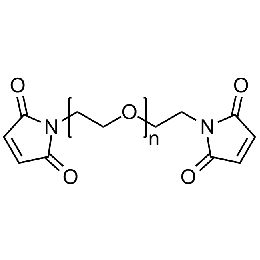 PEG dimaleimide, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26105
PEG dimaleimide, Mp 6000Catalog Number 26105 -
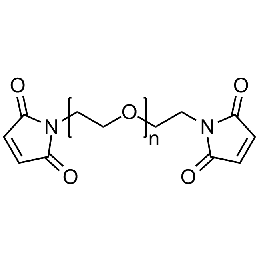 PEG dimaleimide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26106
PEG dimaleimide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26106 -
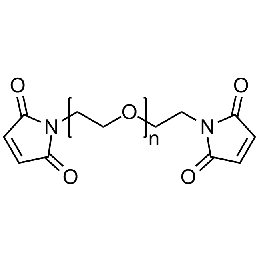 PEG dimaleimide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26107
PEG dimaleimide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26107 -
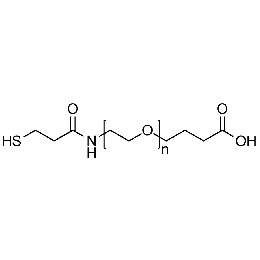 Thiol PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26223
Thiol PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26223 -
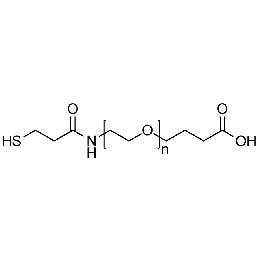 Thiol PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26222
Thiol PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26222 -
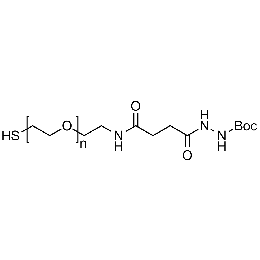 Thiol PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 10,000Catalog Number 26221
Thiol PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 10,000Catalog Number 26221 -
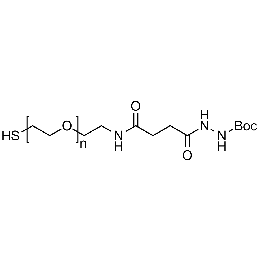 Thiol PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 5,000Catalog Number 26220
Thiol PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 5,000Catalog Number 26220 -
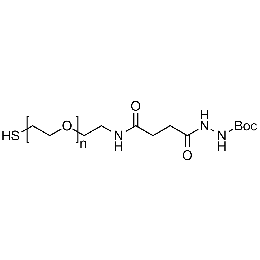 Thiol PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 3,000Catalog Number 26219
Thiol PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 3,000Catalog Number 26219 -
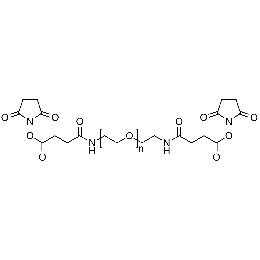 PEG di(NHS), Mp 2000Catalog Number 26113
PEG di(NHS), Mp 2000Catalog Number 26113 -
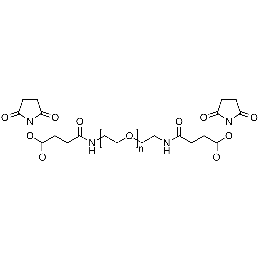 PEG di(NHS), Mp 3000Catalog Number 26114
PEG di(NHS), Mp 3000Catalog Number 26114 -
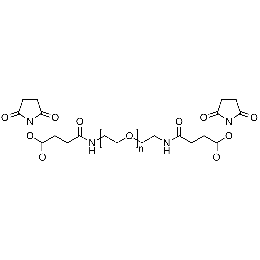 PEG di(NHS), Mp 6000Catalog Number 26115
PEG di(NHS), Mp 6000Catalog Number 26115 -
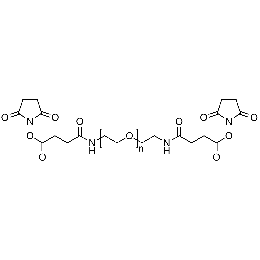 PEG di(NHS), Mp 10000Catalog Number 26116
PEG di(NHS), Mp 10000Catalog Number 26116 -
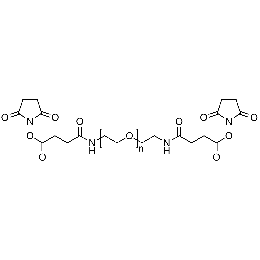 PEG di(NHS), Mp 20000Catalog Number 26117
PEG di(NHS), Mp 20000Catalog Number 26117 -
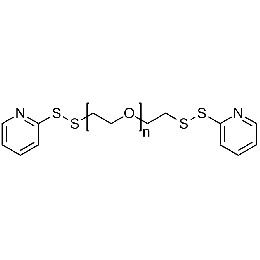 PEG di(OPSS), Mp 2000Catalog Number 26118
PEG di(OPSS), Mp 2000Catalog Number 26118 -
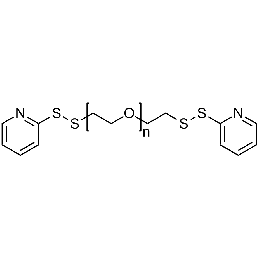 PEG di(OPSS), Mp 3000Catalog Number 26119
PEG di(OPSS), Mp 3000Catalog Number 26119 -
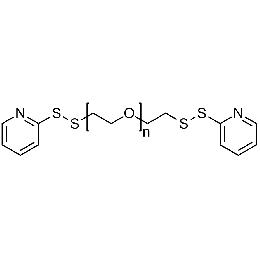 PEG di(OPSS), Mp 6000Catalog Number 26120
PEG di(OPSS), Mp 6000Catalog Number 26120 -
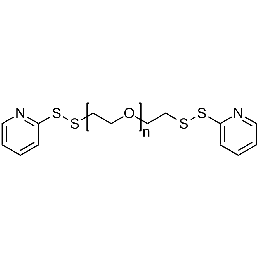 PEG di(OPSS), Mp 10000Catalog Number 26121
PEG di(OPSS), Mp 10000Catalog Number 26121 -
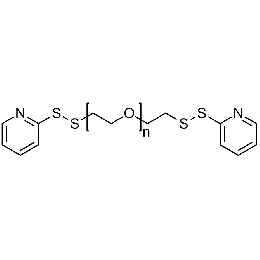 PEG di(OPSS), Mp 20000Catalog Number 26122
PEG di(OPSS), Mp 20000Catalog Number 26122 -
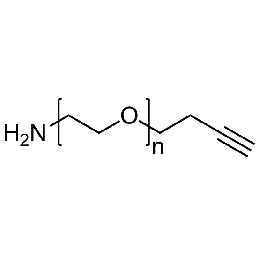 Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26123
Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26123 -
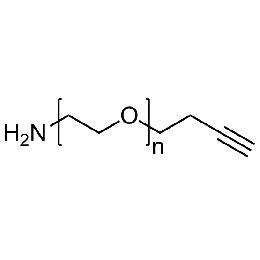 Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26124
Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26124 -
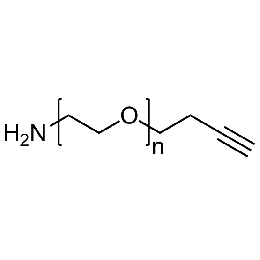 Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26125
Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26125 -
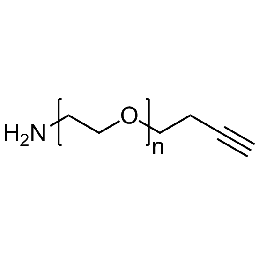 Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26126
Amine PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26126 -
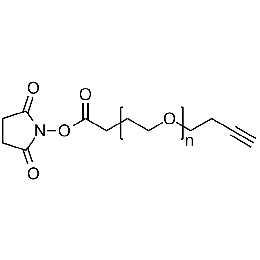 NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26127
NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26127 -
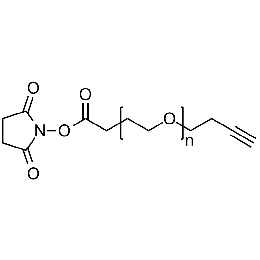 NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26128
NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26128 -
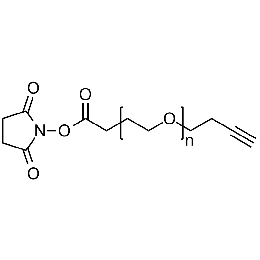 NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26129
NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26129 -
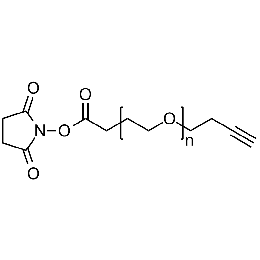 NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26130
NHS PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26130 -
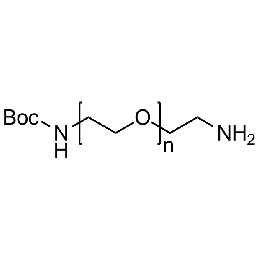 Amine PEG Boc-amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26131
Amine PEG Boc-amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26131 -
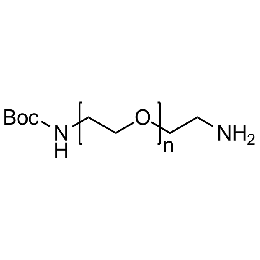 Amine PEG Boc-amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26132
Amine PEG Boc-amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26132 -
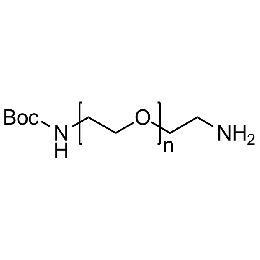 Amine PEG Boc-amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26133
Amine PEG Boc-amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26133 -
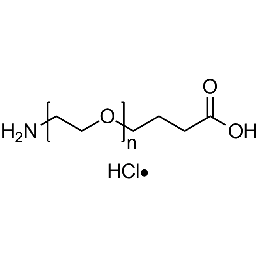 Amine PEG carboxylic acid hydrochloride, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26134
Amine PEG carboxylic acid hydrochloride, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26134 -
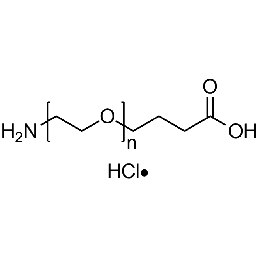 Amine PEG carboxylic acid hydrochloride, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26135
Amine PEG carboxylic acid hydrochloride, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26135 -
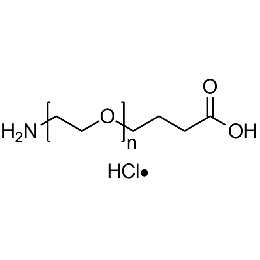 Amine PEG carboxylic acid hydrochloride, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26136
Amine PEG carboxylic acid hydrochloride, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26136 -
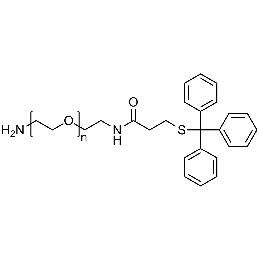 Amine PEG tritylthiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26137
Amine PEG tritylthiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26137 -
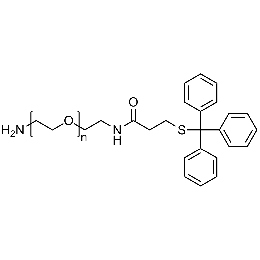 Amine PEG tritylthiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26138
Amine PEG tritylthiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26138 -
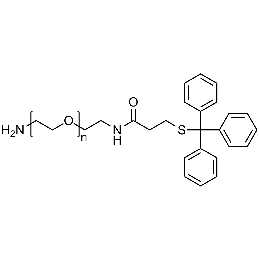 Amine PEG tritylthiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26139
Amine PEG tritylthiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26139 -
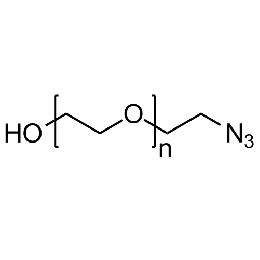 Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26140
Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26140 -
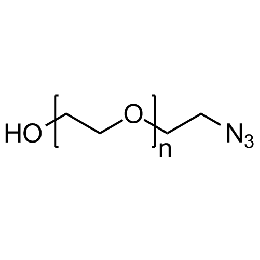 Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26141
Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26141 -
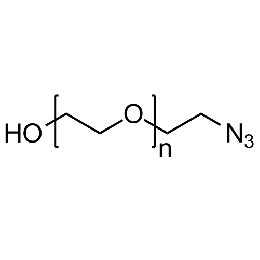 Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26142
Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26142 -
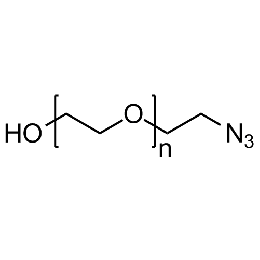 Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26143
Hydroxyl PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26143 -
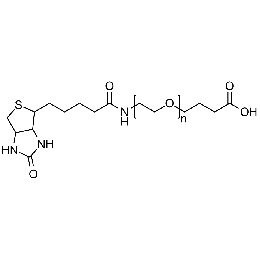 Biotin PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26147
Biotin PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26147 -
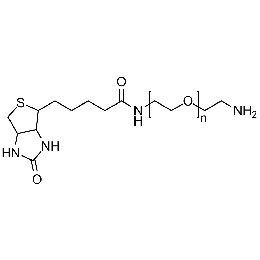 Biotin PEG amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26145
Biotin PEG amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26145 -
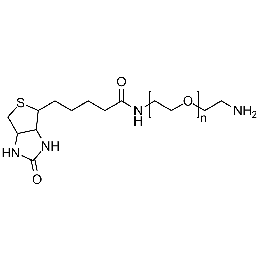 Biotin PEG amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26146
Biotin PEG amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26146 -
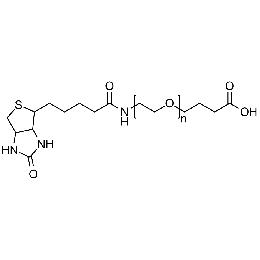 Biotin PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26148
Biotin PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26148 -
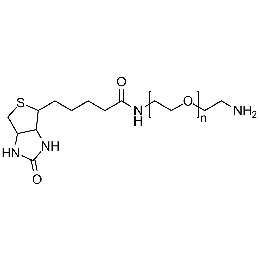 Biotin PEG amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26144
Biotin PEG amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26144 -
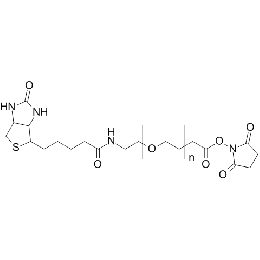 Biotin PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26150
Biotin PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26150 -
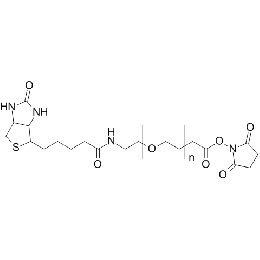 Biotin PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26151
Biotin PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26151 -
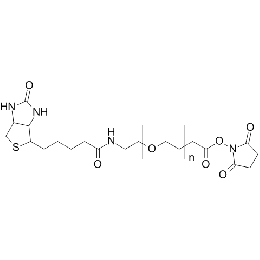 Biotin PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26152
Biotin PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26152 -
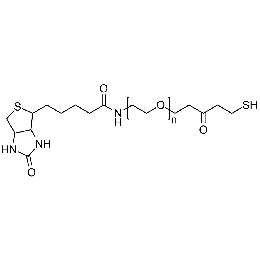 Biotin PEG thiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26153
Biotin PEG thiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26153 -
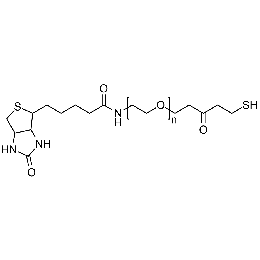 Biotin PEG thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26154
Biotin PEG thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26154 -
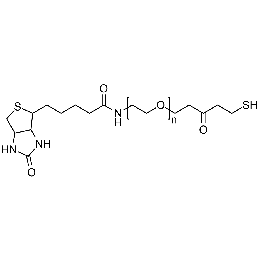 Biotin PEG thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26155
Biotin PEG thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26155 -
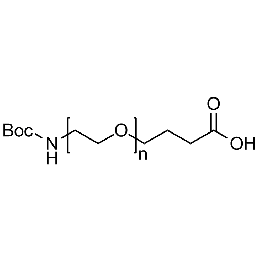 Boc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26156
Boc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26156 -
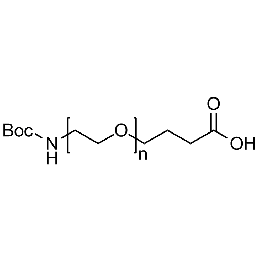 Boc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26157
Boc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26157 -
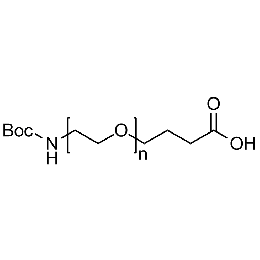 Boc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26158
Boc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26158 -
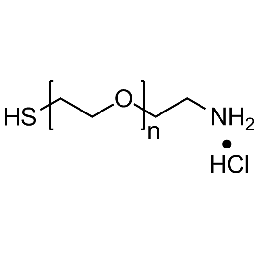 Thiol PEG amine hydrochloride, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26218
Thiol PEG amine hydrochloride, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26218 -
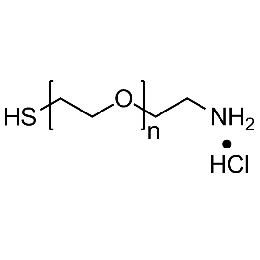 Thiol PEG amine hydrochloride, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26217
Thiol PEG amine hydrochloride, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26217 -
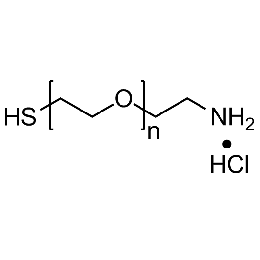 Thiol PEG amine hydrochloride, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26216
Thiol PEG amine hydrochloride, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26216 -
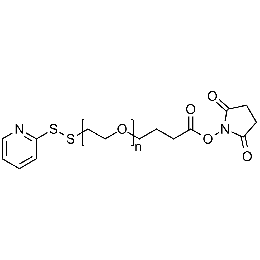 NHS PEG OPSS, MP 20,000Catalog Number 26215
NHS PEG OPSS, MP 20,000Catalog Number 26215 -
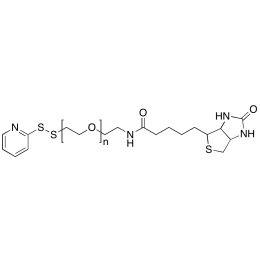 Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 20,000Catalog Number 26211
Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 20,000Catalog Number 26211 -
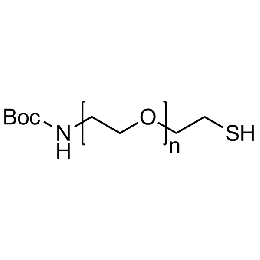 Boc-amine PEG thiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26159
Boc-amine PEG thiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26159 -
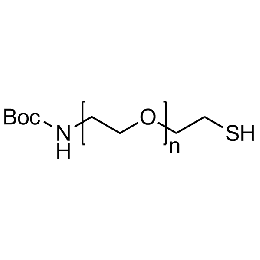 Boc-amine PEG thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26160
Boc-amine PEG thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26160 -
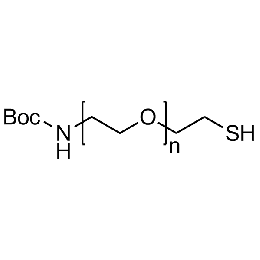 Boc-amine PEG thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26161
Boc-amine PEG thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26161 -
