-
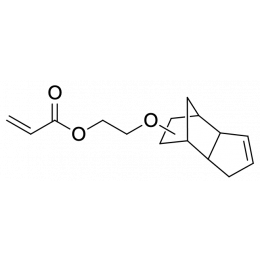 Dicyclopentenyloxyethyl acrylateCatalog Number 15797
Dicyclopentenyloxyethyl acrylateCatalog Number 15797Double bond in dicyclopentenyl does not participate in polymerization but can be post-reacted, e.g., by oxidative crosslinking
-
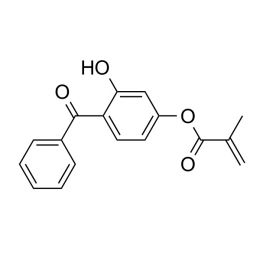 4-Methacryloxy-2-hydroxybenzophenone, min 99%Catalog Number 23350
4-Methacryloxy-2-hydroxybenzophenone, min 99%Catalog Number 23350UV absorbing monomer, especially for ophthalmic and optic applications
Min. 99% λ max (MeOH) 205nm (e = 3.03 x 104) 275nm (e = 1.18 x 104) 325nm (e = 7.23 x 103)
-
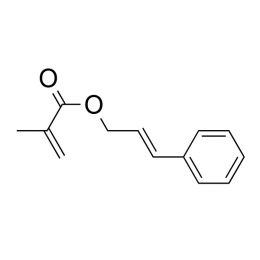 Cinnamyl methacrylateCatalog Number 02092
Cinnamyl methacrylateCatalog Number 02092Photocrosslinking monomer
-
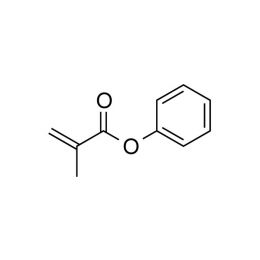 Phenyl methacrylate, ≥ 97%Catalog Number 02644
Phenyl methacrylate, ≥ 97%Catalog Number 02644Moderate UV absorbing monomer.
-
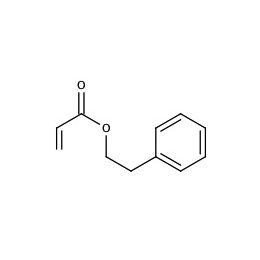 2-Phenylethyl acrylate, min. 92%Catalog Number 02834
2-Phenylethyl acrylate, min. 92%Catalog Number 02834Moderate UV absorbing monomer useful for ophthalmic applications. Polymer n = ~1.55
-
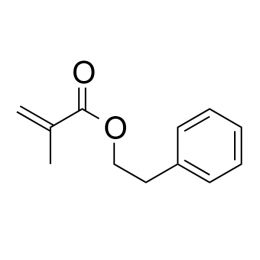 2-Phenylethyl methacrylate, min. 99%Catalog Number 02911
2-Phenylethyl methacrylate, min. 99%Catalog Number 02911Moderate UV absorbing monomer useful for ophthalmic applications. Polymer n = 1.55
-
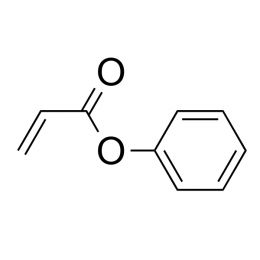 Phenyl acrylate, min. 95%Catalog Number 02642
Phenyl acrylate, min. 95%Catalog Number 02642UV absorbing monomer. Polymer n = ~1.55
-
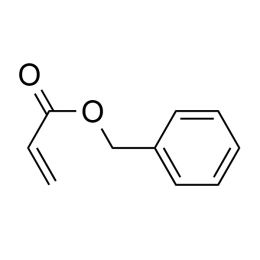 Benzyl acrylate, ≥ 99%Catalog Number 26296
Benzyl acrylate, ≥ 99%Catalog Number 26296 -
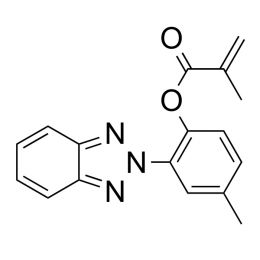 2-(2’-Methacryloxy-5’-methylphenyl)benzotriazoleCatalog Number 21871
2-(2’-Methacryloxy-5’-methylphenyl)benzotriazoleCatalog Number 21871UV absorbing monomer.
UV (light) Active Monomers
Polymers with aliphatic backbones often show little absorbance of light and usually do not absorb in the near and mid UV spectral range. UV absorbing monomers improve the capture of light at these wavelengths. These absorbers can be used to shield the polymer system or an underlying substrate from degradation by UV light, e.g. phenethyl methacrylate containing polymers for optical lenses. Additionally, some UV absorbing materials can act as sensitizers to promote photochemical reactions.
