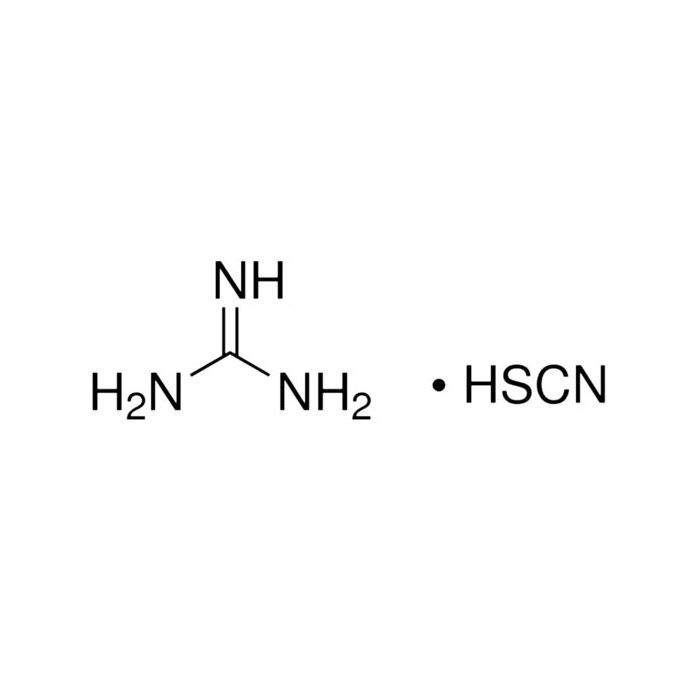
Guanidine Thiocyanate
A common obstacle faced when attempting to extract DNA and RNA from cells of interest is the release of denaturing enzymes like DNase and RNase during cell lysis. Guanidine Thiocyanate is a cost effective chemical tool that prevents these nucleases from degrading precious nucleic acids by irreversibly inhibiting their catalytic activity.
Guanidine Thiocyanate also has the added benefit of being a chaotropic agent. This feature allows it to decrease the action of hydrogen bonds in water as well as disrupts intramolecular interactions within proteins and other macromolecules – further increasing solubility of unwanted cellular components.
Assay: ≥99.5%
Thompson, J., & Gillespie, D. (1987). Molecular hybridization with RNA probes in concentrated solutions of guanidine thiocyanate. Analytical Biochemistry, 163(2), 281–291. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(87)90225-9
McGookin, R. (n.d.). RNA Extraction by the Guanidine Thiocyanate Procedure. Nucleic Acids, 113–116. doi:10.1385/0-89603-064-4:113
Kaabache, T., Barraud, B., Feldmann, G., Bernuau, D., & Lardeux, B. (1995). Direct Solution Hybridization of Guanidine Thiocyanate-Solubilized Cells for Quantitation of mRNAs in Hepatocytes. Analytical Biochemistry, 232(2), 225–230. doi:10.1006/abio.1995.0011
Jacobsen, N. (2004). Direct isolation of poly(A)+ RNA from 4 M guanidine thiocyanate-lysed cell extracts using locked nucleic acid-oligo(T) capture. Nucleic Acids Research, 32(7), e64–e64. doi:10.1093/nar/gnh056