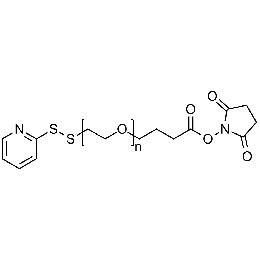 NHS PEG OPSS, MP 5,000Catalog Number 26213
NHS PEG OPSS, MP 5,000Catalog Number 26213 -
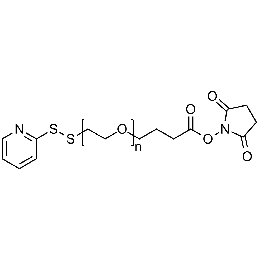 NHS PEG OPSS, MP 3,000Catalog Number 26212
NHS PEG OPSS, MP 3,000Catalog Number 26212 -
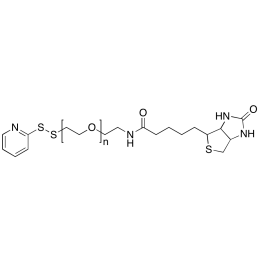 Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 10,000Catalog Number 26210
Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 10,000Catalog Number 26210 -
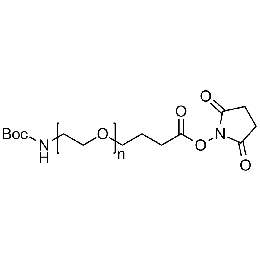 Boc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26162
Boc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26162 -
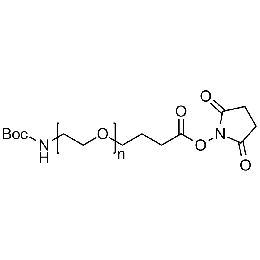 Boc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26163
Boc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26163 -
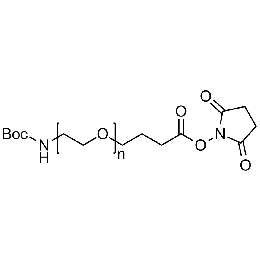 Boc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26164
Boc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26164 -
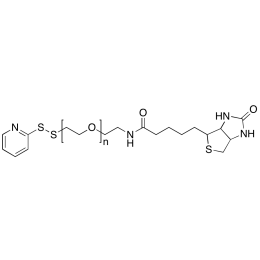 Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 3,000Catalog Number 26208
Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 3,000Catalog Number 26208 -
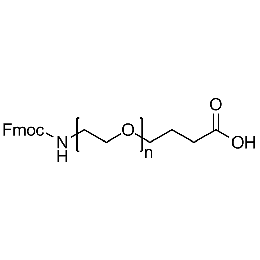 Fmoc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26165
Fmoc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26165 -
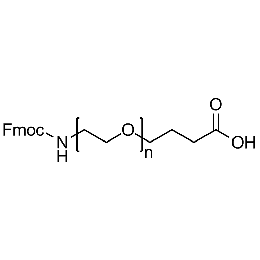 Fmoc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26166
Fmoc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26166 -
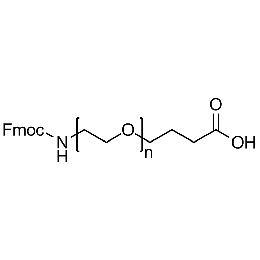 Fmoc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26167
Fmoc-amine PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26167 -
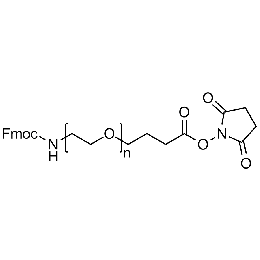 Fmoc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26168
Fmoc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26168 -
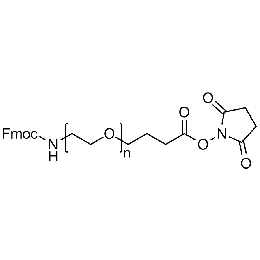 Fmoc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26169
Fmoc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26169 -
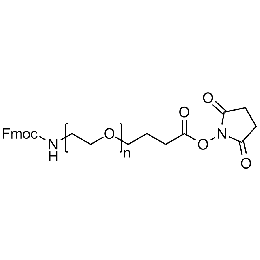 Fmoc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26170
Fmoc-amine PEG NHS, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26170 -
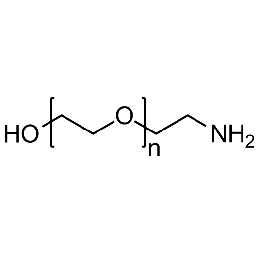 Hydroxyl PEG amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26171
Hydroxyl PEG amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26171 -
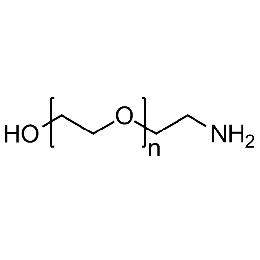 Hydroxyl PEG amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26172
Hydroxyl PEG amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26172 -
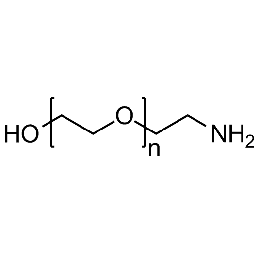 Hydroxyl PEG amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26173
Hydroxyl PEG amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26173 -
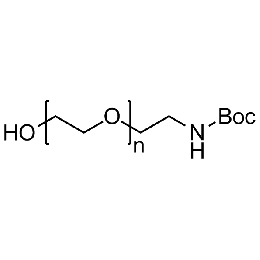 Hydroxyl PEG boc-amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26174
Hydroxyl PEG boc-amine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26174 -
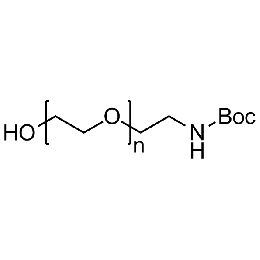 Hydroxyl PEG boc-amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26175
Hydroxyl PEG boc-amine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26175 -
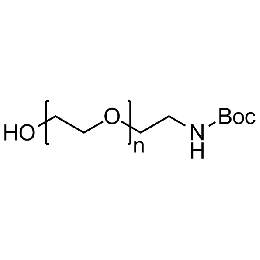 Hydroxyl PEG boc-amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26176
Hydroxyl PEG boc-amine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26176 -
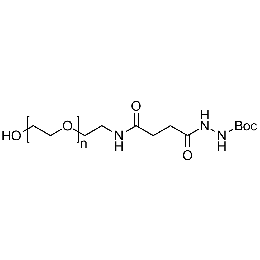 Hydroxyl PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26177
Hydroxyl PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26177 -
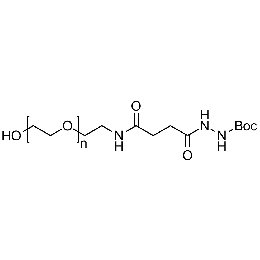 Hydroxyl PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26178
Hydroxyl PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26178 -
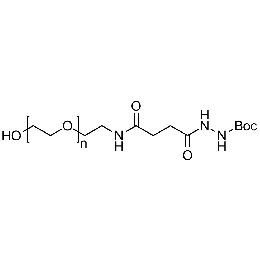 Hydroxyl PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26179
Hydroxyl PEG Boc-hydrazine, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26179 -
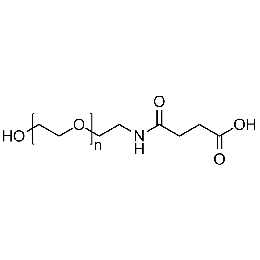 Hydroxyl PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26180
Hydroxyl PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26180 -
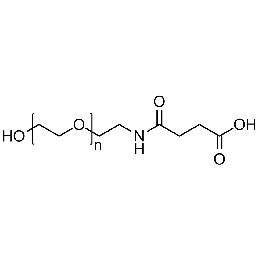 Hydroxyl PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26181
Hydroxyl PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26181 -
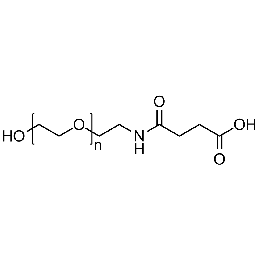 Hydroxyl PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26182
Hydroxyl PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26182 -
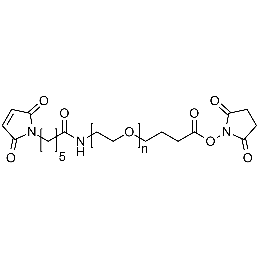 Maleimide PEG NHS, MP 10,000Catalog Number 26207
Maleimide PEG NHS, MP 10,000Catalog Number 26207 -
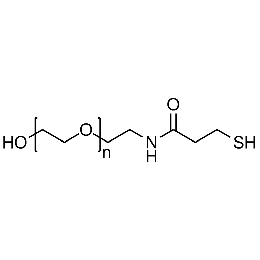 Hydroxyl PEG thiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26183
Hydroxyl PEG thiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26183 -
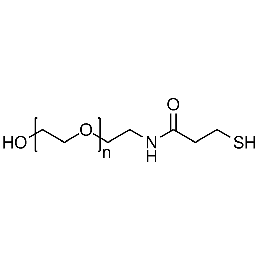 Hydroxyl PEG thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26184
Hydroxyl PEG thiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26184 -
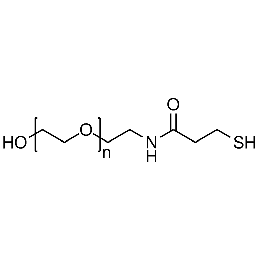 Hydroxyl PEG thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26185
Hydroxyl PEG thiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26185 -
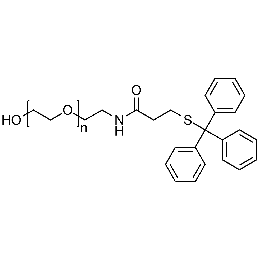 Hydroxyl PEG tritylthiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26186
Hydroxyl PEG tritylthiol, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26186 -
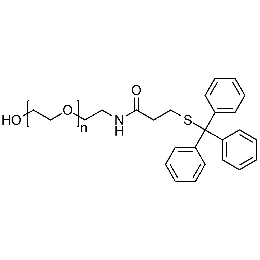 Hydroxyl PEG tritylthiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26187
Hydroxyl PEG tritylthiol, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26187 -
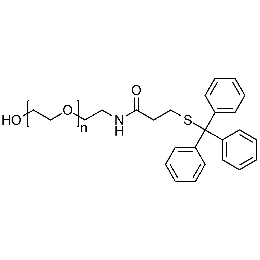 Hydroxyl PEG tritylthiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26188
Hydroxyl PEG tritylthiol, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26188 -
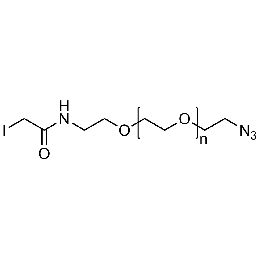 Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26189
Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26189 -
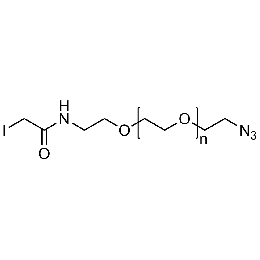 Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26190
Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26190 -
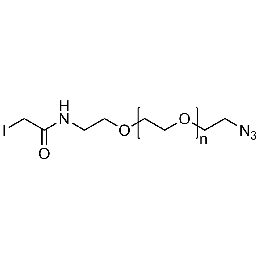 Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26191
Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26191 -
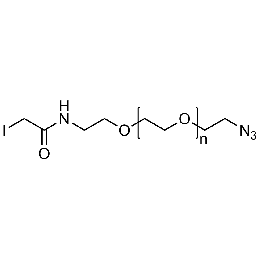 Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26192
Iodoacetamide PEG azide, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26192 -
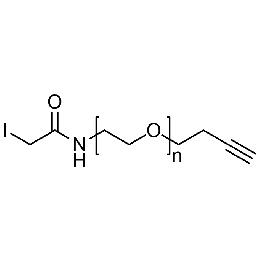 Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26193
Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26193 -
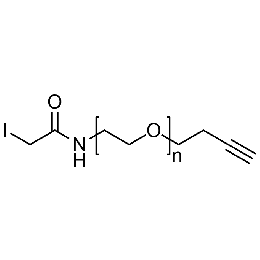 Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26194
Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26194 -
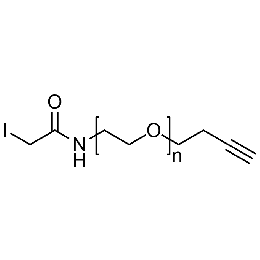 Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26195
Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26195 -
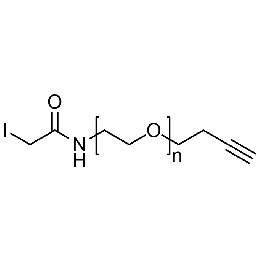 Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26196
Iodoacetamide PEG alkyne, Mp 20000Catalog Number 26196 -
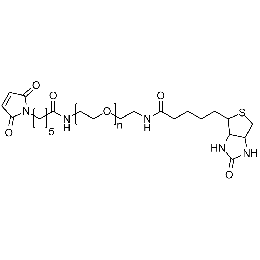 Maleimide PEG biotin, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26199
Maleimide PEG biotin, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26199 -
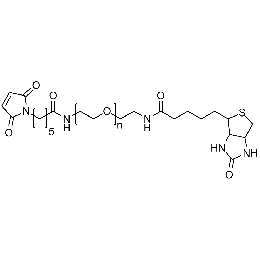 Maleimide PEG biotin, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26200
Maleimide PEG biotin, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26200 -
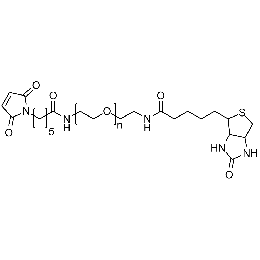 Maleimide PEG biotin, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26201
Maleimide PEG biotin, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26201 -
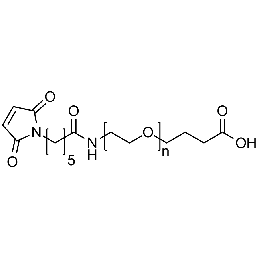 Maleimide PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26202
Maleimide PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26202 -
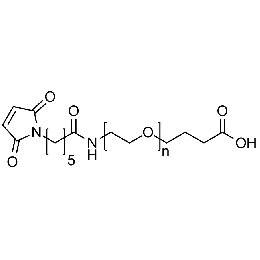 Maleimide PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26203
Maleimide PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26203 -
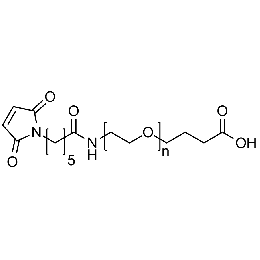 Maleimide PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26204
Maleimide PEG carboxylic acid, Mp 10000Catalog Number 26204 -
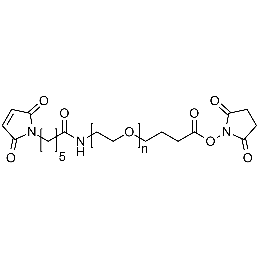 Maleimide PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26205
Maleimide PEG NHS, Mp 3000Catalog Number 26205 -
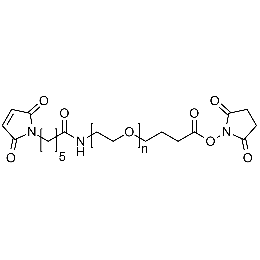 Maleimide PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26206
Maleimide PEG NHS, Mp 5000Catalog Number 26206 -
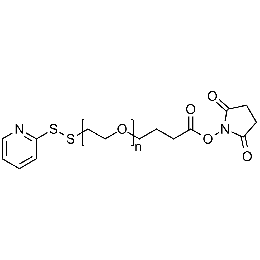 NHS PEG OPSS, MP 10,000Catalog Number 26214
NHS PEG OPSS, MP 10,000Catalog Number 26214 -
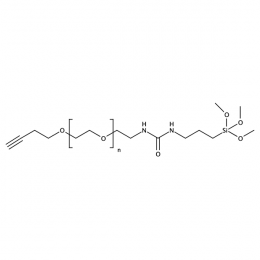 Silane PEG alkyne, MP 3000Catalog Number 26228
Silane PEG alkyne, MP 3000Catalog Number 26228 -
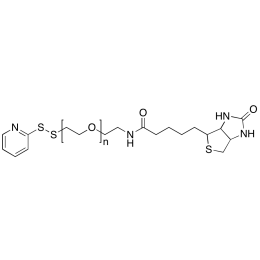 Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 5,000Catalog Number 26209
Biotin PEG OPSS, MP 5,000Catalog Number 26209 -
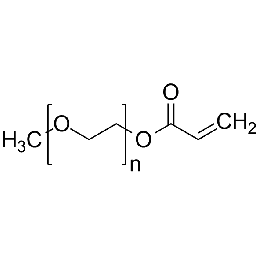 Poly(ethylene glycol) methylether acrylate, MW 10000 (mPEG-Ac 10K)Catalog Number 26277
Poly(ethylene glycol) methylether acrylate, MW 10000 (mPEG-Ac 10K)Catalog Number 26277 -
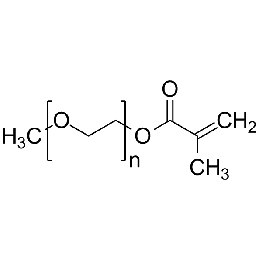 Poly(ethylene glycol) methylether methacrylate (mPEG-MAc 10K)Catalog Number 26278
Poly(ethylene glycol) methylether methacrylate (mPEG-MAc 10K)Catalog Number 26278 -
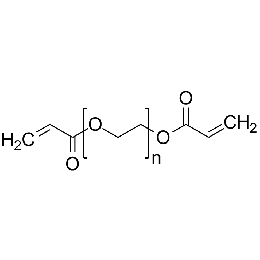 Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, MW 10000 (PEGDA 10K)Catalog Number 26279
Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, MW 10000 (PEGDA 10K)Catalog Number 26279 -
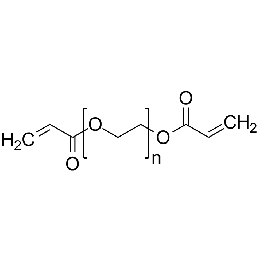 Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, MW 20000 (PEGDA 20K)Catalog Number 26280
Poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate, MW 20000 (PEGDA 20K)Catalog Number 26280 -
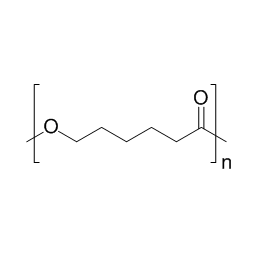 Polycaprolactone, MW 25000Catalog Number 26287
Polycaprolactone, MW 25000Catalog Number 26287 -
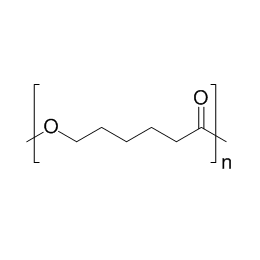 Polycaprolactone, MW 80000Catalog Number 26290
Polycaprolactone, MW 80000Catalog Number 26290 -
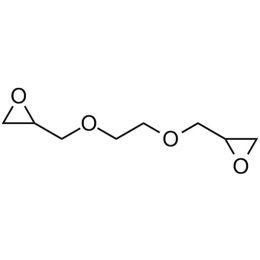 Ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (EGDGE)Catalog Number 01479
Ethylene glycol diglycidyl ether (EGDGE)Catalog Number 01479 -
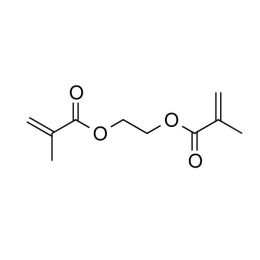 Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate, 99.7% (EGDMA)Catalog Number 24896High purity monomer for contact lens applications. Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate is useful as a high purity crosslinker with bridging/specialty capability between polymer chains.
Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate, 99.7% (EGDMA)Catalog Number 24896High purity monomer for contact lens applications. Ethylene Glycol Dimethacrylate is useful as a high purity crosslinker with bridging/specialty capability between polymer chains. -
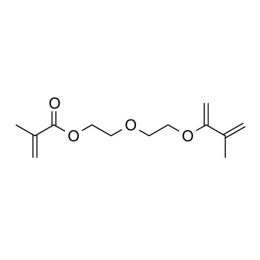 Diethylene glycol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 02214
Diethylene glycol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 02214 -
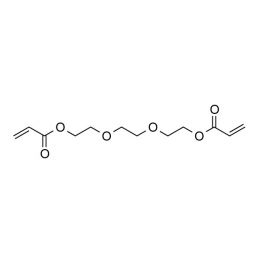 Triethylene glycol diacrylate (TriEGDA)Catalog Number 02655
Triethylene glycol diacrylate (TriEGDA)Catalog Number 02655 -
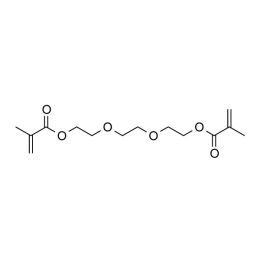 Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate, min 95%Catalog Number 24034
Triethylene glycol dimethacrylate, min 95%Catalog Number 24034 -
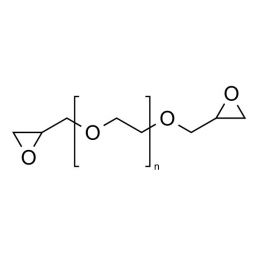 Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 200)Catalog Number 08209
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 200)Catalog Number 08209 -
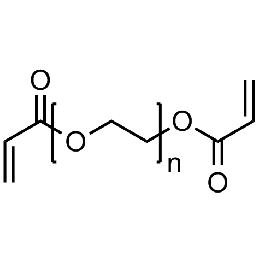 Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 400)Catalog Number 01871
Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 400)Catalog Number 01871 -
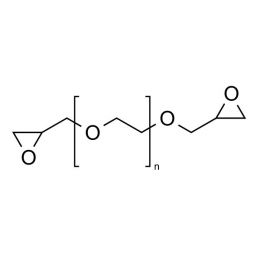 Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 400)Catalog Number 08210
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 400)Catalog Number 08210 -
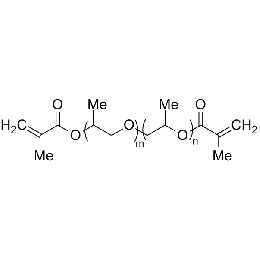 Poly(propylene glycol) (400) dimethacrylate (PPGDMA 400)Catalog Number 04380
Poly(propylene glycol) (400) dimethacrylate (PPGDMA 400)Catalog Number 04380 -
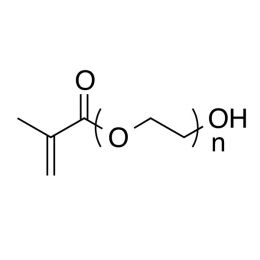 Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 440)Catalog Number 24890
Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 440)Catalog Number 24890 -
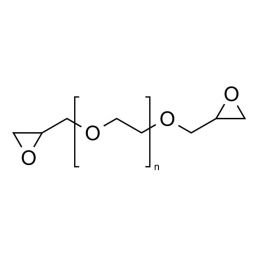 Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 600)Catalog Number 08211
Poly(ethylene glycol) diglycidyl ether (PEGDGE 600)Catalog Number 08211 -
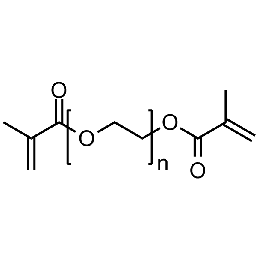 Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 1000)Catalog Number 15178
Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 1000)Catalog Number 15178 -
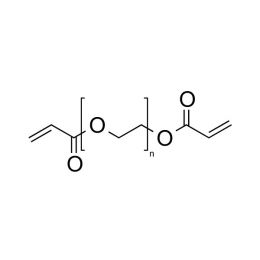 Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 4000)Catalog Number 15246
Polyethylene glycol diacrylate (PEGDA 4000)Catalog Number 15246 -
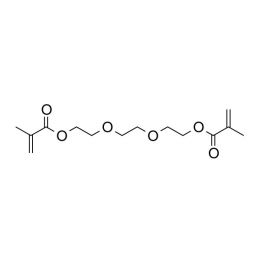 Triethylene glycol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 01319
Triethylene glycol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 01319 -
![Poly(acrylic acid), powder [MW ~ 1,000,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06500_1.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), powder [MW ~ 1,000,000]Catalog Number 06500
Poly(acrylic acid), powder [MW ~ 1,000,000]Catalog Number 06500 -
![Poly(acrylic acid), powder [MW ~ 4,000,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06501_1.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), powder [MW ~ 4,000,000]Catalog Number 06501
Poly(acrylic acid), powder [MW ~ 4,000,000]Catalog Number 06501 -
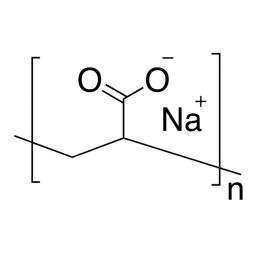 Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, powder (MW ~ 2,000)Catalog Number 06568
Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, powder (MW ~ 2,000)Catalog Number 06568 -
![Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 40% soln. in water [MW ~ 3,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/8/18608_2.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 40% soln. in water [MW ~ 3,000]Catalog Number 18608
Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 40% soln. in water [MW ~ 3,000]Catalog Number 18608 -
![Poly(acrylic acid), 25% soln. in water [Mw ~345,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/3/03326_1.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), 25% soln. in water [Mw ~345,000]Catalog Number 03326
Poly(acrylic acid), 25% soln. in water [Mw ~345,000]Catalog Number 03326Important anionic water-soluble polymer. Can be crosslinked covalently or ionically to form hydrogels.
- Mw/Mn 6.2
- 25% soln. in water (62.5g polymer)
- Mw determined by GPC versus polystyrene standards is 200,000
- Mw determined by GPC versus polyacrylic acid standards is 345,000
-
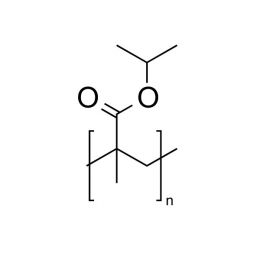 Poly(iso-propyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 07052
Poly(iso-propyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 07052 -
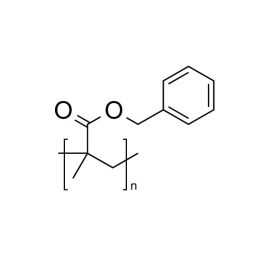 Poly(benzyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 06562
Poly(benzyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 06562Aromatic methacrylate ester polymer.
-
![Poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) fine powder, [η] = 0.60](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/2/02452_1.jpg) Poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) fine powder, [η] = 0.60Catalog Number 02452
Poly(iso-butyl methacrylate) fine powder, [η] = 0.60Catalog Number 02452Firm, water-insensitive, polymer.
[η]=0.60
-
![Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 1.25]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/4/04552_1.jpg) Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 1.25]Catalog Number 04552
Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 1.25]Catalog Number 04552Hard, stable, non-yellowing polymer used in coating and in molded clear plastic objects.
i.v. 1.25 atactic beads Polydispersity 2.7
-
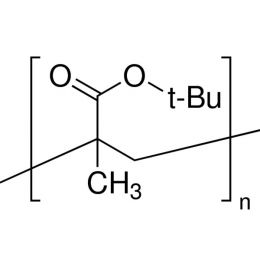 Poly(tert-butyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 07037
Poly(tert-butyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 07037Hard, thermally sensitive, methacrylate ester. Decomposes thermally to poly(methacrylic acid).
-
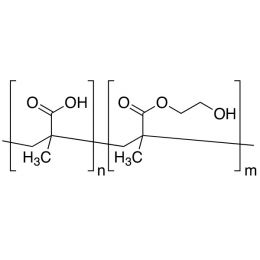 Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) 90:10Catalog Number 08725
Poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) 90:10Catalog Number 08725Hydrophilic polymer, more readily water-soluble than poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate), in the presence of alkali, aqueous, 90% methanol.
-
![Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 0.40]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/4/04553_1.jpg) Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 0.40]Catalog Number 04553
Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 0.40]Catalog Number 04553Hard, stable, non-yellowing polymer used in coating and in molded clear plastic objects.
i.v. 0.40 atactic beads, 200µm Polydispersity ~2.8
-
![Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 0.18]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/4/04554_1.jpg) Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 0.18]Catalog Number 04554
Poly(methyl methacrylate) [i.v. 0.18]Catalog Number 04554Hard, stable, non-yellowing polymer used in coating and in molded clear plastic objects. i.v. 0.18 atactic beads, 200µm Polydispersity ~3.0
-
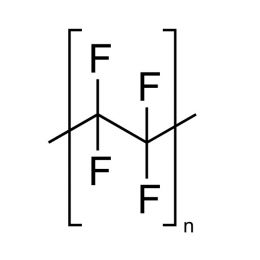 Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (Teflon™ 7A)Catalog Number 08816
Poly(tetrafluoroethylene) (Teflon™ 7A)Catalog Number 08816Inert polymer.
Nominal diameter: 35µm
-
![Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) [MW 200,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/4/24882.jpg) Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) [MW 200,000]Catalog Number 24882
Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) [MW 200,000]Catalog Number 24882Neutral, water soluble, polymer. Also soluble in DMF, lower alcohols, methyl ethyl ketone and methylene chloride. Tg = ~70º higher molecular weights.
Polydispersity ~3.4
-
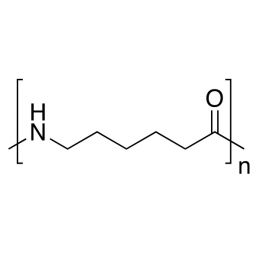 Polycaprolactam (MW 35,000)Catalog Number 18179
Polycaprolactam (MW 35,000)Catalog Number 18179Widely used in fibers.
Nylon 6
4.1 rel. visc.
-
![Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) [MW 500,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/7/17810.jpg) Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) [MW 500,000]Catalog Number 17810Email: [email protected]
Poly(2-ethyl-2-oxazoline) [MW 500,000]Catalog Number 17810Email: [email protected]Neutral, water soluble, polymer. Also soluble in DMF, lower alcohols, methyl ethyl ketone, and methylene chloride.
Polydispersity ~3.4
-
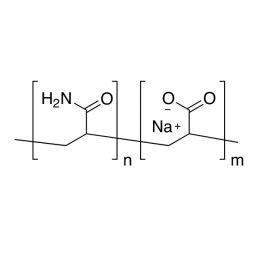 Poly(acrylamide/acrylic acid)Catalog Number 04652
Poly(acrylamide/acrylic acid)Catalog Number 04652Anionic acrylamide polymer.
Residual Monomer <0.03% 90:10, Na salt
-
![Poly(acrylamide/acrylic acid) [60:40]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/8/18545.jpg) Poly(acrylamide/acrylic acid) [60:40]Catalog Number 18545
Poly(acrylamide/acrylic acid) [60:40]Catalog Number 18545Anionic acrylamide polymer.
Residual Monomer <0.03% 60:40, Na salt pH 9.1
-
![Poly(acrylamide/sodium acrylate) [70:30]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/8/18522.jpg) Poly(acrylamide/sodium acrylate) [70:30]Catalog Number 18522Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(acrylamide/sodium acrylate) [70:30]Catalog Number 18522Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Important nonionic water-soluble polymer. High MW polymer is used primarily as a flocculant. Tg of high MW (>100,000) polymers = 165º. Unit weights are weights of solution.
d 1.302 for AQ solution
-
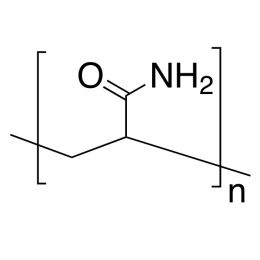 Polyacrylamide (MW 5,000,000), 1% aq solnCatalog Number 21485
Polyacrylamide (MW 5,000,000), 1% aq solnCatalog Number 21485Important nonionic water-soluble polymer. High MW polymer is used primarily as a flocculant. Tg of high MW (>100,000) polymers = 165º. Unit weights are weights of solution.
d 1.302 for AQ solution 1% soln. in water (2.5g polymer)
-
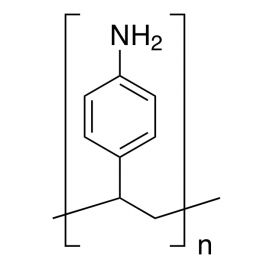 Poly(4-aminostyrene)Catalog Number 02823
Poly(4-aminostyrene)Catalog Number 02823Polymeric aromatic primary amine. Prone to oxidative crosslinking.
- Insoluble in organic solvents
- Nitrogen content ~11%
-
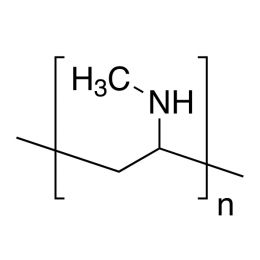 Poly(N-methylvinylamine)Catalog Number 24038Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(N-methylvinylamine)Catalog Number 24038Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Water-soluble all-secondary polyamine.
-
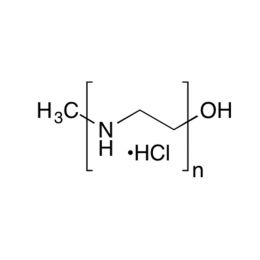 Polyethylenimine Hydrochloride, Linear (MW 4,000)Catalog Number 24885Email: [email protected]
Polyethylenimine Hydrochloride, Linear (MW 4,000)Catalog Number 24885Email: [email protected]Polyethylenimine HCl MAX, Linear, Mw 4,000 (PEI MAX® 4000) is a fully hydrolyzed (deacylated), highly water soluble hydrochloride salt form of our Polyethylenimine, Linear, Mw 2,500 (PEI 2500, Catalog # 24313).
-
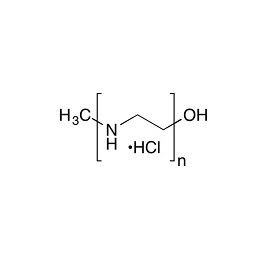 Polyethylenimine Hydrochloride, Linear (MW 160,000)Catalog Number 25439Email: [email protected]
Polyethylenimine Hydrochloride, Linear (MW 160,000)Catalog Number 25439Email: [email protected]Linear Polyethylenimine HCl MAX, Mw 160,000 (PEI MAX® 160000) is a fully hydrolyzed (deacylated), highly water soluble hydrochloride salt form of our Linear Polyethylenimine, Mw 100,000 (PEI 100000, Catalog # 25414).
-
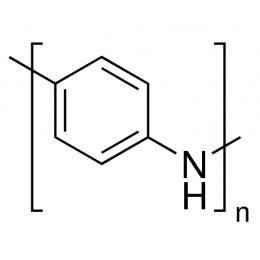 Polyaniline, Emeraldine form (undoped)Catalog Number 24043
Polyaniline, Emeraldine form (undoped)Catalog Number 24043Conductive polymer. Undoped. Conductivity 10-10 S/cm.
-
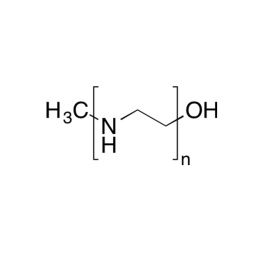 Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 100,000Catalog Number 25414Email: [email protected]
Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 100,000Catalog Number 25414Email: [email protected]Linear polyethylenimines (PEIs) contain all secondary amines, in contrast to branched PEIs which contain primary, secondary and tertiary amino groups.
The linear PEIs are solids at room temperature where branched PEIs are liquids at all molecular weights.
Insouble in: benzene, ethyl ether, acetone and cold water.
-
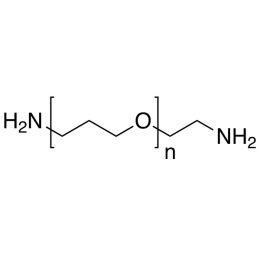 Poly(ethylene glycol) bis (2-aminoethyl), MW 10,000Catalog Number 24303
Poly(ethylene glycol) bis (2-aminoethyl), MW 10,000Catalog Number 24303A bifunctional Poly(ethylene glycol) derivative that can be used to conjugate proteins and drug substances for targeted drug delivery studies. Shelf life: stable when stored at room temperature
Synonym: Poly(oxy-1,2-ethanediyl) α 2-aminoethyl ω 2-aminoethoxy
-
![Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) [MW ~ 240,000], Powder](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/7/17338_1.png) Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) [MW ~ 240,000], PowderCatalog Number 17338
Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) [MW ~ 240,000], PowderCatalog Number 17338Linear, cationic, aliphatic, quaternary ammonium cyclopolymer.
-
![Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) [MW ~ 240,000], 28 wt. % in H2O](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/9/19898_1.png) Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) [MW ~ 240,000], 28 wt. % in H2OCatalog Number 19898
Poly(diallyldimethylammonium chloride) [MW ~ 240,000], 28 wt. % in H2OCatalog Number 19898Linear, cationic, aliphatic, quaternary ammonium cyclopolymer.
28% soln. in water (70g polymer)
-
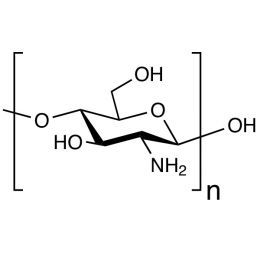 Chitosan, Purified Powder MW ~15,000Catalog Number 21161
Chitosan, Purified Powder MW ~15,000Catalog Number 21161Cationic polymer prepared by deacetylation of chitin. Soluble in water at low (4-6) pH.
poly[d-glucosamine] Purified powder Degree of deacetylation: minimum 85%
-
![Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 50,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/8/18619.jpg) Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 50,000]Catalog Number 18619
Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 50,000]Catalog Number 18619Cationic polymer. Used for promotion of cell adhesion to glass surfaces.
-
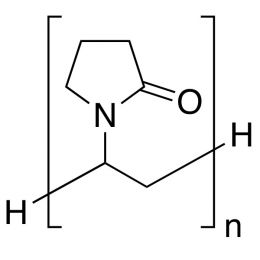 Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 40,000Catalog Number 01051
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 40,000Catalog Number 01051Water-soluble polymer used as a thickener, protective colloid.
-
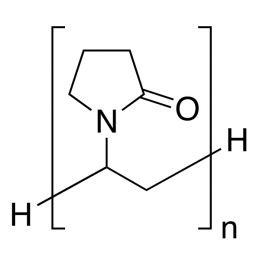 Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 10,000Catalog Number 03315
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 10,000Catalog Number 03315Water-soluble polymer used as a thickener, protective colloid.
Polydispersity 3.6
-
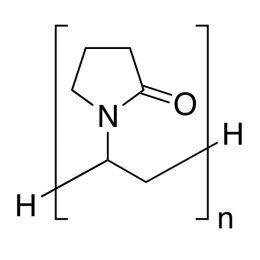 Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 1,000,000Catalog Number 06067
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 1,000,000Catalog Number 06067Water-soluble polymer used as a thickener, protective colloid.
Polydispersity ~2.00
-
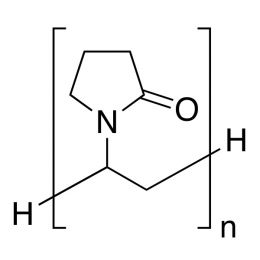 Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 2,500 (PVP 2500)Catalog Number 16693
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 2,500 (PVP 2500)Catalog Number 16693Water-soluble polymer used as a thickener, protective colloid.
Polydispersity 1.9
-
![Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 120,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/1/21430.jpg) Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 120,000]Catalog Number 21430
Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 120,000]Catalog Number 21430Cationic polymer. Used for promotion of cell adhesion to solid surfaces.
-
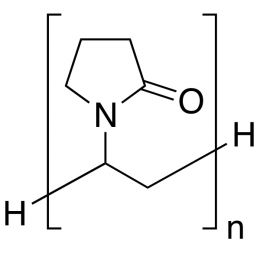 Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), Pharmaceutical grade, MW 40,000Catalog Number 01052
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), Pharmaceutical grade, MW 40,000Catalog Number 01052Water-soluble polymer used as a thickener, protective colloid.
Pharmaceutical grade
Polydispersity 3.33
-
![Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 300,000-400,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/7/17770_1.jpg) Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 300,000-400,000]Catalog Number 17770Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 300,000-400,000]Catalog Number 17770Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Water-soluble at low pH has adhesive-promoting properties.
-
![Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 200,000-400,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/9/19238_1.jpg) Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 200,000-400,000]Catalog Number 19238
Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 200,000-400,000]Catalog Number 19238Water-soluble at low pH has adhesive-promoting properties.
-
![Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 40,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/1/21382_1.jpg) Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 40,000]Catalog Number 21382
Poly(2-vinylpyridine) [MW 40,000]Catalog Number 21382Water-soluble at low pH has adhesive-promoting properties.
-
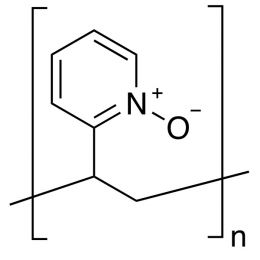 Poly(2-vinylpyridine N-oxide)Catalog Number 01564
Poly(2-vinylpyridine N-oxide)Catalog Number 01564Water-soluble cationic resin.
-
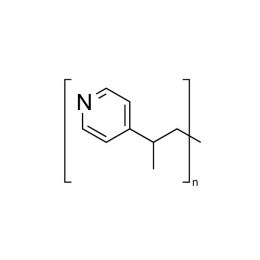 Poly(4-vinylpyridine)Catalog Number 22176
Poly(4-vinylpyridine)Catalog Number 22176Water-soluble at low pH—has adhesive-promoting properties.
-
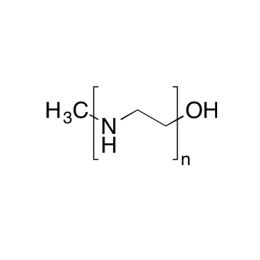 Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 2,500 (PEI 2500)Catalog Number 24313Email: [email protected]
Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 2,500 (PEI 2500)Catalog Number 24313Email: [email protected]Linear polyethylenimines (PEIs) contain all secondary amines, in contrast to branched PEIs which contain primary, secondary and tertiary amino groups.
The linear PEIs are solids at room temperature where branched PEIs are liquids at all molecular weights.
Insoluble in bezene, ethyl ether, acetone, and cold water.
-
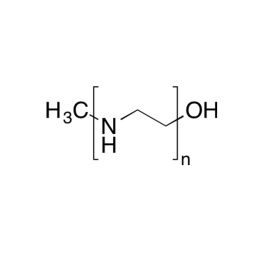 Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 250,000 (PEI 250000)Catalog Number 24314Email: [email protected]Linear polyethylenimine (PEI) is a high-charge cationic polymer that readily binds highly anionic substrates. Industrially, linear PEI can improve the appearance of negatively charged dyes by modulating their properties and improving their adherence to surfaces.
Polyethylenimine, Linear, MW 250,000 (PEI 250000)Catalog Number 24314Email: [email protected]Linear polyethylenimine (PEI) is a high-charge cationic polymer that readily binds highly anionic substrates. Industrially, linear PEI can improve the appearance of negatively charged dyes by modulating their properties and improving their adherence to surfaces. -
 Poly/Bed 502 ResinCatalog Number 00552
Poly/Bed 502 ResinCatalog Number 00552WPE is Weight Per Epoxide equivalent. From this value, one determines the optimum amount of DDSA or NMA in grams to combine with 100 grams of resin for stoichiometric balance minimizing unreacted starting materials and producing reproducibly stainable, embedding blocks.
-
 12-Tungstosilicic AcidCatalog Number 03424
12-Tungstosilicic AcidCatalog Number 03424Catalyst for organic synthesis, minerals separation, reagent for alkaloids.
(silicotungstic Acid)
-
![Poly[(R )-3-Hydroxybutyric Acid] (PHB)](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16916_1.jpg) Poly[(R )-3-Hydroxybutyric Acid] (PHB)Catalog Number 16916
Poly[(R )-3-Hydroxybutyric Acid] (PHB)Catalog Number 16916Biodegradable polymer.
-
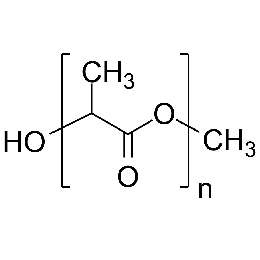 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.4 dl/gCatalog Number 16585
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.4 dl/gCatalog Number 16585Amorphous, biodegradable polymer. Soluble in: MDC, THF, ethyl acetate, acetone
i.v. 0.35-0.45 Polydispersity 1.8
-
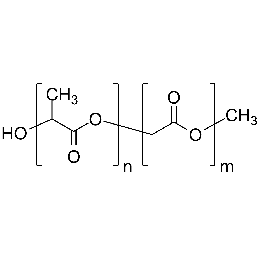 Poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide), 70:30, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 16587
Poly(L-lactide-co-glycolide), 70:30, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 16587Biodegradable polymers
70:30 i.v. 0.15-0.30 Polydispersity 1.8
-
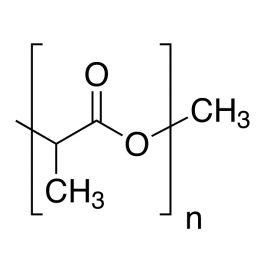 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 2.0 dl/gCatalog Number 23976
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 2.0 dl/gCatalog Number 23976Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is an ubiquitous biodegradable polymer. It is typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions. The well-researched release profile also allows for drug-release functionalization with calculable results.1 Owing to its extensive history, PDLLA is one of the most understood and affordable biodegradable polymers for medical devices today.
Synonyms: PDLLA, DL-PLA, PDLA
Specifications
Inherent Viscosity (ηinh): 1.6 - 2.4 dL/g (25°C; CH3Cl, 1.0 g/dL)
Properties
Soluble in: dichloromethane (DCM), tetrahydrofuran (THF), ethyl acetate, acetone
-
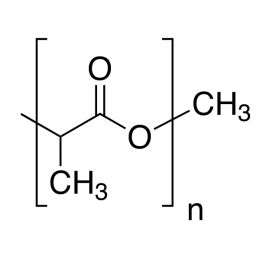 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 22505Inherent Viscosity (ηinh): 0.10 - 0.3 dL/g (25°C; CH3Cl, 1.8 g/dL)
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 22505Inherent Viscosity (ηinh): 0.10 - 0.3 dL/g (25°C; CH3Cl, 1.8 g/dL) -
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~1000](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16932_1.jpg) Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~1000Catalog Number 16932
Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~1000Catalog Number 16932Polyhydroxybutyrates (PHBs)are the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and were first discovered in prokaryotes as a high molecular weight storage molecule in cytoplasmic granules in prokaryotes.
There has been interest in the use of PHBs and PHB copolymers in the biodegradable plastics industry. The biodegradable and non-toxic effect of PHBs also make them a strong possibility for many medical applications, including drug release, bone regeneration, and nerve guidance.
Purity 99.5%
-
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~2000](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16934_1.jpg) Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~2000Catalog Number 16934
Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~2000Catalog Number 16934Polyhydroxybutyrates (PHBs)are the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and were first discovered in prokaryotes as a high molecular weight storage molecule in cytoplasmic granules in prokaryotes.
There has been interest in the use of PHBs and PHB copolymers in the biodegradable plastics industry. The biodegradable and non-toxic effect of PHBs also make them a strong possibility for many medical applications, including drug release, bone regeneration, and nerve guidance.
Purity 99.5%
-
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~3000](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16936_1.jpg) Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~3000Catalog Number 16936
Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~3000Catalog Number 16936Polyhydroxybutyrates (PHBs)are the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and were first discovered in prokaryotes as a high molecular weight storage molecule in cytoplasmic granules in prokaryotes.
There has been interest in the use of PHBs and PHB copolymers in the biodegradable plastics industry. The biodegradable and non-toxic effect of PHBs also make them a strong possibility for many medical applications, including drug release, bone regeneration, and nerve guidance.
Purity 99.5%
-
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~10,000](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16940_1.jpg) Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~10,000Catalog Number 16940
Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~10,000Catalog Number 16940Polyhydroxybutyrates (PHBs)are the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and were first discovered in prokaryotes as a high molecular weight storage molecule in cytoplasmic granules in prokaryotes.
There has been interest in the use of PHBs and PHB copolymers in the biodegradable plastics industry. The biodegradable and non-toxic effect of PHBs also make them a strong possibility for many medical applications, including drug release, bone regeneration, and nerve guidance.
Purity 99.5%
-
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~500](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16930_1.jpg) Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~500Catalog Number 16930
Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~500Catalog Number 16930Polyhydroxybutyrates (PHBs) are the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and were first discovered in prokaryotes as a high molecular weight storage molecule in cytoplasmic granules in prokaryotes.
There has been interest in the use of PHBs and PHB copolymers in the biodegradable plastics industry. The biodegradable and non-toxic effect of PHBs also make them a strong possibility for many medical applications, including drug release, bone regeneration, and nerve guidance.
Purity 99.5%
-
![Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~5000](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16938_1.jpg) Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~5000Catalog Number 16938
Poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate], MW ~5000Catalog Number 16938Polyhydroxybutyrates (PHBs)are the most common type of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) and were first discovered in prokaryotes as a high molecular weight storage molecule in cytoplasmic granules in prokaryotes.
There has been interest in the use of PHBs and PHB copolymers in the biodegradable plastics industry. The biodegradable and non-toxic effect of PHBs also make them a strong possibility for many medical applications, including drug release, bone regeneration, and nerve guidance.
Purity 99.5%
-
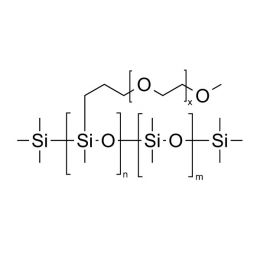 Poly(dimethylsiloxane-b-ethylene oxide), methyl terminatedCatalog Number 09780
Poly(dimethylsiloxane-b-ethylene oxide), methyl terminatedCatalog Number 09780Surfactant-like diblock copolymers. 25:75
-
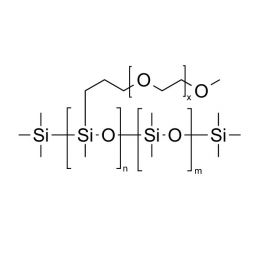 Poly(dimethylsiloxane-b-ethylene oxide), methyl terminatedCatalog Number 21870
Poly(dimethylsiloxane-b-ethylene oxide), methyl terminatedCatalog Number 21870Surfactant-like diblock copolymers.
Ratio 20:80
-
![Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 0.15:1]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16273.jpg) Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 0.15:1]Catalog Number 16273
Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 0.15:1]Catalog Number 16273Water-soluble or water-dispersible polymers with surfactant properties. Chains are hydroxyl terminated. Polymers are p(EO/PO/EO) triblocks
ratio 0.15:1,
-
![Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 3:1]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16276.jpg) Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 3:1]Catalog Number 16276
Poly(ethylene oxide-b-propylene oxide) [ratio 3:1]Catalog Number 16276Water-soluble or water-dispersible polymers with surfactant properties. Chains are hydroxyl terminated. Polymers are p(EO/PO/EO) triblocks.
ratio 3:1
-
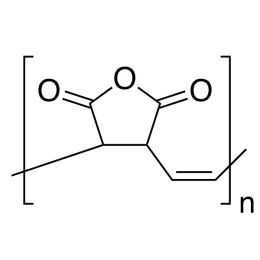 Poly(butadiene/maleic anhydride) 1:1 (molar), 25% soln. in acetoneCatalog Number 07788Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(butadiene/maleic anhydride) 1:1 (molar), 25% soln. in acetoneCatalog Number 07788Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Reactive polymer capable of reacting at anhydride or backbone unsaturation.
125g polymer
-
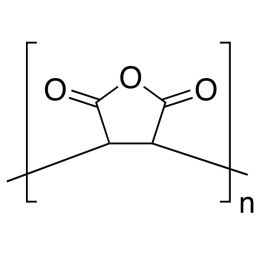 Poly(maleic anhydride)Catalog Number 02348
Poly(maleic anhydride)Catalog Number 02348Polymer reacts with amines, alcohols.
-
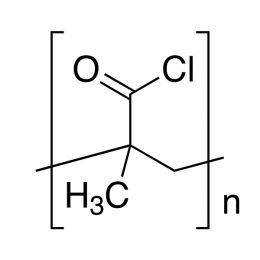 Poly(methacryloyl chloride), 25% soln. in dioxaneCatalog Number 04315
Poly(methacryloyl chloride), 25% soln. in dioxaneCatalog Number 04315Polymer reacts readily with alcohols and amines. Can be used to prepare polymers bearing bioactive molecules. Firm, slightly tacky polymer. Can be transesterified or amidated readily.
2.5g polymer
-
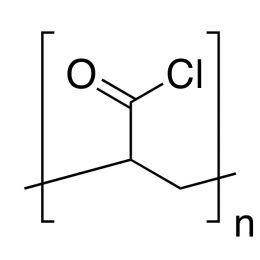 Poly(acryloyl chloride), 25% soln. in dioxaneCatalog Number 04293
Poly(acryloyl chloride), 25% soln. in dioxaneCatalog Number 04293Reactive polymer
2.5g polymer
-
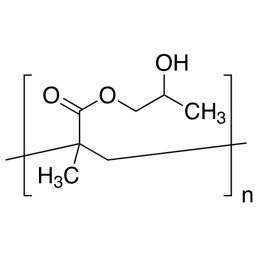 Poly(2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 09690
Poly(2-hydroxypropyl methacrylate)Catalog Number 09690Hydrophilic polymer.
-
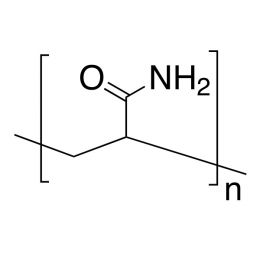 Polyacrylamide 10% in water (MW 400,000 - 1,000,000)Catalog Number 19901
Polyacrylamide 10% in water (MW 400,000 - 1,000,000)Catalog Number 19901Important nonionic water-soluble polymer. High MW polymer is used primarily as a flocculant. Tg of high MW (>100,000) polymers = 165º. Unit weights are weights in solution.
10% soln. in water (25g polymer)
(Contains small amounts of formalin as fungicide)
-
 Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 600 (bPEI 600)Catalog Number 02371Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 600 (bPEI 600) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 600 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio.
Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 600 (bPEI 600)Catalog Number 02371Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 600 (bPEI 600) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 600 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio. -
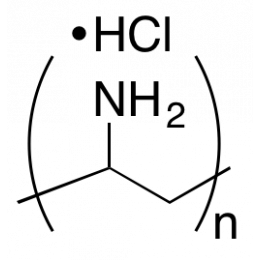 Poly(vinylamine) hydrochlorideCatalog Number 23965
Poly(vinylamine) hydrochlorideCatalog Number 23965Water-soluble all-primary polyamine.
-
 Poly(L-lysine hydrobromide), MW 125K, 0.1% aq. soln.Catalog Number 09730
Poly(L-lysine hydrobromide), MW 125K, 0.1% aq. soln.Catalog Number 09730Cationic polymer. Used to improve cell adhesion to solid surfaces.
0.1% soln. in water
-
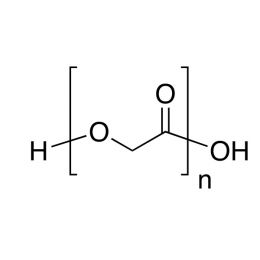 Poly(glycolic acid) [i.v. 1.0-2.0]Catalog Number 06525
Poly(glycolic acid) [i.v. 1.0-2.0]Catalog Number 06525Biodegradable polymer. Decomposes in 6 months at 37° at pH 9.0.
-
 Poly(methacrylic acid) sodium salt, 30% soln. in waterCatalog Number 21170
Poly(methacrylic acid) sodium salt, 30% soln. in waterCatalog Number 21170Low molecular weight, water-soluble polymer. Forms insoluble polysalts with polyamines. Used as a pigment dispersant.
-
![2,2-Bis[4-(2-hydroxy-3-methacryloxypropoxy)phenyl]propane structure](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/3/03344.jpg) 2,2-Bis[4-(2-hydroxy-3-methacryloxypropoxy)phenyl]propaneCatalog Number 03344
2,2-Bis[4-(2-hydroxy-3-methacryloxypropoxy)phenyl]propaneCatalog Number 03344Rigid, hydrophobic, Crosslinking monomer
(Bis-GMA)
-
 Tricyclodecane dimethanol diacrylateCatalog Number 25110
Tricyclodecane dimethanol diacrylateCatalog Number 25110High refractive index monomer which exhibits low volume shrinkage in polymerization.
Used in optical lens and optical fiber applications due to its high refractive index. Has also been used in dental composite applications for its low volume shrinkage.
-
![Halocarbon 200 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 200 centistokes] structure](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25073.jpg) Halocarbon 200 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 200 centistokes]Catalog Number 25073
Halocarbon 200 Oil [Poly(chlorotrifluoroethylene), 200 centistokes]Catalog Number 25073Inert, non-flammable lubricating oil. Polymer is a blend of oligomers. Also used as an inert medium in transgenic studies of fruit fly Drosophilia embryos.
- Pour Point: 10° F (-12° C)
- Cloud Point: 35° F (2° C)
-
 Poly(4-vinylphenol)Catalog Number 06527
Poly(4-vinylphenol)Catalog Number 06527Reactive polyphenol. Has applications in photoresists.
Polydispersity 1.5-2.2
-
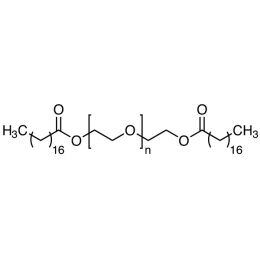 Poly(ethylene glycol) distearate 400Catalog Number 01048
Poly(ethylene glycol) distearate 400Catalog Number 01048A removable embedding medium for thin and thick sections. In thicker sections the exterior surface of mitochondria can be observed whereas in resin-embedded thin sections the mitochondria are most frequently observed in a cross section. DGD is used to prepare tissue for immunofluorescent localization of cytoskeletal components. It is also used for tissue preparation for in situ hybridization with nucleic acid probes.
MW = Molecular weight of PEG.
-
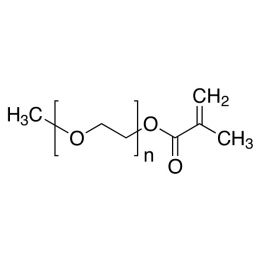 Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 200)Catalog Number 16664
Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 200)Catalog Number 16664Hydrophilic macromonomers used to introduce hydrophilic sites into polymers, to stabilize polymer emulsions, and in synthesis of comb polymers. MW of PEG unit = 400.
-
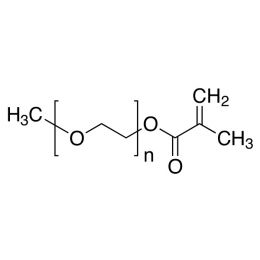 Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 1000)Catalog Number 16666
Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 1000)Catalog Number 16666Hydrophilic macromonomers used to introduce hydrophilic sites into polymers, to stabilize polymer emulsions, and in synthesis of comb polymers. (n) value is MW of PEG unit.
-
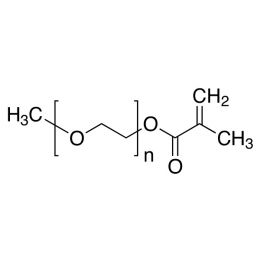 Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 400)Catalog Number 16665
Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 400)Catalog Number 16665Hydrophilic macromonomers used to introduce hydrophilic sites into polymers, to stabilize polymer emulsions, and in synthesis of comb polymers. MW of PEG unit = 400.
-
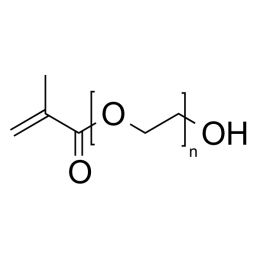 Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 2000)Catalog Number 25427
Polyethylene glycol monomethacrylate (PEGMA 2000)Catalog Number 25427Hydrophilic macromonomer used to introduce hydrophilic sites into polymers, to stabilize polymer emulsions, and in synthesis of comb polymers.
-
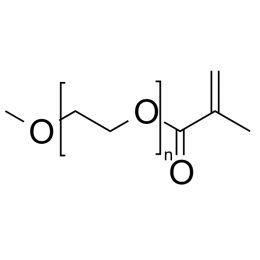 Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 5000)Catalog Number 25426
Polyethylene glycol monomethyl ether monomethacrylate (PEGMMA 5000)Catalog Number 25426Hydrophilic macromonomer used to introduce hydrophilic sites into polymers, to stabilize polymer emulsions, and in synthesis of comb polymers.
-
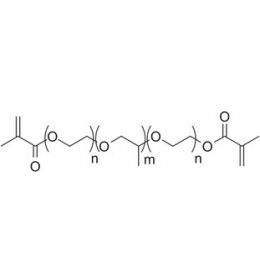 PEO(5800)-b-PPO(3000)-b-PEO(5800) dimethacrylateCatalog Number 25430
PEO(5800)-b-PPO(3000)-b-PEO(5800) dimethacrylateCatalog Number 25430Long-chain hydrophilic, crosslinking macromonomer. Triblock copolymer with methacrylate endgroups contains blocks of PEO and PPO to provide a balance of hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties.
-
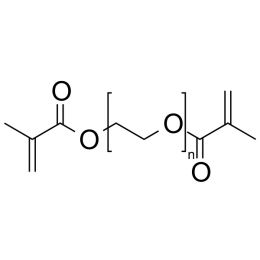 Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 8000)Catalog Number 25428
Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 8000)Catalog Number 25428Long-chain hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer. Molecular weight of PEG unit is approximately 8,000.
-
![Poly(acrylic acid), 30% soln. in water [MW ~ 30,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/4/24771_1.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), 30% soln. in water [MW ~ 30,000]Catalog Number 24771
Poly(acrylic acid), 30% soln. in water [MW ~ 30,000]Catalog Number 24771Important anionic water-soluble polymer. Can be crosslinked covalently or ionically to form hydrogels.
-
![Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [90:10]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/8/08207.jpg) Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [90:10]Catalog Number 08207
Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [90:10]Catalog Number 08207Random copolymer. Used in positive electron beam photoresists.
Soluble in: ethyl cellosolve acetate, 9:1 IPA-water.
90:10
-
![Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [75:25]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/8/08208.jpg) Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [75:25]Catalog Number 08208Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [75:25]Catalog Number 08208Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Random copolymer. Used in positive electron beam photoresists.
Soluble in: ethyl cellosolve acetate, 9:1 IPA-water.
75:25
-
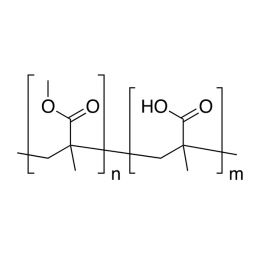 Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid)Catalog Number 19629
Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid)Catalog Number 19629Random copolymer. Used in positive electron beam photoresists.
Soluble in: ethyl cellosolve acetate, 9:1 IPA-water.
95:5 Dispersity ~4
-
![Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [80:20]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/8/08221.jpg) Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [80:20]Catalog Number 08221
Poly(methyl methacrylate/methacrylic acid) [80:20]Catalog Number 08221Random copolymer. Used in positive electron beam photoresists.
80:20
-
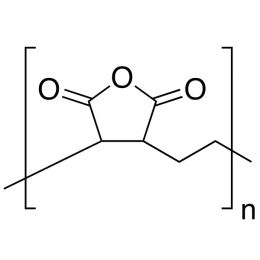 Poly(ethylene/maleic anhydride) 1:1 (molar)Catalog Number 02308
Poly(ethylene/maleic anhydride) 1:1 (molar)Catalog Number 02308Alternating copolymer, reactive with alcohols and amines. Hydrolyzes in water to a water-soluble anionic polymer.
-
![Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 35% soln. in water [MW ~ 120,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/8/18611_1.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 35% soln. in water [MW ~ 120,000]Catalog Number 18611Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 35% soln. in water [MW ~ 120,000]Catalog Number 18611Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Water-soluble anionic polymer. Used at low molecular weights as pigment dispersant and at higher molecular weights as a flocculant. Polymer can form complexes with poly(ethylene oxide) and with nucleotides
35% soln. in water (87.5g polymer)
-
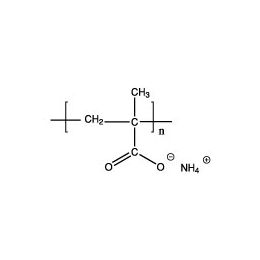 Poly(methacrylic acid) ammonium salt, 30% soln. in waterCatalog Number 21169Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(methacrylic acid) ammonium salt, 30% soln. in waterCatalog Number 21169Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Low molecular weight, water-soluble polymer. Forms insoluble polysalts with polyamines. Used as a pigment dispersant
7.5g polymer
-
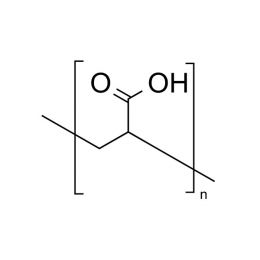 Poly(acrylic acid), Powder, Mw ~ 450,000 (PAA 450K)Catalog Number 03312
Poly(acrylic acid), Powder, Mw ~ 450,000 (PAA 450K)Catalog Number 03312Important anionic water-soluble polymer. Can be crosslinked covalently or ionically to form hydrogels.
Tg of high MW (>100,000) polymers = 106º
-
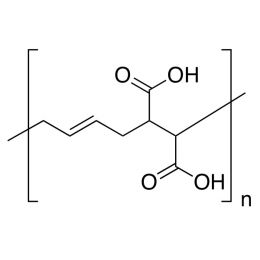 Poly(butadiene/maleic acid) 1:1, 42% soln. in waterCatalog Number 07787
Poly(butadiene/maleic acid) 1:1, 42% soln. in waterCatalog Number 07787Anionic, water-soluble, polymer capable of reaction through acid groups or backbone unsaturation.
210g polymer
-
![Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, powder [MW ~ 6,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06567.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, powder [MW ~ 6,000]Catalog Number 06567
Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, powder [MW ~ 6,000]Catalog Number 06567Water-soluble anionic polymer. Used at low molecular weights as pigment dispersant and at higher molecular weights as a flocculant. Polymer can form complexes with poly(ethylene oxide) and with nucleotides.
Mw/Mn 2.4
-
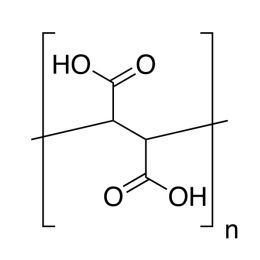 Poly(maleic acid), 50% soln. in waterCatalog Number 09732Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(maleic acid), 50% soln. in waterCatalog Number 09732Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(maleic acid) soln in water
-
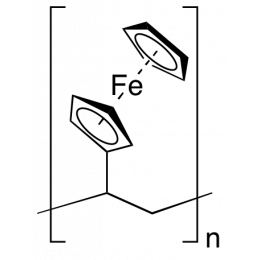 Poly(vinylferrocene)Catalog Number 09746
Poly(vinylferrocene)Catalog Number 09746Polymer containing organometallic units.
-
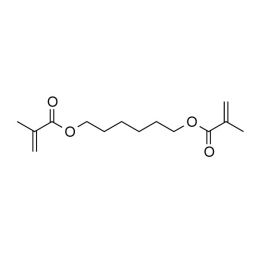 1,6-Hexanediol dimethacrylate, min 98%Catalog Number 23672
1,6-Hexanediol dimethacrylate, min 98%Catalog Number 23672Crosslinking monomer
-
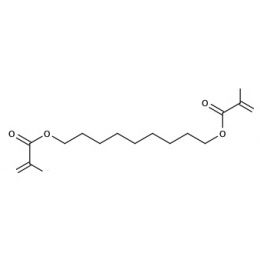 1,9-Nonanediol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 00801
1,9-Nonanediol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 00801Long-chain crosslinking monomer.
-
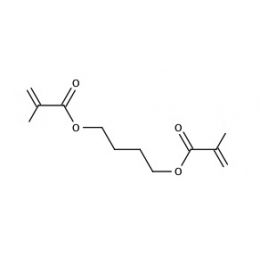 1,4-Butanediol dimethacrylate, min. 90%Catalog Number 05973
1,4-Butanediol dimethacrylate, min. 90%Catalog Number 05973Crosslinking monomer
-
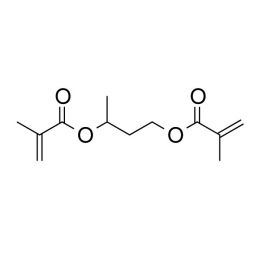 1,3-Butanediol dimethacrylate, 98%Catalog Number 02047
1,3-Butanediol dimethacrylate, 98%Catalog Number 02047Crosslinking monomer.
-
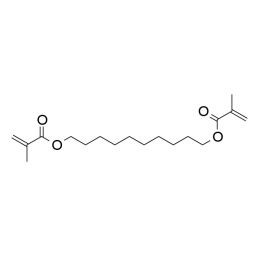 1,10-Decanediol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 02140
1,10-Decanediol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 02140Hydrophobic, long-chain crosslinking monomer.
-
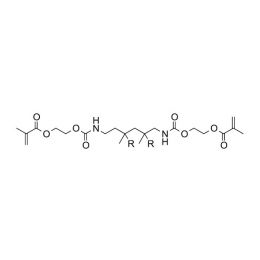 Diurethane Dimethacrylate (DUDMA)Catalog Number 21619
Diurethane Dimethacrylate (DUDMA)Catalog Number 21619(Diurethane dimethacrylate) Long chain-length crosslinking monomer
-
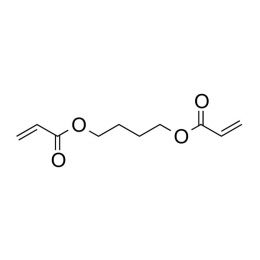 1,4-Butanediol diacrylate, min. 85%Catalog Number 02049
1,4-Butanediol diacrylate, min. 85%Catalog Number 02049Crosslinking monomer
-
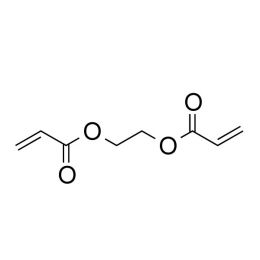 Ethylene glycol diacrylate (EGDA)Catalog Number 02302
Ethylene glycol diacrylate (EGDA)Catalog Number 02302Crosslinking monomer EGDA
-
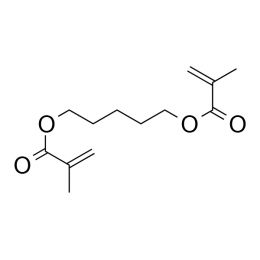 1,5-Pentanediol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 04260
1,5-Pentanediol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 04260Crosslinking monomer.
-
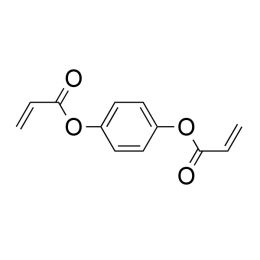 1,4-Phenylene diacrylateCatalog Number 06389
1,4-Phenylene diacrylateCatalog Number 06389Rigid aromatic crosslinking monomer
-
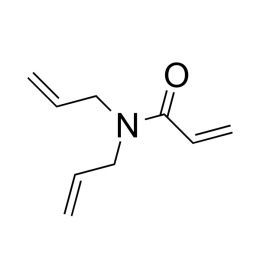 N,N-DiallylacrylamideCatalog Number 01848
N,N-DiallylacrylamideCatalog Number 01848 -
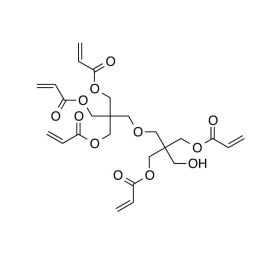 Dipentaerythritol pentaacrylate (mixture of tetra-, penta-, hexaacrylate)Catalog Number 16311
Dipentaerythritol pentaacrylate (mixture of tetra-, penta-, hexaacrylate)Catalog Number 16311Highly efficient crosslinking monomer, used especially in UV curing coatings.
-
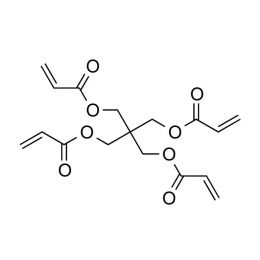 Pentaerythritol tetraacrylateCatalog Number 01547
Pentaerythritol tetraacrylateCatalog Number 01547Crosslinking monomer
-
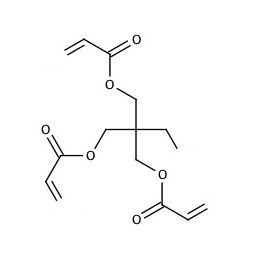 1,1,1- Trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TriMPTA)Catalog Number 02658
1,1,1- Trimethylolpropane triacrylate (TriMPTA)Catalog Number 02658Crosslinking monomer
-
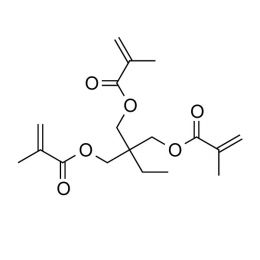 1,1,1-Trimethylolpropane trimethacrylateCatalog Number 02659
1,1,1-Trimethylolpropane trimethacrylateCatalog Number 02659Crosslinking monomer
-
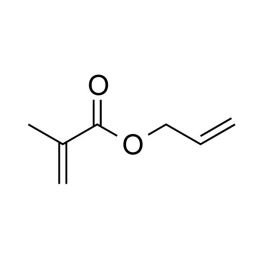 Allyl methacrylateCatalog Number 01643
Allyl methacrylateCatalog Number 01643Contains polymerizable units of differing reactivity, methacrylate moiety being more reactive than allyl.
-
 PAMAM Dendrimer G3.5 (water solution)Catalog Number 14531PAMAM Dendrimer, ethylenediamine core, generation 3.5 solution is a polyamidoamine dendrimer with a carboxylate termini.
PAMAM Dendrimer G3.5 (water solution)Catalog Number 14531PAMAM Dendrimer, ethylenediamine core, generation 3.5 solution is a polyamidoamine dendrimer with a carboxylate termini. -
 PAMAM Dendrimer G5.0 Amine (water solution)Catalog Number 14541PAMAM Dendrimer, ethylenediamine core, generation 5.0 solution is a polyamidoamine dendrimer with a carboxylate termini.
PAMAM Dendrimer G5.0 Amine (water solution)Catalog Number 14541PAMAM Dendrimer, ethylenediamine core, generation 5.0 solution is a polyamidoamine dendrimer with a carboxylate termini. -
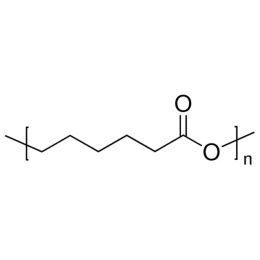 Polycaprolactone, IV 0.2 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50310Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder.
Polycaprolactone, IV 0.2 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50310Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder. -
 Polycaprolactone, IV 0.6 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50311Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder.
Polycaprolactone, IV 0.6 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50311Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder. -
 Polycaprolactone, IV 1.0 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50312Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder.
Polycaprolactone, IV 1.0 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50312Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder. -
 Polycaprolactone, IV 1.5 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50313Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder.
Polycaprolactone, IV 1.5 dL/g, PowderCatalog Number 50313Suitable for biomedical research. Supplied as a powder. -
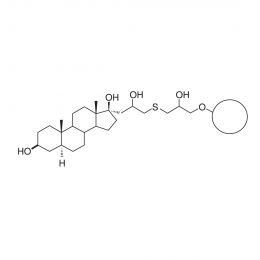 Androstan Sepharose® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid BeadsCatalog Number 24858
Androstan Sepharose® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid BeadsCatalog Number 24858Sepharose® 6B affinity chromatography beads covalently modified with steroids or other ligands such that ligand binding to receptors is not compromised resulting in high receptor-binding specificity.
-
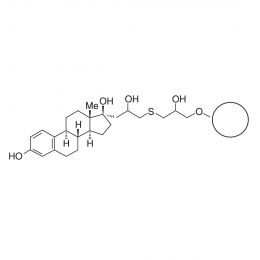 Estradiol Sepharose® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid BeadsCatalog Number 24861
Estradiol Sepharose® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid BeadsCatalog Number 24861Sepharose® 6B affinity chromatography beads covalently modified with steroids or other ligands such that ligand binding to receptors is not compromised resulting in high receptor-binding specificity.
-
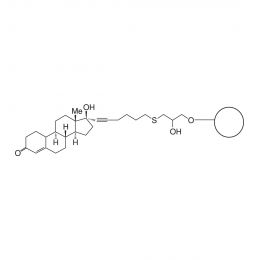 Nortestosterone Sepharose® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid BeadsCatalog Number 24860
Nortestosterone Sepharose® 6B Novel Immobilized Steroid BeadsCatalog Number 24860Sepharose® 6B affinity chromatography beads covalently modified with steroids or other ligands such that ligand binding to receptors is not compromised resulting in high receptor-binding specificity.
-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW ~ 20,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/7/17172.jpg) Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW ~ 20,000]Catalog Number 17172
Poly(ethylene glycol) [MW ~ 20,000]Catalog Number 17172Water-soluble (also soluble in benzene, chloroform, dimethylformamide, esters, alcohols)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.13
-
 Poly(methyl methacrylate), 75K, reference standardCatalog Number 08287
Poly(methyl methacrylate), 75K, reference standardCatalog Number 08287Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, methyl ethyl ketone, ethyl acetate)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.04
-
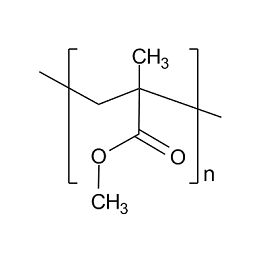 Poly(methyl methacrylate), 185K, reference standardCatalog Number 18756
Poly(methyl methacrylate), 185K, reference standardCatalog Number 18756Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, methyl ethyl ketone, ethyl acetate)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.10
-
![Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 4,600]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 4,600]Catalog Number 16248
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 4,600]Catalog Number 16248Water-soluble
Mw/Mn ~ 1.10
-
![Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 8,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 8,000]Catalog Number 16249
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 8,000]Catalog Number 16249Water-soluble
Mw/Mn ~ 1.10
-
![Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 18,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16250.jpg) Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 18,000]Catalog Number 16250
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 18,000]Catalog Number 16250Water-soluble
Mw/Mn ~ 1.10
-
![Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 220,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 220,000]Catalog Number 16254
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 220,000]Catalog Number 16254Water-soluble
MW ~ 220,000 Mw/Mn ~ 1.10
-
![Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 1,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/4/24812.jpg) Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 1,000]Catalog Number 24812
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 1,000]Catalog Number 24812Water-soluble
Mw/Mn < 1.2
-
![Polyethylene, linear [MW ~ 52,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Polyethylene, linear [MW ~ 52,000]Catalog Number 09829
Polyethylene, linear [MW ~ 52,000]Catalog Number 09829NIST Standard for determining melt flow rate in polymers. Melt flow rate is widely used in polymer technology as a product specification since this value, which includes a statement of the load and temperature under which it is obtained, gives an indication of the processing properties of the polymer.
-
![Polystyrene [MW ~ 100,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Polystyrene [MW ~ 100,000]Catalog Number 00867
Polystyrene [MW ~ 100,000]Catalog Number 00867Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons,
tetrahydrofuran, esters)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.06
-
![Polystyrene [MW ~ 20,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Polystyrene [MW ~ 20,000]Catalog Number 01844
Polystyrene [MW ~ 20,000]Catalog Number 01844Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, tetrahydrofuran, esters)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.06
-
![Polystyrene [MW ~ 600]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Polystyrene [MW ~ 600]Catalog Number 08279
Polystyrene [MW ~ 600]Catalog Number 08279Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, tetrahydrofuran, esters)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.30
-
![Polystyrene [MW ~ 1,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Polystyrene [MW ~ 1,000]Catalog Number 16227
Polystyrene [MW ~ 1,000]Catalog Number 16227Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons,
tetrahydrofuran, esters)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.30
-
![Polystyrene [MW ~ 9,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Polystyrene [MW ~ 9,000]Catalog Number 16231
Polystyrene [MW ~ 9,000]Catalog Number 16231Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons,
tetrahydrofuran, esters)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.04
-
![Polystyrene [MW ~ 20,000,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/placeholder/default/PSIgreenblueoutlines_4.png) Polystyrene [MW ~ 20,000,000]Catalog Number 16244
Polystyrene [MW ~ 20,000,000]Catalog Number 16244Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons, tetrahydrofuran, esters)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.20
-
![Polystyrene [MW ~ 30,000,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/6/16315.jpg) Polystyrene [MW ~ 30,000,000]Catalog Number 16315Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Polystyrene [MW ~ 30,000,000]Catalog Number 16315Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Solvent-soluble (aromatic hydrocarbons, chlorinated hydrocarbons,
tetrahydrofuran, esters)
Mw/Mn ~ 1.30
-
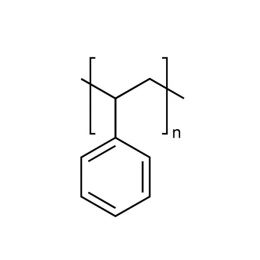 Polystyrene, atactic pelletsCatalog Number 00574
Polystyrene, atactic pelletsCatalog Number 00574Widely used high Tg polymer.
-
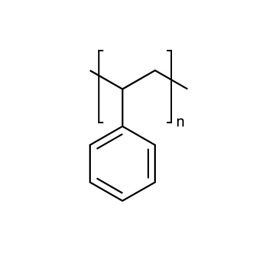 Polystyrene (MW 50,000)Catalog Number 18544
Polystyrene (MW 50,000)Catalog Number 18544Widely used high Tg polymers.
atactic flakes, bimodal with MW ~50,000 & 1500
-
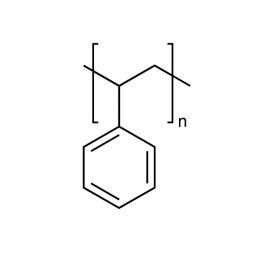 Polystyrene (MW 40,000)Catalog Number 23637
Polystyrene (MW 40,000)Catalog Number 23637Widely used high Tg polymers.
Softening point 125°
-
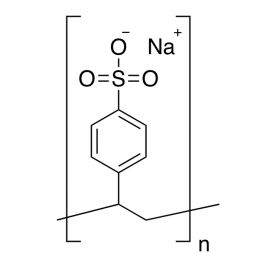 Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt (MW 75,000)Catalog Number 08772
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt (MW 75,000)Catalog Number 08772Water-soluble ionic polymer in salt form.
Polydispersity 3-5
-
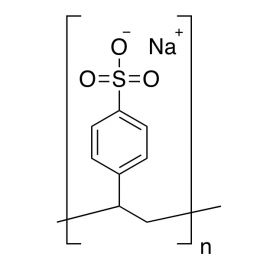 Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt (MW 1,000,000)Catalog Number 08773
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt (MW 1,000,000)Catalog Number 08773Water-soluble ionic polymer in salt form.
Polydispersity 3-30
-
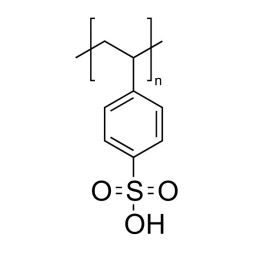 Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), 30% soln. in waterCatalog Number 08770
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), 30% soln. in waterCatalog Number 08770Water-soluble ionic polymer in acid form. (75g polymer)
-
![Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone/vinyl acetate) [70:30]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/9/09716_3.png) Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone/vinyl acetate) [70:30]Catalog Number 09716Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone/vinyl acetate) [70:30]Catalog Number 09716Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Hydrophilic neutral polymer.
(70:30), 50% soln. in isopropanol (50g polymer)
-
![Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone/vinyl acetate) [30:70]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/9/09718.png) Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone/vinyl acetate) [30:70]Catalog Number 09718
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone/vinyl acetate) [30:70]Catalog Number 09718Hydrophilic neutral polymer.
(30:70), 50% soln. in isopropanol (50g polymer)
-
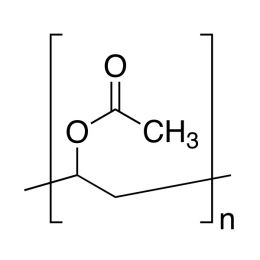 Poly(vinyl acetate)Catalog Number 06069
Poly(vinyl acetate)Catalog Number 06069Water sensitive resin, readily hydrolyzed. Used to prepare poly(vinyl alcohol) of varying degrees of hydrolysis.
-
![Poly(Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride) [Mw ~ 8,500], 28 wt. % H2O](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/4/24828_1.png) Poly(Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride) [Mw ~ 8,500], 28 wt. % H2OCatalog Number 24828
Poly(Diallyl Dimethyl Ammonium Chloride) [Mw ~ 8,500], 28 wt. % H2OCatalog Number 24828Water soluble cationic polymer. High cationic charge density in ready to use aqueous solution form. Material is quaternized cyclic amine supplied as the quarternary amine chloride.
The ability to modify surfaces and provide cationic character allows the user to selectively attract negatively charged functional groups to the coated surface or to the dissolved water soluble cationic polymers.
This feature is useful in the following types of applications:
- heavy metal removal by chelation
- promotion of precipitation or flocculation of dissolved solids
- imparting antistatic properties
- adding anti-microbial character
- binding of dyes or inks
- anionic pigment binding
- decolorizing agent
- binding to aldehydes
- corrosion inhibition on metal surfaces
- polymer bridging to link functionalized polymer systems 28% Solids in water Available in several molecular weight ranges. If other molecular weights are required, please call us for a custom quotation.
-
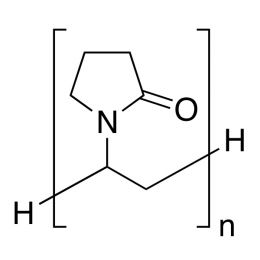 Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 4,000 - 6,000Catalog Number 24737Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone), MW 4,000 - 6,000Catalog Number 24737Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]This low molecular weight version of Poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) allows the user to obtain maximum dispersive properties with the polymer but at lower solution viscosity than the higher molecular weight siblings.
For example, a 10% w/w solution of the 4,000 - 6,000K molecular weight polymer in water has a measured Brookfield viscosity of under 6,000 mPa.s at 25 degrees C.
-
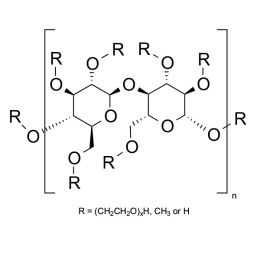 Cellulose, methyl hydroxyethyl etherCatalog Number 21275
Cellulose, methyl hydroxyethyl etherCatalog Number 21275Water-soluble cellulose derivative
8,000 cps (2% soln. in H2O)
-
![Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether [MW 1,900]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/4/04242.jpg) Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether [MW 1,900]Catalog Number 04242
Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl ether [MW 1,900]Catalog Number 04242Neutral, water-soluble, polymers with hydroxyl group at one end only
-
![Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 1,000,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/1/21295.jpg) Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 1,000,000]Catalog Number 21295
Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 1,000,000]Catalog Number 21295Water-soluble polymer in a white, free flowing powder. Used to impart viscosity to and modify flow of aqueous solutions. See poly(ethylene glycol) for lower molecular weight analogs. Poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: acetone, alcohol, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEO
-
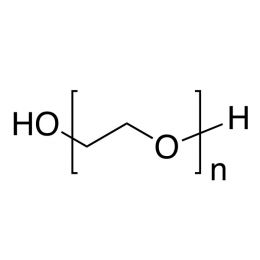 Poly(ethylene oxide), MW 200,000 (PEO 200000)Catalog Number 17503
Poly(ethylene oxide), MW 200,000 (PEO 200000)Catalog Number 17503Water-soluble polymer in a white, free flowing powder. Used to impart viscosity to and modify flow of aqueous solutions. See poly(ethylene glycol) for lower molecular weight analogs. Poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from ~0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: acetone, alcohol, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEO
-
 Dextran, FITCCatalog Number 15759
Dextran, FITCCatalog Number 15759Fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) labeled Dextrans are valuable materials for studying permeability and microcirculation in vivo. These are used to trace neuronal projections and active transport in live and unfixed tissue and as neuronal tracers in a variety of species.
-
![Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 4,000,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/4/04030.jpg) Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 4,000,000]Catalog Number 04030
Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 4,000,000]Catalog Number 04030Water-soluble polymer in a white, free flowing powder. Used to impart viscosity to and modify flow of aqueous solutions. See poly(ethylene glycol) for lower molecular weight analogs. Poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
-
![Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 5,000,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/4/04031.jpg) Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 5,000,000]Catalog Number 04031
Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 5,000,000]Catalog Number 04031Water-soluble polymer in a white, free flowing powder. Used to impart viscosity to and modify flow of aqueous solutions.
See poly(ethylene glycol) for lower molecular weight analogs. Poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: acetone, alcohol, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEG
-
![Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 600,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06106.jpg) Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 600,000]Catalog Number 06106
Poly(ethylene oxide) [MW 600,000]Catalog Number 06106Water-soluble polymer in a white, free flowing powder. Used to impart viscosity to and modify flow of aqueous solutions. See poly(ethylene glycol) for lower molecular weight analogs. Poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: acetone, alcohol, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEO
-
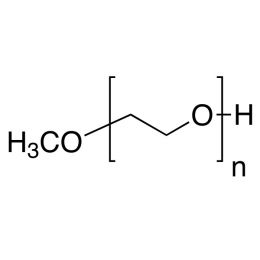 Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl etherCatalog Number 05986
Poly(ethylene glycol) monomethyl etherCatalog Number 05986Neutral, water-soluble, polymers with hydroxyl group at one end only
-
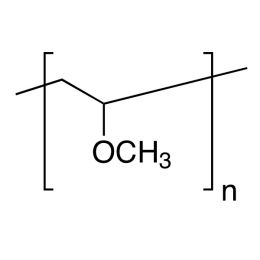 Poly(vinyl methyl ether), 50% aqueous solutionCatalog Number 03032
Poly(vinyl methyl ether), 50% aqueous solutionCatalog Number 03032Tacky resin. Water-insoluble above 28º. Used to prepare heat-sensitive latex.
50% Aq. Soln.
-
 Dextran sulfate, sodium saltCatalog Number 00407
Dextran sulfate, sodium saltCatalog Number 00407Anionic dextran derivative.
Sulfur 19% pH of AQ 6.9
-
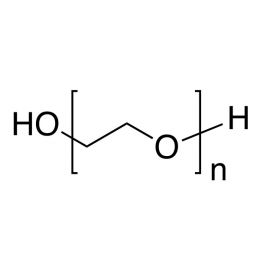 Poly(ethylene oxide), MW 8,000,000 (PEO 8000000)Catalog Number 21296Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(ethylene oxide), MW 8,000,000 (PEO 8000000)Catalog Number 21296Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Water-soluble polymer in a white, free flowing powder. Used to impart viscosity to and modify flow of aqueous solutions. See poly(ethylene glycol) for lower molecular weight analogs. Poly(ethylene glycol) has a broad molecular weight distribution ranging from~ 0.5x to 1.5x the values shown.
Soluble in: acetone, alcohol, chloroform, toluene, dichloromethane
PEO
-
 Poly(oxyethylene) sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20®)Catalog Number 06110
Poly(oxyethylene) sorbitan monolaurate (Tween 20®)Catalog Number 06110Water-soluble surfactant.
-
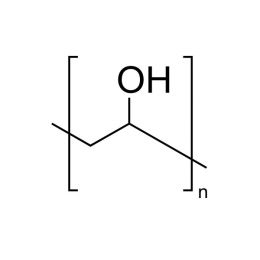 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 133000, 99% hydrolyzed (PVA 133K 99%)Catalog Number 02815
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 133000, 99% hydrolyzed (PVA 133K 99%)Catalog Number 02815Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
99 mol% hydrolyzed Polydispersity ~2.4
-
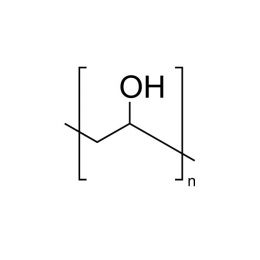 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 25000, 88% hydrolyzed (PVA 25K 88%)Catalog Number 02975
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 25000, 88% hydrolyzed (PVA 25K 88%)Catalog Number 02975Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
88 mol% hydrolyzed Polydispersity ~1.9
-
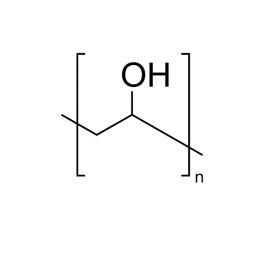 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 125000, 88% hydrolyzed (PVA 125K 88%)Catalog Number 04398
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 125000, 88% hydrolyzed (PVA 125K 88%)Catalog Number 04398Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
Soluble in: hot glycerol, hot glycols, hot water.
88 mol% hydrolyzed Polydispersity ~2.0
-
 Plastic weighing dish (1 carton)Catalog Number 19803A
Plastic weighing dish (1 carton)Catalog Number 19803AThis is our Peel-A-Way® weighing "tray" and designed for easy pouring. These handy little dishes can be used for all sorts of applications in the laboratory in addition to their intended use of weighing materials.
-
 Polyethylene, branchedCatalog Number 08277
Polyethylene, branchedCatalog Number 08277NIST Standard for determining melt flow rate in polymers. Melt flow rate is widely used in polymer technology as a product specification since this value, which includes a statement of the load and temperature under which it is obtained, gives an indication of the processing properties of the polymer.1, 2
-
 Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(styrenesulfonate), aqueous dispersion (PEDT/PSS)Catalog Number 24215
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)/poly(styrenesulfonate), aqueous dispersion (PEDT/PSS)Catalog Number 24215Conductive polymer.
Surface resistancy 730 KOhm/sq sm. Solid content 1.24% sodium 280 ppm
-
![Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 275,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/5/25724.jpg) Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 275,000]Catalog Number 25724Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(l-lysine hydrobromide) [MW 275,000]Catalog Number 25724Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Cationic polymer. Used for promotion of cell adhesion to solid surfaces.
-
![Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 450,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/2/6/26252.jpg) Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 450,000]Catalog Number 26252
Poly(styrenesulfonic acid), sodium salt [MW ~ 450,000]Catalog Number 26252Water-soluble. Mw/Mn < 1.20. MW ~450,000
-
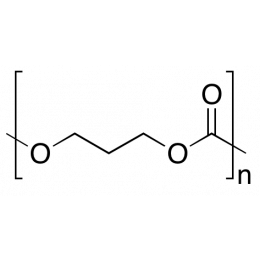 Poly(trimethylene carbonate), 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 26404
Poly(trimethylene carbonate), 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 26404 -
 Poly(ethylene glycol) 2000 dimethacrylateCatalog Number 26415
Poly(ethylene glycol) 2000 dimethacrylateCatalog Number 26415 -
![Poly(4-vinylphenol) [MW 22,000] | Polysciences, Inc.](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/8/18980_1_2.jpg) Poly(4-vinylphenol) [MW 22,000]Catalog Number 18980
Poly(4-vinylphenol) [MW 22,000]Catalog Number 18980Reactive polyphenol. Has applications in photoresists.
Soluble in: THF, lower alcohols, dioxane.
Polydispersity ~5
-
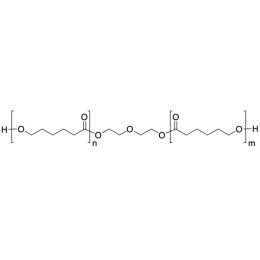 Polycaprolactone diol (MW 1,250)Catalog Number 09706Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Polycaprolactone diol (MW 1,250)Catalog Number 09706Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Biodegradable polymer. Can be used to make block copolymers.
Hydroxyl number 90mg KOH/ g of polymer.
-
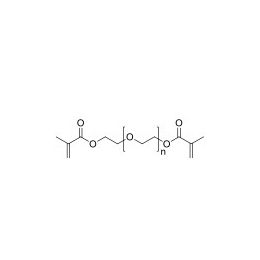 Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 400)Catalog Number 15179
Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 400)Catalog Number 15179Long-chain hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer. Molecular weight of PEG unit is approximately 400.
-
 Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 10,000 (bPEI 10000)Catalog Number 19850Email: [email protected]Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 10,000 (bPEI 10000) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 10000 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio.
Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 10,000 (bPEI 10000)Catalog Number 19850Email: [email protected]Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 10,000 (bPEI 10000) is highly branched liquid water soluble polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 10000 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio. -
 Poly(Acrylic Acid) Highly Pure MW 10,000Catalog Number 13511Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(Acrylic Acid) Highly Pure MW 10,000Catalog Number 13511Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polysciences offers ultrapure poly(acrylic acid) for use as an electronics industry CMP slurry dispersant.
-
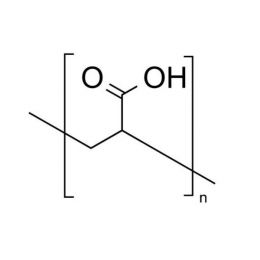 Poly(Acrylic Acid) Ultrapure MW 2,000Catalog Number 14433Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(Acrylic Acid) Ultrapure MW 2,000Catalog Number 14433Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polysciences offers ultrapure poly(acrylic acid) for use as an electronics industry CMP slurry dispersant.
-
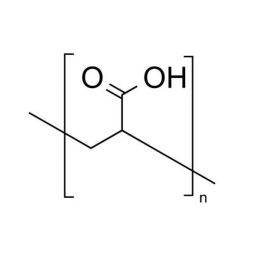 Poly(Acrylic Acid) Highly Pure MW 2,000Catalog Number 14176Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]
Poly(Acrylic Acid) Highly Pure MW 2,000Catalog Number 14176Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polysciences offers ultrapure poly(acrylic acid) for use as an electronics industry CMP slurry dispersant.
-
 Parafilm M, 2" x 250'Catalog Number 3989B
Parafilm M, 2" x 250'Catalog Number 3989BA versatile, stretchable, moldable, waterproof, odorless, and self-adhering thermoplastic parafilm roll is used for sealing or protecting vessels such as flasks or cuvettes.
-
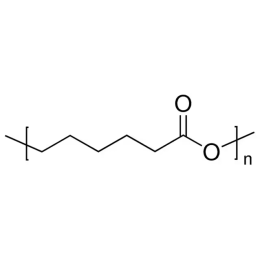 Polycaprolactone, IV 0.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50001Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 0.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50001Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
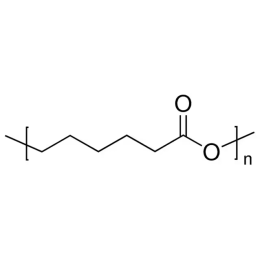 Polycaprolactone, IV 0.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50002Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 0.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50002Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
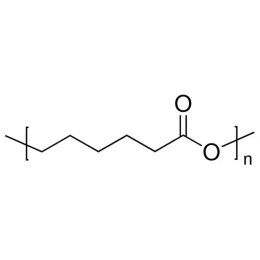 Polycaprolactone, IV 0.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50003Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 0.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50003Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
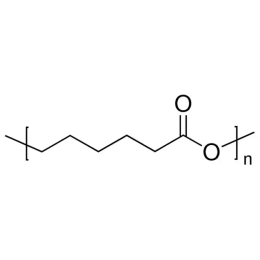 Polycaprolactone, IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50004Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50004Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
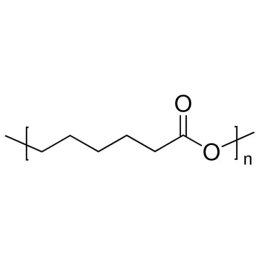 Polycaprolactone, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50005Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50005Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
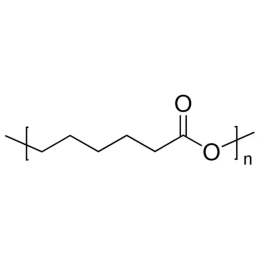 Polycaprolactone, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50006Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50006Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
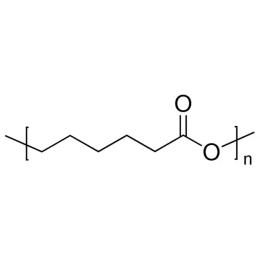 Polycaprolactone, IV 2.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50007Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 2.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50007Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
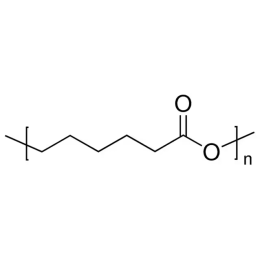 Polycaprolactone, IV 2.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50008Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles.
Polycaprolactone, IV 2.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50008Polycaprolactone (PCL) is a biodegradable polymer that is suitable for applications requiring years of stability. In recent years it is becoming of increased interest to manufacturers of medical devices and drug delivery particles. -
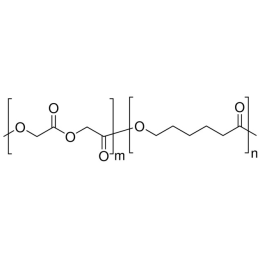 Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 95:5, IV 1.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50009Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 95:5, IV 1.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50009Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
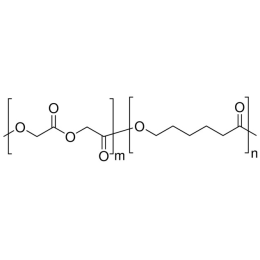 Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 0.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50010Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 0.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50010Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
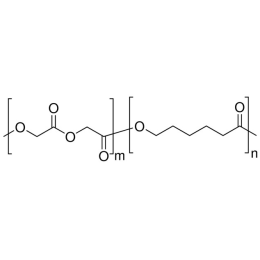 Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50011Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50011Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
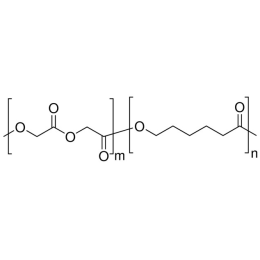 Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 85:15, IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50012Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 85:15, IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50012Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
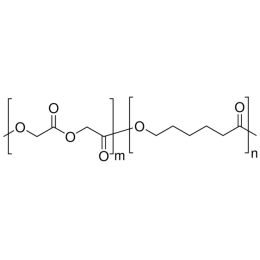 Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 85:15, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50013Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide), 85:15, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50013Poly(Caprolactone-co-glycolide) (PCLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer with a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
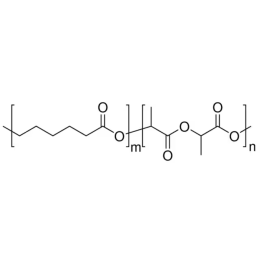 Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 95:5, IV 2.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50014Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 95:5, IV 2.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50014Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
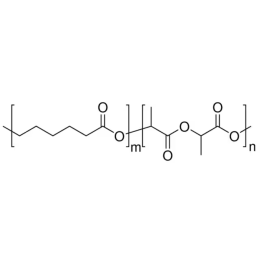 Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 90:10, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50015Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 90:10, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50015Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
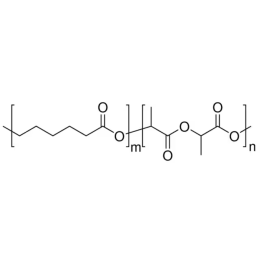 Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 85:15, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50016Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 85:15, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50016Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
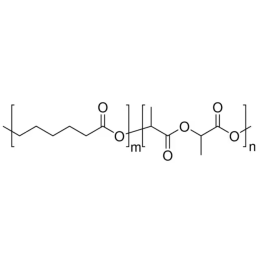 Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 85:15, IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50017Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries.
Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide), 85:15, IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50017Poly(Caprolactone-co-L-lactide) or (PCLLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries. -
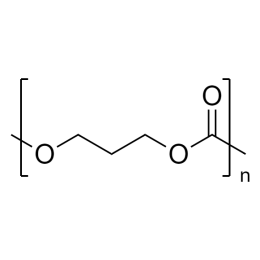 Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 0.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50018Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 0.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50018Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications. -
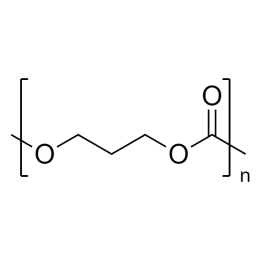 Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 1.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50019Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 1.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50019Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications. -
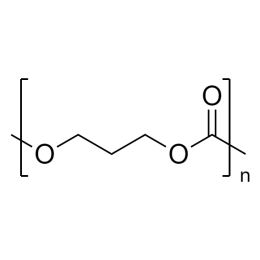 Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50020Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50020Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications. -
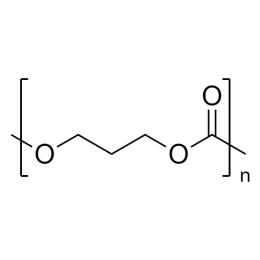 Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50021Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate), IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50021Poly(trimethylene carbonate) (PTMC) is a highly amorphous, aliphatic polycarbonate known for its flexibility which yields unique functionality in biomedical applications. -
 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone), 90:10, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50022Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone) (PTMC-co-PCL) is a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries and is commonly used as a material for medical devices, 3D printing, tissue engineering scaffolds, and drug delivery.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone), 90:10, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50022Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone) (PTMC-co-PCL) is a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries and is commonly used as a material for medical devices, 3D printing, tissue engineering scaffolds, and drug delivery. -
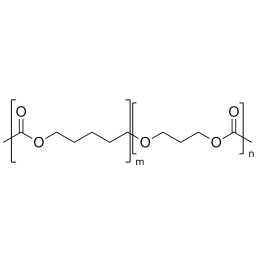 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone), 80:20, IV 1.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50023Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone) (PTMC-co-PCL) is a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries and is commonly used as a material for medical devices, 3D printing, tissue engineering scaffolds, and drug delivery.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone), 80:20, IV 1.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50023Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-caprolactone) (PTMC-co-PCL) is a biodegradable and biocompatible polymer that has a range of potential applications in the biomedical and pharmaceutical industries and is commonly used as a material for medical devices, 3D printing, tissue engineering scaffolds, and drug delivery. -
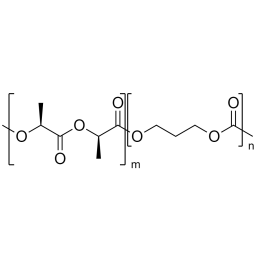 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 90:10, IV 0.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50024Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 90:10, IV 0.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50024Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
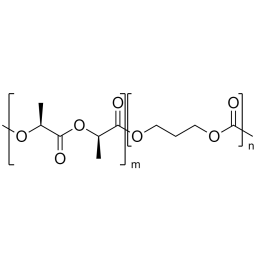 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 80:20, IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50025Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 80:20, IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50025Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
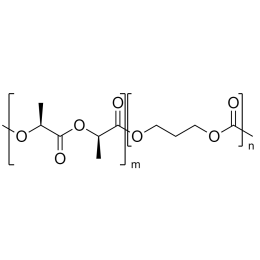 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 80:20, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50026Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 80:20, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50026Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
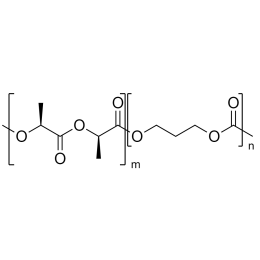 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 60:40, IV 1.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50027Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 60:40, IV 1.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50027Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
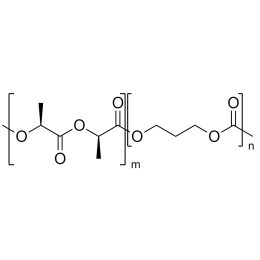 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 60:40, IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50028Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 60:40, IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50028Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
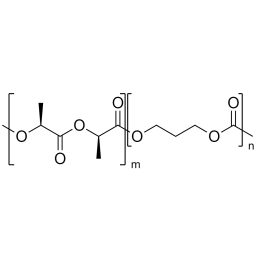 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 50:50, IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50029Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 50:50, IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50029Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
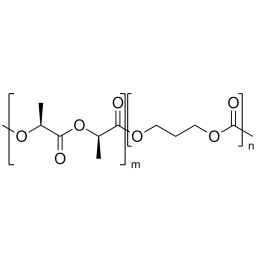 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 50:50, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50030Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide), 50:50, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50030Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
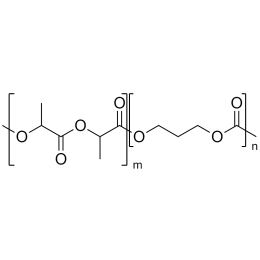 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-D,L-lactide), 50:50, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50031Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-D,L-lactide), 50:50, IV 1.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50031Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
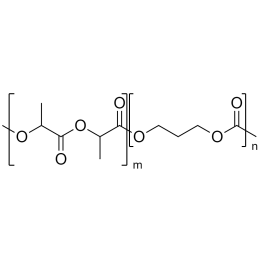 Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-D,L-lactide), 50:50, IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50032Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-D,L-lactide), 50:50, IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50032Poly(trimethylene carbonate-co-L-lactide) (PTMCLLA) is a biodegradable copolymer that has gained popularity in various biomedical applications, including drug delivery, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
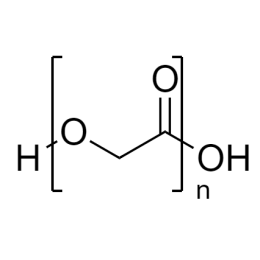 Polyglycolide, IV 0.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50033Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation.
Polyglycolide, IV 0.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50033Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation. -
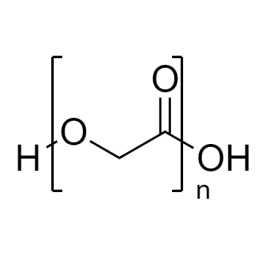 Polyglycolide, IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50034Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation.
Polyglycolide, IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50034Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation. -
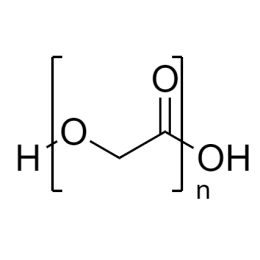 Polyglycolide, IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50035Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation.
Polyglycolide, IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50035Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation. -
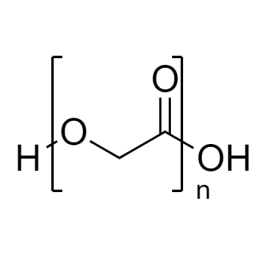 Polyglycolide, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50036Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation.
Polyglycolide, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50036Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation. -
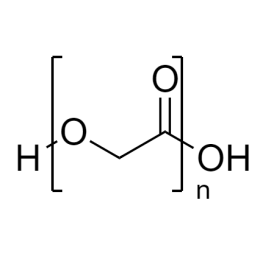 Polyglycolide, IV 2.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50037Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation.
Polyglycolide, IV 2.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50037Polyglycolide (PGA) is an aliphatic polyester with moderate to high crystallinity that is well known for extensive use in biomedical applications which require expedited biodegradation. -
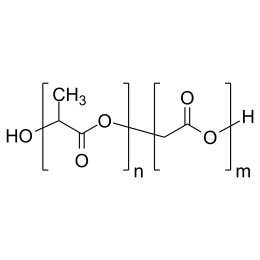 Poly(glycolide-co-lactide), 95:5, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50038Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PGLA) is a biodegradable copolymer widely used in medical applications, such as sutures, drug delivery systems, 3D printing, and tissue engineering, due to its excellent biocompatibility and controlled biodegradability.
Poly(glycolide-co-lactide), 95:5, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50038Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PGLA) is a biodegradable copolymer widely used in medical applications, such as sutures, drug delivery systems, 3D printing, and tissue engineering, due to its excellent biocompatibility and controlled biodegradability. -
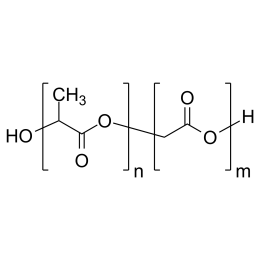 Poly(glycolide-co-lactide), 90:10, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50039Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PGLA) is a biodegradable copolymer widely used in medical applications, such as sutures, drug delivery systems, 3D printing, and tissue engineering, due to its excellent biocompatibility and controlled biodegradability.
Poly(glycolide-co-lactide), 90:10, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50039Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PGLA) is a biodegradable copolymer widely used in medical applications, such as sutures, drug delivery systems, 3D printing, and tissue engineering, due to its excellent biocompatibility and controlled biodegradability. -
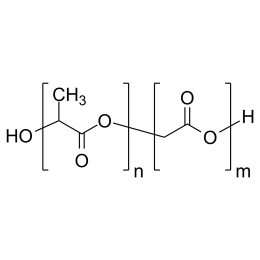 Poly(glycolide-co-lactide), 80:20, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50040Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PGLA) is a biodegradable copolymer widely used in medical applications, such as sutures, drug delivery systems, 3D printing, and tissue engineering, due to its excellent biocompatibility and controlled biodegradability.
Poly(glycolide-co-lactide), 80:20, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50040Poly(glycolide-co-lactide) (PGLA) is a biodegradable copolymer widely used in medical applications, such as sutures, drug delivery systems, 3D printing, and tissue engineering, due to its excellent biocompatibility and controlled biodegradability. -
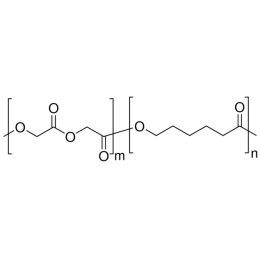 Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 75:25, 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50041Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 75:25, 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50041Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
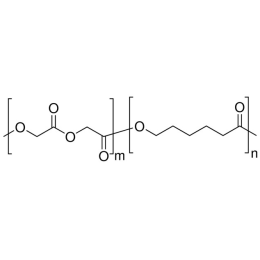 Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 60:40, 1.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50042Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 60:40, 1.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50042Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
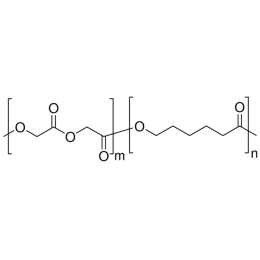 Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 60:40, 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50043Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 60:40, 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50043Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
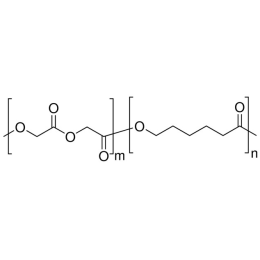 Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 55:45, 1.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50044Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing.
Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone), 55:45, 1.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50044Poly(glycolide-co-caprolactone) (PGCL) is a biodegradable copolymer suitable for medical and pharmaceutical applications, such as drug delivery systems, 3D printing, tissue engineering, and wound healing. -
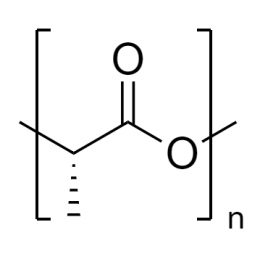 Poly(L-lactide), IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50045Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide), IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50045Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
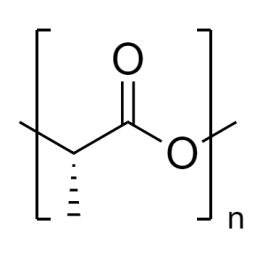 Poly(L-lactide), IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50046Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide), IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50046Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
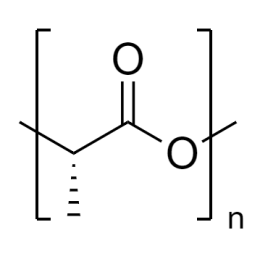 Poly(L-lactide), IV 2.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50047Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide), IV 2.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50047Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
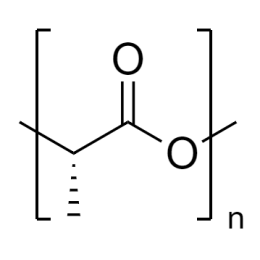 Poly(L-lactide), IV 3.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50048Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide), IV 3.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50048Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
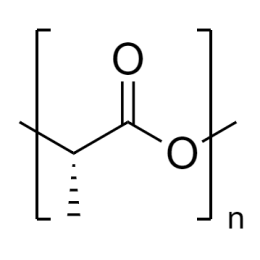 Poly(L-lactide), IV 3.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50049Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide), IV 3.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50049Poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate resorbable medical devices that degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
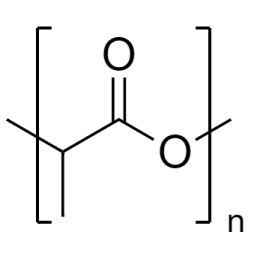 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.4 dL/g, acid terminatedCatalog Number 50050Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.4 dL/g, acid terminatedCatalog Number 50050Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
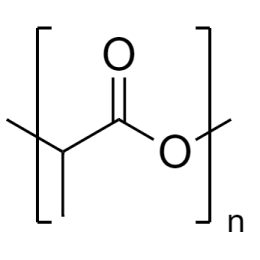 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50051Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50051Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
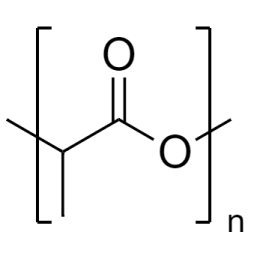 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50052Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50052Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
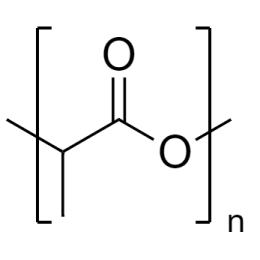 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50053Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 0.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50053Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
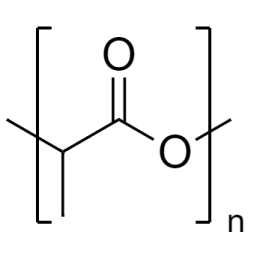 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50054Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 1.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50054Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
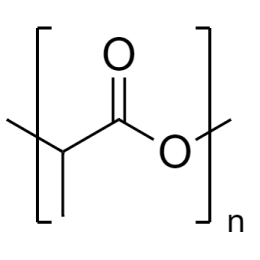 Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50055Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions.
Poly(D,L-lactic acid), IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50055Poly(DL-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over months in physiological conditions. -
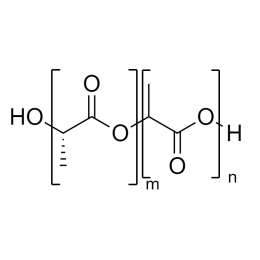 Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 2.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50056Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 2.4 dL/gCatalog Number 50056Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions. -
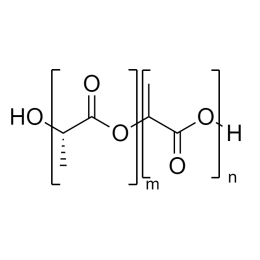 Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 2.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50057Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 2.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50057Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions. -
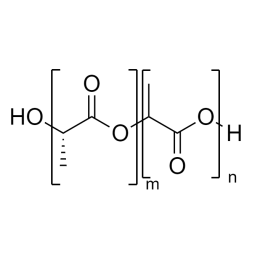 Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 2.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50058Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 2.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50058Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions. -
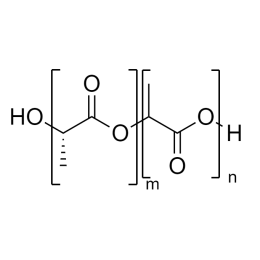 Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 3.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50059Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 3.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50059Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions. -
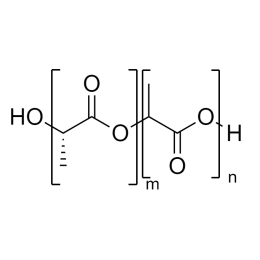 Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 6.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50060Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 70:30, IV 6.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50060Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions. -
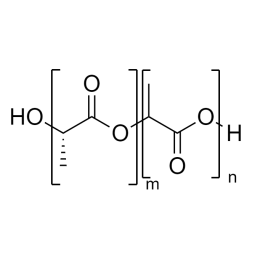 Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 80:20, IV 3.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50061Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 80:20, IV 3.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50061Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions. -
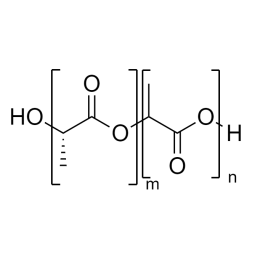 Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 80:20, IV 5.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50062Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions.
Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide), 80:20, IV 5.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50062Poly(L-lactide-co-D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) is a biodegradable polymer typically used to fabricate medical devices that predictably degrade over years in physiological conditions. -
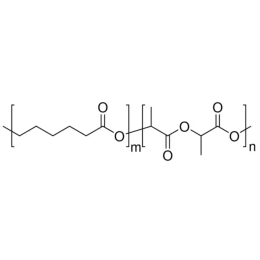 Poly(L-lactide co-Caprolactone), 60:40, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50063Poly(L-lactide co-caprolactone) is a biodegradable copolymer with applications in various fields, including tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and packaging materials due to its longer degradation profile and compatibility with biological systems.
Poly(L-lactide co-Caprolactone), 60:40, IV 1.8 dL/gCatalog Number 50063Poly(L-lactide co-caprolactone) is a biodegradable copolymer with applications in various fields, including tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and packaging materials due to its longer degradation profile and compatibility with biological systems. -
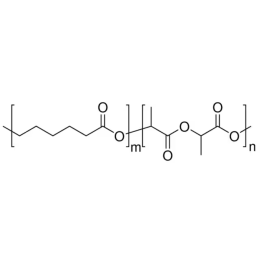 Poly(L-lactide co-Caprolactone), 70:30, IV 1.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50064Poly(L-lactide co-caprolactone) is a biodegradable copolymer with applications in various fields, including tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and packaging materials due to its longer degradation profile and compatibility with biological systems.
Poly(L-lactide co-Caprolactone), 70:30, IV 1.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50064Poly(L-lactide co-caprolactone) is a biodegradable copolymer with applications in various fields, including tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and packaging materials due to its longer degradation profile and compatibility with biological systems. -
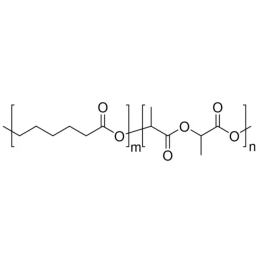 Poly(DL-lactide co-Caprolactone), 80:20, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50065Poly(DL-lactide co-caprolactone) is a biodegradable copolymer with applications in various fields, including tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and packaging materials due to its longer degradation profile and compatibility with biological systems.
Poly(DL-lactide co-Caprolactone), 80:20, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50065Poly(DL-lactide co-caprolactone) is a biodegradable copolymer with applications in various fields, including tissue engineering, drug delivery systems, and packaging materials due to its longer degradation profile and compatibility with biological systems. -
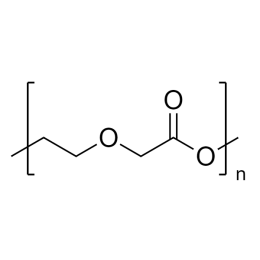 Polydioxanone, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50066Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices.
Polydioxanone, IV 1.7 dL/gCatalog Number 50066Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices. -
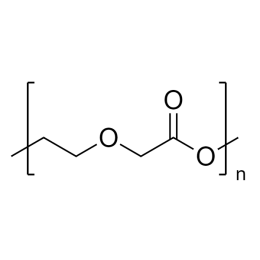 Polydioxanone, IV 1.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50067Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices.
Polydioxanone, IV 1.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50067Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices. -
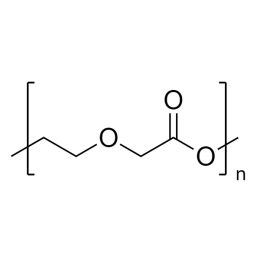 Polydioxanone, IV 2.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50068Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices.
Polydioxanone, IV 2.5 dL/gCatalog Number 50068Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices. -
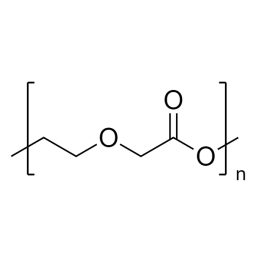 Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50069Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices.
Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 1.6 dL/gCatalog Number 50069Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices. -
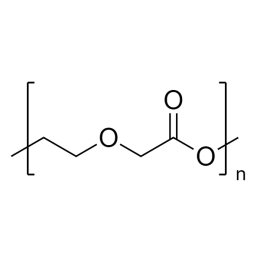 Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50070Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices.
Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50070Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices. -
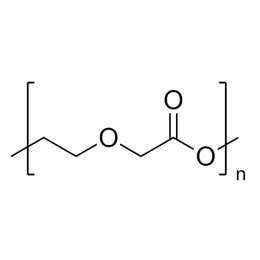 Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 2.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50071Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices.
Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 2.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50071Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices. -
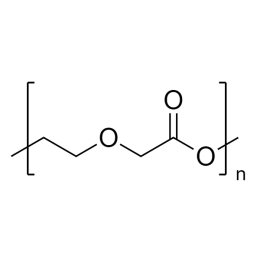 Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 3.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50072Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices.
Polydioxanone, dyed, IV 3.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50072Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Polydioxanone (PDO) is a polylactone ester with high degrees of crystallinity and is known for its use in filament sutures, meshes, clips, and other flexible absorbable devices. -
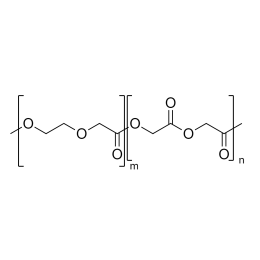 Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 1.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50073Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide) (PDOGA) is a biodegradable copolymer tuned for quick absorption and has applications with biomedical devices including surgical sutures, staples, meshes, and controlled drug delivery.
Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 1.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50073Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide) (PDOGA) is a biodegradable copolymer tuned for quick absorption and has applications with biomedical devices including surgical sutures, staples, meshes, and controlled drug delivery. -
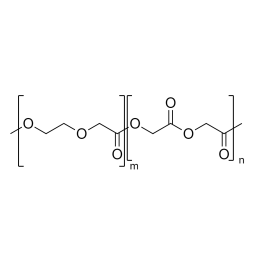 Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 2.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50074Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide) (PDOGA) is a biodegradable copolymer tuned for quick absorption and has applications with biomedical devices including surgical sutures, staples, meshes, and controlled drug delivery.
Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide), 90:10, IV 2.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50074Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(Dioxanone-co-glycolide) (PDOGA) is a biodegradable copolymer tuned for quick absorption and has applications with biomedical devices including surgical sutures, staples, meshes, and controlled drug delivery. -
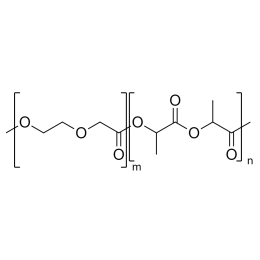 Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 95:5, IV 1.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50075Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery.
Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 95:5, IV 1.9 dL/gCatalog Number 50075Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery. -
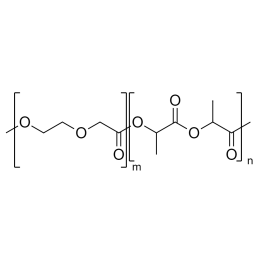 Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 92:8, IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50076Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery.
Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 92:8, IV 1.3 dL/gCatalog Number 50076Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery. -
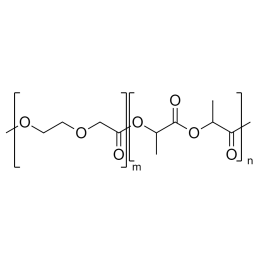 Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 90:10, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50077Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery.
Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 90:10, IV 2.0 dL/gCatalog Number 50077Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery. -
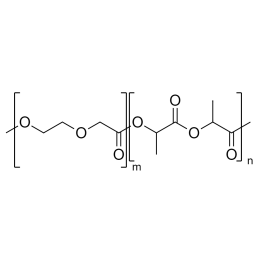 Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 85:15, IV 2.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50078Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery.
Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide), 85:15, IV 2.1 dL/gCatalog Number 50078Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(dioxanone-co-L-lactide) (PDO-PLA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery. -
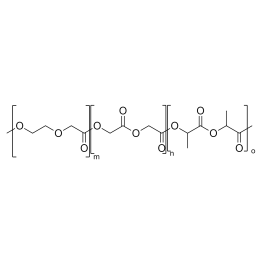 Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide-co-glycolide), 90:5:5, IV 2.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50079Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide-co-glycolide) (PDO-PLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery.
Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide-co-glycolide), 90:5:5, IV 2.2 dL/gCatalog Number 50079Inquire for availability.Phone: 1(800)523-2575Email: [email protected]Poly(Dioxanone-co-lactide-co-glycolide) (PDO-PLGA) is a biodegradable and biocompatible copolymer used in biomedical devices including staples, sutures, meshes, coatings, and controlled drug delivery. -
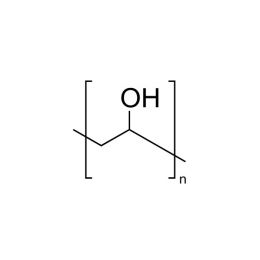 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 108000, 99+% hydrolyzed (PVA 108K 99+%)Catalog Number 04324
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 108000, 99+% hydrolyzed (PVA 108K 99+%)Catalog Number 04324Water-soluble resin of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydroyzed resin requiring onlyn 85°C for solution.
Soluble in: hot glycerol, hot glycols, hot water.
99.7 mol% hydrolyzed Polydispersity ~1.7
-
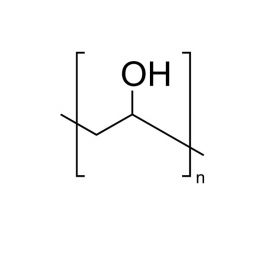 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 25000, 98% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 04397
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 25000, 98% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 04397Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
98 mol% hydrolyzed
-
 PEI MAX® - Transfection Grade Linear Polyethylenimine Hydrochloride (MW 40,000)Catalog Number 24765Email: [email protected]
PEI MAX® - Transfection Grade Linear Polyethylenimine Hydrochloride (MW 40,000)Catalog Number 24765Email: [email protected]Polyethylenimine “Max” (PEI MAX) is a highly efficient transfection reagent which is compatible for a wide range of cell lines/types including the most commonly used HEK293 and CHO cells grown in adherent and suspension cultures.
-
![Poly(acrylic acid), 50% soln. in water [MW ~ 5,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/6/06519_2.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), 50% soln. in water [MW ~ 5,000]Catalog Number 06519
Poly(acrylic acid), 50% soln. in water [MW ~ 5,000]Catalog Number 06519 -
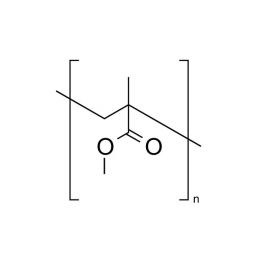 Poly(methyl methacrylate), MW 100000 (PMMA 100K)Catalog Number 17913
Poly(methyl methacrylate), MW 100000 (PMMA 100K)Catalog Number 17913Hard, stable, non-yellowing polymer used in coating and in molded clear plastic objects.
-
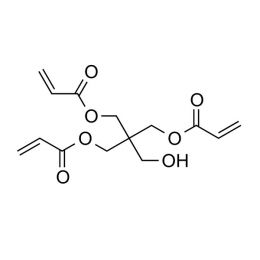 Pentaerythritol triacrylateCatalog Number 04259
Pentaerythritol triacrylateCatalog Number 04259Crosslinking monomer
-
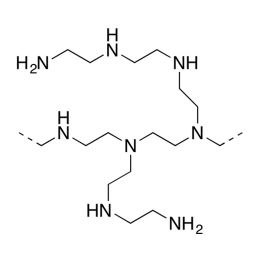 Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 10,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 10000 30% soln.)Catalog Number 17938Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 10,000, 30 % w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 10000 30% soln.) is highly branched polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 10000 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio.
Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 10,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 10000 30% soln.)Catalog Number 17938Branched Polyethylenimine, Mw 10,000, 30 % w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 10000 30% soln.) is highly branched polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 10000 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio. -
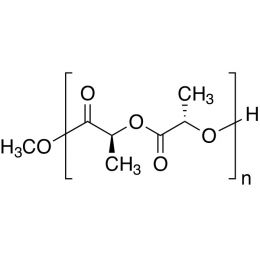 Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 0.15 dl/gCatalog Number 18580
Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 0.15 dl/gCatalog Number 18580Biodegradable polymer. Degradation rate is inversely related to polymer molecular weight.
Crystalline polymer with higher molecular weight polymers having a crystallinity of about 70%.
-
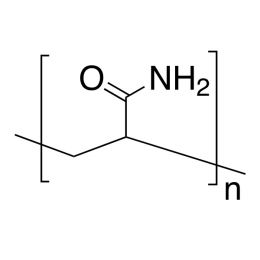 Polyacrylamide, MW 6,000,000Catalog Number 02806
Polyacrylamide, MW 6,000,000Catalog Number 02806Important nonionic water-soluble polymer. High MW polymer is used primarily as a flocculant. Tg of high MW (>100,000) polymers = 165º. Unit weights are weights of solution.
-
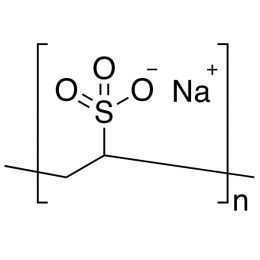 Poly(vinylsulfonic acid) sodium salt, 25% soln. in waterCatalog Number 04392
Poly(vinylsulfonic acid) sodium salt, 25% soln. in waterCatalog Number 04392Water-soluble anionic polymer. Has been used as a pigment dispersant.
-
 Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 70,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 70000 30% soln.)Catalog Number 06090Branched Polyethylenimine,, Mw 70,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 70000 soln.) is highly branched polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 70000 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio.
Polyethylenimine, Branched, Mw 70,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 70000 30% soln.)Catalog Number 06090Branched Polyethylenimine,, Mw 70,000, 30% w/v aq. soln. (bPEI 70000 soln.) is highly branched polyamine with high cationic charge density. bPEI 70000 contains primary, secondary, and tertiary amine groups in approximately 25/50/25 ratio. -
 Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide)Catalog Number 08794
Poly(2,6-dimethyl-1,4-phenylene oxide)Catalog Number 08794High softening point (90º)
Mn 20,000 Polydispersity ~2.5
-
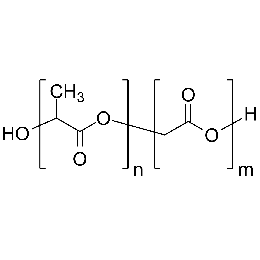 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.4 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26270
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.4 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26270 -
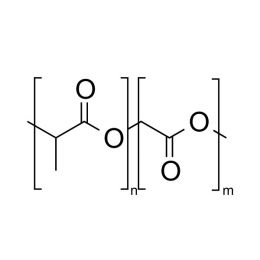 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.6 dl/gCatalog Number 23986
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.6 dl/gCatalog Number 23986Biodegradable polymers. Copolymers are easier to fabricate than homopolymers.
Soluble in: MDC, THF, ethyl acetate, acetone
50/50 i.v. 0.50-0.65
-
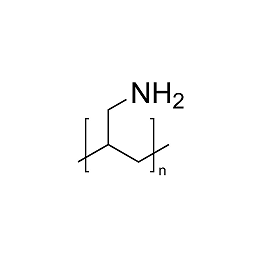 Poly(allylamine), MW 15000, 15% aq. soln.Catalog Number 24826
Poly(allylamine), MW 15000, 15% aq. soln.Catalog Number 24826Water soluble cationic polymer with primary amino groups (free base types) for chemical reactions. High cationic charge density in ready to use aqueous solution form. The structure of these materials is a repeating polymer of the allyl amine group shown at right.
Ability to modify surfaces and provide cationic character allows the user to selectively attract negatively charged functional groups to the coated surface or to the dissolved water soluble cationic polymers.
-
![Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 20% soln. in water [MW ~ 225,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/1/8/18613_1.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 20% soln. in water [MW ~ 225,000]Catalog Number 18613
Poly(acrylic acid), sodium salt, 20% soln. in water [MW ~ 225,000]Catalog Number 18613Water-soluble anionic polymer. Used at low molecular weights as pigment dispersant and at higher molecular weights as a flocculant. Polymer can form complexes with poly(ethylene oxide) and with nucleotides
Mw/Mn 6.1
20% soln. in water (50g polymer)
-
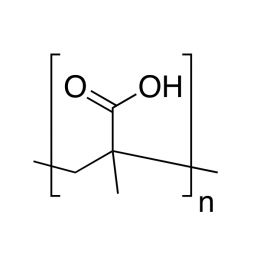 Poly(methacrylic acid)Catalog Number 00578
Poly(methacrylic acid)Catalog Number 00578Water-soluble polymer.
Soluble in: water, methanol, alkaline water.
-
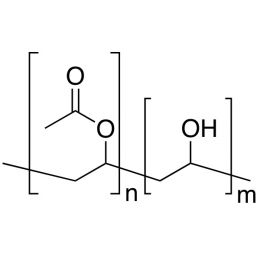 Poly(vinyl acetate), 40% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 17561
Poly(vinyl acetate), 40% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 17561Hydrophilic polymer, highly swolllen in water.
-
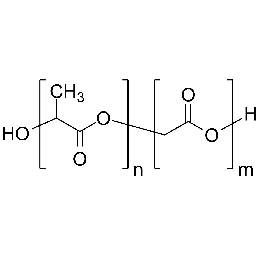 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 75:25, IV 0.2 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26268
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 75:25, IV 0.2 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26268 -
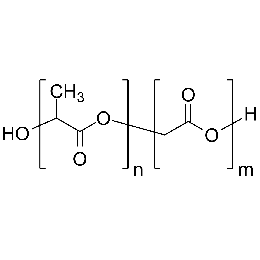 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.2 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26269
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.2 dl/g, acid-terminatedCatalog Number 26269 -
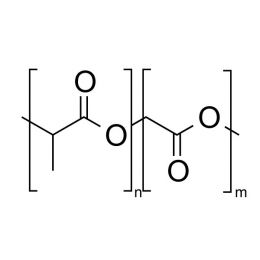 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 70:30, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 19247
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 70:30, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 19247Biodegradable polymers. Copolymers are easier to fabricate than homopolymers.
Soluble in: MDC, THF, ethyl acetate, acetone
70:30 i.v. 0.12-0.30 dl/g
-
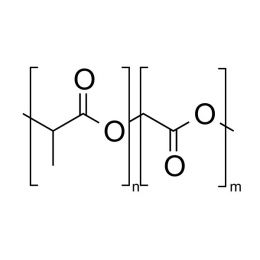 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 80:20, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 19077
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 80:20, IV 0.2 dl/gCatalog Number 19077Biodegradable polymers. Copolymers are easier to fabricate than homopolymers.
Soluble in: MDC, THF, ethyl acetate, acetone
80:20 i.v. 0.15-0.30
-
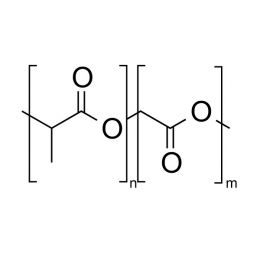 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 75:25, IV 0.65 dl/gCatalog Number 25107
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 75:25, IV 0.65 dl/gCatalog Number 25107Biodegradable polymers. Copolymers are easier to fabricate than homopolymers.
75:25
-
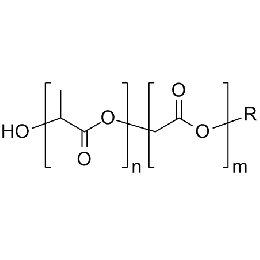 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 1.0 dl/gCatalog Number 23987
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 1.0 dl/gCatalog Number 23987Biodegradable polymer. Copolymers are easier to fabricate than homopolymers.
[50:50] i.v. 0.8-1.2
Soluble in: MDC, THF, ethyl acetate, acetone
-
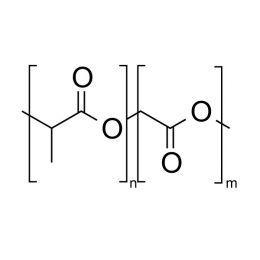 Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.40 dl/gCatalog Number 26297
Poly(D,L-lactide-co-glycolide), 50:50, IV 0.40 dl/gCatalog Number 26297 -
![Poly(acrylic acid), 25% soln. in water [PAA ~50,000]](https://www.polysciences.com/media/catalog/product/cache/41caa8e834a03fb3ab31ba2c24269124/0/0/00627_1.jpg) Poly(acrylic acid), 25% soln. in water [PAA ~50,000]Catalog Number 00627
Poly(acrylic acid), 25% soln. in water [PAA ~50,000]Catalog Number 00627 -
 Tetraethylene glycol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 02654
Tetraethylene glycol dimethacrylateCatalog Number 02654 -
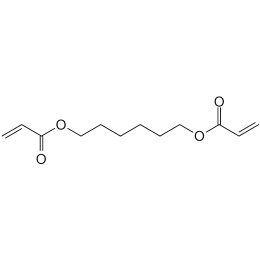 1,6-Hexanediol diacrylateCatalog Number 23671
1,6-Hexanediol diacrylateCatalog Number 23671Crosslinking monomer.
-
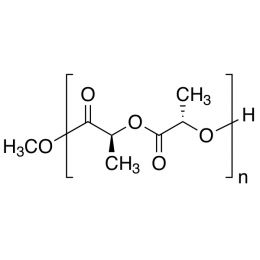 Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 1.0 dL/gCatalog Number 06529
Poly(L-lactic acid), IV 1.0 dL/gCatalog Number 06529Biodegradable polymer. Degradation rate is inversely related to polymer molecular weight.
Crystalline polymer with higher molecular weight polymers having a crystallinity of about 70%.
i.v. 0.80-1.20 Polydispersity ~1.8
-
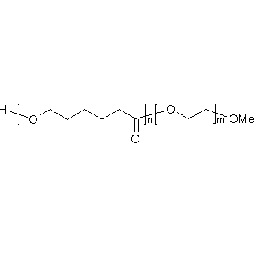 PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(2,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25011
PCL(1,000)-b-PEG(2,000), Diblock PolymerCatalog Number 25011Caprolactone itself is a biodegradable polyester with a relatively low melting point (60C) but a glass transition temperature (Tg) around -60C. The high crystallinity in the polyester accounts for this property balance. It is made by metal catalyzed ring opening polymerization of epsilon caprolactone. A typical molecular weight of standard polycaprolactone homopolymer is 188k Daltons. By comparison, a 100% polylactic acid homopolymer with Mw 330k Daltons has a (Tg) temperature of +55C and a melting temperature, Tm of about 175C.
-
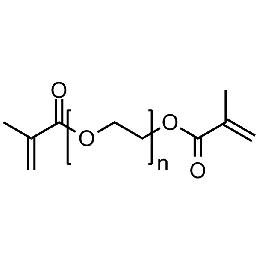 Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 20000)Catalog Number 25406
Polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA 20000)Catalog Number 25406Long-chain hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer.
Molecular Weight of PEG unit is approximately 20,000.
-
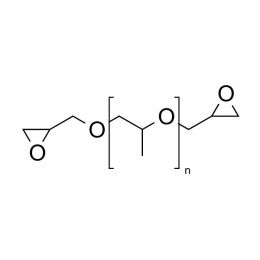 D.E.R. (Dow epoxy resins), Grade 732Catalog Number 02922
D.E.R. (Dow epoxy resins), Grade 732Catalog Number 02922From this value, one determines the optimum amount of DDSA or NMA in grams to combine with 100 grams of resin for stoichiometric balance, minimizing unreacted starting materials and producing reproducibly stainable, sectionable embedding blocks. Exact WPE value for each lot of Araldite resin is on the label of each container.
Grade: 732 WPE: 305 - 33 (Weight Per Epoxide equivalent)
-
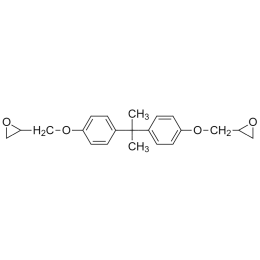 D.E.R. (Dow epoxy resins), Grade 331Catalog Number 02924
D.E.R. (Dow epoxy resins), Grade 331Catalog Number 02924D.E.R. 331 Epoxy Resin is the most widely used general purpose liquid epoxy resin. It is recognized as the standard from which many variations have been developed.
-
 Poly(4-vinylpyridine)Catalog Number 00112
Poly(4-vinylpyridine)Catalog Number 00112Water-soluble at low pH—has adhesive-promoting properties.
-
 Poly(methyl methacrylate), MW 15000Catalog Number 26293
Poly(methyl methacrylate), MW 15000Catalog Number 26293Methyl methacrylate polymer (PMMA) is hard, stable, non-yellowing polymer used in coating and in molded clear plastic objects.
-
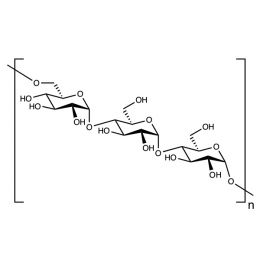 Pullulan, desalinizedCatalog Number 21115
Pullulan, desalinizedCatalog Number 21115Natural polysaccharide from Aureobasidium pullulans
Mn ~200,000
-
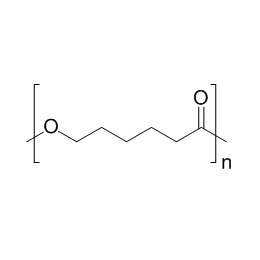 Polycaprolactone, MW 37000Catalog Number 26288
Polycaprolactone, MW 37000Catalog Number 26288 -
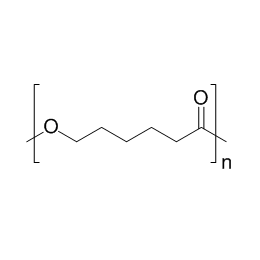 Polycaprolactone, MW 50000 PelletsCatalog Number 26289
Polycaprolactone, MW 50000 PelletsCatalog Number 26289 -
 Poly(2-vinyl-1-methylpyridinium bromide), 20% soln. in waterCatalog Number 21477
Poly(2-vinyl-1-methylpyridinium bromide), 20% soln. in waterCatalog Number 21477Cationic quaternary ammonium polymer.
20% soln. in water (2g polymer) Degree of quaternization 50%
-
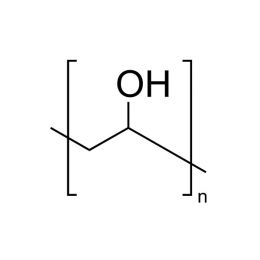 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 78000, 99+% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 15129
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 78000, 99+% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 15129Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
99.7 mol% hydrolyzed Polydispersity ~1.7
-
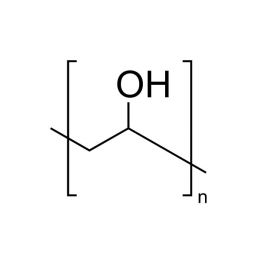 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 78000, 98% hydrolyzed (PVA 78K 98%)Catalog Number 15130
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 78000, 98% hydrolyzed (PVA 78K 98%)Catalog Number 15130Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
98 mol% hydrolyzed
-
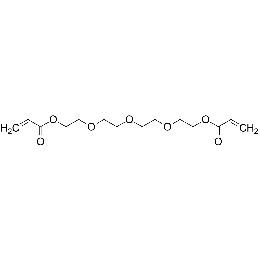 Tetraethylene glycol diacrylate (TetEGDA)Catalog Number 01668
Tetraethylene glycol diacrylate (TetEGDA)Catalog Number 01668Long-chain hydrophilic, crosslinking monomer.
-
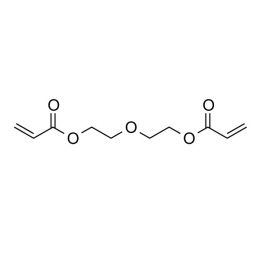 Diethylene glycol diacrylate (DEGDA)Catalog Number 02215
Diethylene glycol diacrylate (DEGDA)Catalog Number 02215 -
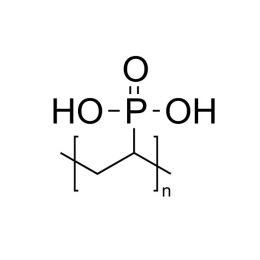 Poly(vinylphosphonic acid), 30% Soln.Catalog Number 24297
Poly(vinylphosphonic acid), 30% Soln.Catalog Number 24297Water-soluble polymeric phosphonic acid.
Polydispersity ~1.24
-
 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 78000, 88% hydrolyzed (PVA 78K 88%)Catalog Number 15132
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 78000, 88% hydrolyzed (PVA 78K 88%)Catalog Number 15132Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
88 mol% hydrolyzed Polydispersity ~1.9
-
 Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 6000, 80% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 22225
Poly(vinyl alcohol), MW 6000, 80% hydrolyzedCatalog Number 22225Water-soluble resins of low toxicity. Resins at high % hydrolysis require heating at ~96°C in water for solution. Resins of lower % hydrolysis can be dissolved at progressively lower temperatures with 88% hydrolyzed resin requiring only 85°C for solution.
80 mol% hydrolyzed
Polymers
Polysciences stocks a wide portfolio of Polymers. Such variety provides any scientist the options necessary to design compositions with markedly different performance. These polymers can also be applied as platforms on which to build more complex polymer systems. Please select Polymer products to review from categories in the left navigation menu.